- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,448 (7.50/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
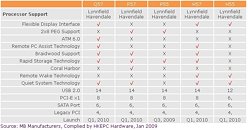
Now faced with delays, Intel's upcoming Ibex-Peak platform, a next-generation mainstream implementation of the Nehalem architecture, is an interesting mix of technologies, where Intel seeks to minimise the platform and energy footprints while delivering value and performance through a clever bit of rearrangement of system components. HKEPC has learned that Intel's 5-Series mainstream chipsets consists of five models: P57, Q57, H57, P55, and H55. The P57 and P55 are built for the consumer PC with discrete graphics. The H57 and H55 chipsets are built for processors with integrated graphics, with support for the Intel FDI. The Q57 is built for the business / enterprise-client PC, it supports a host of exclusive Intel technologies that make the machine easier to manage.
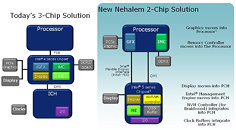
With Intel's upcoming Lynnfield quad-core and Havendale dual-core processors go a step beyond merely housing the memory controllers. They now also integrate PCI-Express root complexes, and some models even feature integrated graphics controllers on-die. This completely eliminates the requirement of a northbridge, leaving a southbridge to handle storage and peripherals. What this design does is that it eliminates a system bus between the CPU and the motherboard, with the components housed in the CPU having an internal QuickPath Interconnect linking all components, which aims to bring down latencies. The only connections the processor ends up having with the motherboard would be the PCI-Express lanes, a DMI connection to the southbridge, connections for the dual-channel DDR3 memory, and for processors with IGPs, a separate connection called Intel Flexible Display interface that routes the IGP to its I/O via the southbridge. The processor uses the newer LGA-1160 socket.

The PCI-Express root complex the processors come with can support up to two graphics cards with 8 PCI-Express 2.0 lanes each, or a single graphics card with full-bandwidth 16 lanes. The ATI CrossFireX multi-GPU technology is supported, while SLI support isn't known as yet. While 8 PCI-E 2.0 lanes to drive today's powerful GPUs sounds like a cause for concern, later down the line, one can expect motherboard vendors work around this bottleneck using PCI-E multiplex chips such as the NVIDIA BR-03, that provide full x16 connections to each graphics card, and attempt to boost performance using data-broadcast functions. All models of the 5-series PCH chipsets support six SATA II connections, and as many as 14 USB 2.0 ports. The 5-series chipset launch schedule spans from Q3 2009 to Q1 2010, though with news emerging of delays in the launch schedule, these could be pushed further away, maybe into 2010 altogether.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site

With Intel's upcoming Lynnfield quad-core and Havendale dual-core processors go a step beyond merely housing the memory controllers. They now also integrate PCI-Express root complexes, and some models even feature integrated graphics controllers on-die. This completely eliminates the requirement of a northbridge, leaving a southbridge to handle storage and peripherals. What this design does is that it eliminates a system bus between the CPU and the motherboard, with the components housed in the CPU having an internal QuickPath Interconnect linking all components, which aims to bring down latencies. The only connections the processor ends up having with the motherboard would be the PCI-Express lanes, a DMI connection to the southbridge, connections for the dual-channel DDR3 memory, and for processors with IGPs, a separate connection called Intel Flexible Display interface that routes the IGP to its I/O via the southbridge. The processor uses the newer LGA-1160 socket.


The PCI-Express root complex the processors come with can support up to two graphics cards with 8 PCI-Express 2.0 lanes each, or a single graphics card with full-bandwidth 16 lanes. The ATI CrossFireX multi-GPU technology is supported, while SLI support isn't known as yet. While 8 PCI-E 2.0 lanes to drive today's powerful GPUs sounds like a cause for concern, later down the line, one can expect motherboard vendors work around this bottleneck using PCI-E multiplex chips such as the NVIDIA BR-03, that provide full x16 connections to each graphics card, and attempt to boost performance using data-broadcast functions. All models of the 5-series PCH chipsets support six SATA II connections, and as many as 14 USB 2.0 ports. The 5-series chipset launch schedule spans from Q3 2009 to Q1 2010, though with news emerging of delays in the launch schedule, these could be pushed further away, maybe into 2010 altogether.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
Last edited:




