What is AGP Aperture size? |
|
|
Author: W1zzard
Date: 2004-05-16 07:55:36
|
|
How big should I set AGP Aperture size in my BIOS?
First of all, AGP Aperture memory will not be used until your video card's on-board memory is running low. That means it will usually not impact your gaming performance because developers are trying hard to not exceed the on-board memory limits.
The bigger your video memory, the smaller your Aperture Size could be. However with later games requiring more and more texture memory a good number seems to be 128MB Aperture Size for all cards with 64 MB to 256 MB Video RAM.
Setting the Aperture Size to HUGE values will not increase performance because this merely sets the maximum amount of physical memory that can be used. It only makes the GART Table bigger because every 4K page has its own entry, no matter if allocated or not.
Setting the Aperture Size to too small values could result in running out of available texture memory especially on a low-mem video card. It is also possible that developers make use of the GART's features by creating textures as 'non-local'.
If you experience in-game stuttering try playing with the size of your Aperture.
What is it from a technical point of view?
When using an AGP card the video memory on the graphics adapter is mapped into the 4 GB memory address space (above the region of the physical installed memory). Any accesses to this memory region are directly forwarded to the video memory, greatly increasing transfer rates. However in earlier days of video cards graphics memory was rather limited and ran out quickly (a single 32-bit 512x512 MIP-mapped texture consumes ~1.5 MB) so AGP added a mechanism to use the system's main memory as additional storage for graphics data such as textures. This is what the AGP Aperture is. Usually directly below the mapped video memory the system reserves a contiguous space of addresses the size of your Aperture (no physical memory will be consumed at this time).
When free video RAM is running low the system dynamically allocates 4K sized pages of system memory for use as AGP Aperture Memory. The problem with this dynamic allocation is that in many cases the pages are spread in a non-contiguous form throughout the physical memory. Accessing these pages directly would hinder performance because of scattering/gathering requiring extra logic. To get around this limitation the GART (Graphics Address Remapping Table) which is implemented in hardware in the Northbridge's Memory Controller Hub provides an automatic physical-to-physical mapping between the scattered pages and the AGP Aperture. See the following illustration:
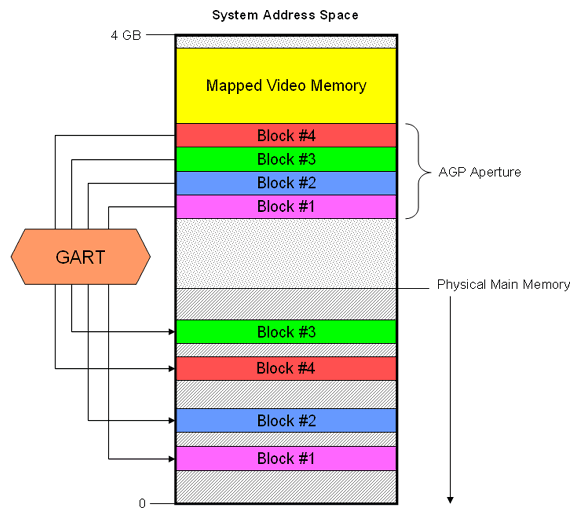
The actual usable amount of this 'virtual' AGP memory is less than half the AGP Aperture size set in the BIOS. This is because the Aperture is divided into two areas. One uncached half and another write-combined area.
First of all, AGP Aperture memory will not be used until your video card's on-board memory is running low. That means it will usually not impact your gaming performance because developers are trying hard to not exceed the on-board memory limits.
The bigger your video memory, the smaller your Aperture Size could be. However with later games requiring more and more texture memory a good number seems to be 128MB Aperture Size for all cards with 64 MB to 256 MB Video RAM.
Setting the Aperture Size to HUGE values will not increase performance because this merely sets the maximum amount of physical memory that can be used. It only makes the GART Table bigger because every 4K page has its own entry, no matter if allocated or not.
Setting the Aperture Size to too small values could result in running out of available texture memory especially on a low-mem video card. It is also possible that developers make use of the GART's features by creating textures as 'non-local'.
If you experience in-game stuttering try playing with the size of your Aperture.
What is it from a technical point of view?
When using an AGP card the video memory on the graphics adapter is mapped into the 4 GB memory address space (above the region of the physical installed memory). Any accesses to this memory region are directly forwarded to the video memory, greatly increasing transfer rates. However in earlier days of video cards graphics memory was rather limited and ran out quickly (a single 32-bit 512x512 MIP-mapped texture consumes ~1.5 MB) so AGP added a mechanism to use the system's main memory as additional storage for graphics data such as textures. This is what the AGP Aperture is. Usually directly below the mapped video memory the system reserves a contiguous space of addresses the size of your Aperture (no physical memory will be consumed at this time).
When free video RAM is running low the system dynamically allocates 4K sized pages of system memory for use as AGP Aperture Memory. The problem with this dynamic allocation is that in many cases the pages are spread in a non-contiguous form throughout the physical memory. Accessing these pages directly would hinder performance because of scattering/gathering requiring extra logic. To get around this limitation the GART (Graphics Address Remapping Table) which is implemented in hardware in the Northbridge's Memory Controller Hub provides an automatic physical-to-physical mapping between the scattered pages and the AGP Aperture. See the following illustration:

The actual usable amount of this 'virtual' AGP memory is less than half the AGP Aperture size set in the BIOS. This is because the Aperture is divided into two areas. One uncached half and another write-combined area.
Mar 27th, 2025 17:03 EDT
change timezone
Latest GPU Drivers
New Forum Posts
- Talk: File system of choice / with encryption / with compression / deduplication (17)
- Gigabyte graphic card - TIM GEL application failure? (1)
- Future-proofing my OLED (19)
- Were fax machines in wide use in late 1990s Germany? (9)
- Post your cooling. (190)
- Do you prefer factory overclocked GPUs? (61)
- Advice on Upgrading Please (3)
- tape v hard disk (12)
- Issues with RTX4090 FE waterblock (Bitspower) (9)
- How is my CPU's temperature? (13)
Popular Reviews
- be quiet! Pure Rock Pro 3 Black Review
- Assassin's Creed Shadows Performance Benchmark Review - 30 GPUs Compared
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Pulse Review
- Samsung 9100 Pro 2 TB Review - The Best Gen 5 SSD
- Pulsar Feinmann F01 Review
- ASRock Phantom Gaming B860I Lightning Wi-Fi Review
- ASRock Radeon RX 9070 XT Taichi OC Review - Excellent Cooling
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Nitro+ Review - Beating NVIDIA
- ASUS ProArt X870E-Creator Wi-Fi Review
- ASUS GeForce RTX 5070 TUF OC Review
Controversial News Posts
- AMD RDNA 4 and Radeon RX 9070 Series Unveiled: $549 & $599 (260)
- MSI Doesn't Plan Radeon RX 9000 Series GPUs, Skips AMD RDNA 4 Generation Entirely (142)
- Microsoft Introduces Copilot for Gaming (123)
- AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT Reportedly Outperforms RTX 5080 Through Undervolting (118)
- NVIDIA Reportedly Prepares GeForce RTX 5060 and RTX 5060 Ti Unveil Tomorrow (115)
- Over 200,000 Sold Radeon RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT GPUs? AMD Says No Number was Given (100)
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5050, RTX 5060, and RTX 5060 Ti Specifications Leak (96)
- Retailers Anticipate Increased Radeon RX 9070 Series Prices, After Initial Shipments of "MSRP" Models (90)