Cervoz Embraces Edge Computing with its M.2 Compact Solutions
Seizing the Edge: Cervoz Adapts to Shifting Data Landscape—The rapid emergence of technologies like AIoT and 5G and their demand for high-speed data processing has accelerated the data transition from the cloud to the edge. This shift exposes data to unpredictable environments with extreme temperature variations, vibrations, and space constraints, making it critical for edge devices to thrive in these settings. Cervoz strategically targets the blooming edge computing sector by introducing an extensive array of compact product lines, enhancing its existing SSDs, DRAM, and Modular Expansion Cards to meet the unique needs of edge computing.
Cervoz Reveals NVMe M.2 SSDs and Connectivity Solutions to Power the Edge
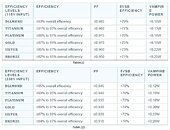
Cervoz introduces its latest compact PCIe Gen. 3x2 SSD offerings, the T421 M.2 2242 (B+M key) and T425 M.2 2230 (A+E key). These space-efficient design and low power consumption feature offer exceptional performance, catering to the storage needs of fanless embedded PCs and motherboards for purpose-built edge applications. Cervoz is also leading the way in developing connectivity solutions, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Serial, USB, and CAN Bus all available in M.2 2230 (A+E key) and M.2 2242/2260/2280 (B+M) form factors. The M.2 (B+M key) 2242/2260/2280 card is a versatile three-in-one solution designed for maximum adaptability. While it initially comes in a 2280 form factor, it can be easily adjusted to fit 2260 or 2242 sizes. It offers an effortless upgrade of existing systems without sacrificing connection capability, especially in edge devices.
Cervoz Reveals NVMe M.2 SSDs and Connectivity Solutions to Power the Edge
Cervoz introduces its latest compact PCIe Gen. 3x2 SSD offerings, the T421 M.2 2242 (B+M key) and T425 M.2 2230 (A+E key). These space-efficient design and low power consumption feature offer exceptional performance, catering to the storage needs of fanless embedded PCs and motherboards for purpose-built edge applications. Cervoz is also leading the way in developing connectivity solutions, including Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Serial, USB, and CAN Bus all available in M.2 2230 (A+E key) and M.2 2242/2260/2280 (B+M) form factors. The M.2 (B+M key) 2242/2260/2280 card is a versatile three-in-one solution designed for maximum adaptability. While it initially comes in a 2280 form factor, it can be easily adjusted to fit 2260 or 2242 sizes. It offers an effortless upgrade of existing systems without sacrificing connection capability, especially in edge devices.