Raevenlord
News Editor
- Joined
- Aug 12, 2016
- Messages
- 3,755 (1.23/day)
- Location
- Portugal
| System Name | The Ryzening |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 9 5900X |
| Motherboard | MSI X570 MAG TOMAHAWK |
| Cooling | Lian Li Galahad 360mm AIO |
| Memory | 32 GB G.Skill Trident Z F4-3733 (4x 8 GB) |
| Video Card(s) | Gigabyte RTX 3070 Ti |
| Storage | Boot: Transcend MTE220S 2TB, Kintson A2000 1TB, Seagate Firewolf Pro 14 TB |
| Display(s) | Acer Nitro VG270UP (1440p 144 Hz IPS) |
| Case | Lian Li O11DX Dynamic White |
| Audio Device(s) | iFi Audio Zen DAC |
| Power Supply | Seasonic Focus+ 750 W |
| Mouse | Cooler Master Masterkeys Lite L |
| Keyboard | Cooler Master Masterkeys Lite L |
| Software | Windows 10 x64 |
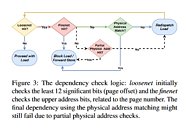
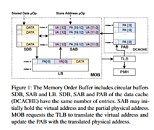
A new security vulnerability has been found that only affects Intel CPUs - AMD users need not concern regarding this issue. Dubbed Spoiler, the newfound security vulnerability was discovered by the Worcester Polytechnic Institute in partnership with the University of Lübeck, and affects all Intel CPUs since the introduction of their Core architecture. This vulnerability too affects Intel's speculative execution design, and according to the researchers, works independent of OS, virtual machine, or sandboxed environments.
As the researchers explain, Intel's speculative execution of certain memory workloads requires the full physical address bits for the information in memory to be known, which could allow for the full address to be available in user space - allowing for privilege escalation and other microarchitectural attacks. According to the researchers, a software solution to this problem is impossible, which means this is yet another silicon-level bug that needs to be addressed in future processor designs.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
As the researchers explain, Intel's speculative execution of certain memory workloads requires the full physical address bits for the information in memory to be known, which could allow for the full address to be available in user space - allowing for privilege escalation and other microarchitectural attacks. According to the researchers, a software solution to this problem is impossible, which means this is yet another silicon-level bug that needs to be addressed in future processor designs.


View at TechPowerUp Main Site






 .
.