Intel iGPU+dGPU Multi-Adapter Tech Shows Promise Thanks to its Realistic Goals
Intel is revisiting the concept of asymmetric multi-GPU introduced with DirectX 12. The company posted an elaborate technical slide-deck it originally planned to present to game developers at the now-cancelled GDC 2020. The technology shows promise because the company isn't insulting developers' intelligence by proposing that the iGPU lying dormant be made to shoulder the game's entire rendering pipeline for a single-digit percentage performance boost. Rather, it has come up with innovating augments to the rendering path such that only certain lightweight compute aspects of the game's rendering be passed on to the iGPU's execution units, so it has a more meaningful contribution to overall performance. To that effect, Intel is on the path of coming up with SDK that can be integrated with existing game engines.
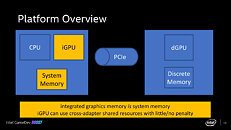
Microsoft DirectX 12 introduced the holy grail of multi-GPU technology, under its Explicit Multi-Adapter specification. This allows game engines to send rendering traffic to any combinations or makes of GPUs that support the API, to achieve a performance uplift over single GPU. This was met with lukewarm reception from AMD and NVIDIA, and far too few DirectX 12 games actually support it. Intel proposes a specialization of explicit multi-adapter approach, in which the iGPU's execution units are made to process various low-bandwidth elements both during the rendering and post-processing stages, such as Occlusion Culling, AI, game physics, etc. Intel's method leverages cross-adapter shared resources sitting in system memory (main memory), and D3D12 asynchronous compute, which creates separate processing queues for rendering and compute.
Microsoft DirectX 12 introduced the holy grail of multi-GPU technology, under its Explicit Multi-Adapter specification. This allows game engines to send rendering traffic to any combinations or makes of GPUs that support the API, to achieve a performance uplift over single GPU. This was met with lukewarm reception from AMD and NVIDIA, and far too few DirectX 12 games actually support it. Intel proposes a specialization of explicit multi-adapter approach, in which the iGPU's execution units are made to process various low-bandwidth elements both during the rendering and post-processing stages, such as Occlusion Culling, AI, game physics, etc. Intel's method leverages cross-adapter shared resources sitting in system memory (main memory), and D3D12 asynchronous compute, which creates separate processing queues for rendering and compute.