- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,537 (7.47/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
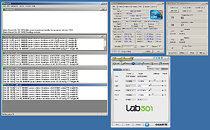
Intel's socket LGA-1156 quad-core processors are closely trailed by the company's first processors based on the 32 nm manufacturing process: Core i5 and Core i3 "Clarkdale" dual-core processors. Engineering samples of these processors were evaluated as early as Q2 2009, but one of the first attempts to show the processors' overclocking potential using air-cooling was made very recently. Even prior to that, a low-voltage overclocking feat by Coolaler showed how engineering samples didn't particularly struggle reaching clock speeds close to 4.00 GHz with vCore as low as 0.832V. Romanian tech community Lab501. Lab501 community leader "Monstru" tested the overclocking headroom of a Core i5 650 LGA-1156 dual-core processor (engineering sample) with air-cooling.
The test-bed included a Gigabyte P55 motherboard, the Core i5 650 processor was cooled by a Noctua NH-U12P, onto which a Coolink SWIF 2 120P fan was strapped. A clock speed of 4.70 GHz (25 x 188 MHz) was achieved (nearly 50% over the stock clock speed of 3.20 GHz). A core voltage of 1.424V was used. A point here to note however, is that the retail Core i5 650 will come with an upwards-locked bus frequency multiplier of 24 (24 x 133 MHz = 3.20 GHz). The processor at 4.70 GHz, was Prime95-stable for over 30 minutes. With an ambient temperature of 24 °C, the two cores heated up to 77 and 68 °C, not to forget that the processor was being air-cooled. Although with the use of an engineering sample (since the retail launch of this processor is tentatively three months away), the scope for inference of this feat is limited, it gives you a coarse indication that Intel is keeping the trend of ferociously fast dual-core processors alive. High(er) overclocking headroom on air-cooling is the fruition of the 32 nm process. Slated for Q1 2010, the siblings (and cousins) of the Core i5 650 include Core i5 660/661 (3.33 GHz, HTT), Core i5 670 (3.46 GHz, HTT), Core i3 540 (3.06 GHz, no HTT), Core i3 530 (2.93 GHz, no HTT), and Pentium G6950 (2.80 GHz, no HTT). Details of the series can be found here.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
The test-bed included a Gigabyte P55 motherboard, the Core i5 650 processor was cooled by a Noctua NH-U12P, onto which a Coolink SWIF 2 120P fan was strapped. A clock speed of 4.70 GHz (25 x 188 MHz) was achieved (nearly 50% over the stock clock speed of 3.20 GHz). A core voltage of 1.424V was used. A point here to note however, is that the retail Core i5 650 will come with an upwards-locked bus frequency multiplier of 24 (24 x 133 MHz = 3.20 GHz). The processor at 4.70 GHz, was Prime95-stable for over 30 minutes. With an ambient temperature of 24 °C, the two cores heated up to 77 and 68 °C, not to forget that the processor was being air-cooled. Although with the use of an engineering sample (since the retail launch of this processor is tentatively three months away), the scope for inference of this feat is limited, it gives you a coarse indication that Intel is keeping the trend of ferociously fast dual-core processors alive. High(er) overclocking headroom on air-cooling is the fruition of the 32 nm process. Slated for Q1 2010, the siblings (and cousins) of the Core i5 650 include Core i5 660/661 (3.33 GHz, HTT), Core i5 670 (3.46 GHz, HTT), Core i3 540 (3.06 GHz, no HTT), Core i3 530 (2.93 GHz, no HTT), and Pentium G6950 (2.80 GHz, no HTT). Details of the series can be found here.

View at TechPowerUp Main Site
Last edited:






 ...
...
