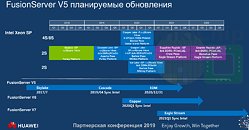
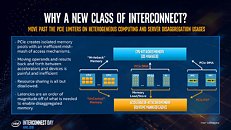
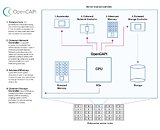
SK Hynix Licenses DBI Ultra 3D Interconnect Technology
Xperi Corporation today announced that it entered into a new patent and technology license agreement with SK hynix, one of the world's largest semiconductor manufacturers. The agreement includes access to Xperi's broad portfolio of semiconductor intellectual property (IP) and a technology transfer of Invensas DBI Ultra 3D interconnect technology focused on next-generation memory.
"We are delighted to announce the extension of our long-standing relationship with SK hynix, a world-renowned technology leader and manufacturer of memory solutions," said Craig Mitchell, President of Invensas, a wholly owned subsidiary of Xperi Corporation. "As the industry increasingly looks beyond conventional node scaling and turns toward hybrid bonding, Invensas stands as a pioneering leader that continues to deliver improved performance, power, and functionality, while also reducing the cost of semiconductors. We are proud to partner with SK hynix to further develop and commercialize our DBI Ultra technology and look forward to a wide range of memory solutions that leverage the benefits of this revolutionary technology platform."
"We are delighted to announce the extension of our long-standing relationship with SK hynix, a world-renowned technology leader and manufacturer of memory solutions," said Craig Mitchell, President of Invensas, a wholly owned subsidiary of Xperi Corporation. "As the industry increasingly looks beyond conventional node scaling and turns toward hybrid bonding, Invensas stands as a pioneering leader that continues to deliver improved performance, power, and functionality, while also reducing the cost of semiconductors. We are proud to partner with SK hynix to further develop and commercialize our DBI Ultra technology and look forward to a wide range of memory solutions that leverage the benefits of this revolutionary technology platform."