- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,243 (7.55/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
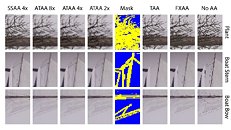
NVIDIA published the first documentation of Adaptive Temporal Anti-Aliasing (ATAA), an evolution of TAA that incorporates real-time ray-tracing, or at least the low light-count method NVIDIA implemented with RTX. Its "adaptive" nature also lets it overcome many of the performance challenges users encounter with TAA in high framerate and rapidly changing 3D scenes, such as in games. Non-gaming scenes, such as those used by real-estate developers, don't face these challenges.
To developers, ATAA promises image quality comparable to 8x supersampling at a cost of under 33 ms frame delay. These numbers were derived on a TITAN V ("Volta"), using Unreal Engine 4. It could take a while for ATAA to make it to games, as developers will need a few months to learn the technique before implementing them in their ongoing or future projects. NVIDIA will introduce ATAA support through driver updates.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
To developers, ATAA promises image quality comparable to 8x supersampling at a cost of under 33 ms frame delay. These numbers were derived on a TITAN V ("Volta"), using Unreal Engine 4. It could take a while for ATAA to make it to games, as developers will need a few months to learn the technique before implementing them in their ongoing or future projects. NVIDIA will introduce ATAA support through driver updates.

View at TechPowerUp Main Site



 they sell it and there was me thinking they shoved it down your throat for free (bundled)
they sell it and there was me thinking they shoved it down your throat for free (bundled)

