- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,617 (7.44/day)
- Location
- Dublin, Ireland
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | Gigabyte B550 AORUS Elite V2 |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 16GB DDR4-3200 |
| Video Card(s) | Galax RTX 4070 Ti EX |
| Storage | Samsung 990 1TB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
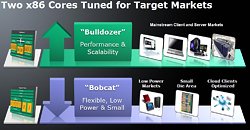
AMD is finally going to embrace a truly next generation x86 processor architecture that is built from ground up. AMD's current architecture, the K10(.5) "Stars" is an evolution of the more market-successful K8 architecture, but it didn't face the kind of market success as it was overshadowed by competing Intel architectures. AMD codenamed its latest design "Bulldozer", and it features an x86 core design that is radically different from anything we've seen from either processor giants. With this design, AMD thinks it can outdo both HyperThreading and Multi-Core approaches to parallelism, in one shot, as well as "bulldoze" through serial workloads with a broad 8 integer pipeline per core, (compared to 3 on K10, and 4 on Westmere). Two almost-individual blocks of integer processing units share a common floating point unit with two 128-bit FMACs.
AMD is also working on a multi-threading technology of its own to rival Intel's HyperThreading, that exploits Bulldozer's branched integer processing backed by shared floating point design, which AMD believes to be so efficient, that each SMT worker thread can be deemed a core in its own merit, and further be backed by competing threads per "core". AMD is working on another micro-architecture codenamed "Bobcat", which is a downscale implementation of Bulldozer, with which it will take on low-power and high performance per Watt segments that extend from all-in-One PCs all the way down to hand-held devices and 8-inch tablets. We will explore the Bulldozer architecture in some detail.
Bulldozer: The Turbo Diesel Engine
In many respects, the Bulldozer architecture is comparable to a diesel engine. Lower RPM (clock-speeds), high torque (instructions per second). When implemented, Bulldozer-based processors could outperform competing processor architectures at much lower clock speeds, due to one critical area AMD seems to have finally addressed: instructions per clock (IPC), unlike with the 65 nm "Barcelona" or 45 nm "Shanghai" architectures that upped IPC synthetically by using other means (such as backing the cores up with a level-3 cache, upping the uncore/northbridge clock speeds), the 32 nm Bulldozer actually features a broad integer unit with eight integer pipelines split into two portions, each portion having its own scheduler and L1 Data cache.

Parallelism: A Radical Approach?
Back when analysts were pinning high hopes on the Barcelona architecture, their hopes were fueled by early reports suggesting that AMD was using wide 128-bit wide floating point units, leading analysts to believe that AMD may have conquered its biggest nemesis - floating point performance, in turn its pure math crunching abilities. However, that wasn't exactly to be. That's because the processor's overall number crunching abilities were pegged to its floating point performance, ignoring the integer units.

AMD split 8 integers per core into two blocks, each block having four integer pipelines, an integer scheduler for those, and an L1 Data cache. These constitute the lowest level of "dedicated components", dedicated to processor threads. There is a shared floating point unit between the two, with two 128-bit FMACs, arbitrated by a floating point scheduler. The Fetch/Decode, an L2 cache, and the FPU constitute "shared" components.
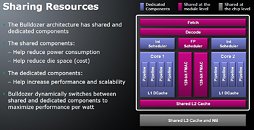
AMD is implementing a simultaneous multithreading (SMT) technology, it can split each of the "dedicated" components (in this case, the integer unit) to deal with a thread of its own, while sharing certain components with the other integer unit, and effectively make each set of dedicated components a "core" in its own merit of efficiency. This way, the actual core of the Bulldozer die is deemed a "module", a superlative of two cores, and the Bulldozer die (chip) features n-number of modules depending on the model.
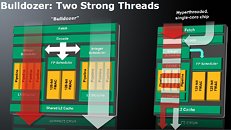
So now you have a chip with eight cores with much lower die sizes and transistor counts compared to a hypothetical 32 nm K10 8-core processor. It is unclear whether AMD wants to further push down SMT to the "core" level and run two threads simultaneously over dedicated components, but one thing for sure is that AMD has embraced SMT in some form or another. In all this, the chip-level parallelism is transparent to the operating system, it will only see a fixed number of logical processors, without any special software or driver requirement.
So in one go, AMD shot up its integer performance. Either a thread makes use of one integer unit with its four pipelines, or deals with both the integer units arbitrated by the fetch/decode, and the shared FPU.
Outside the modules
At the chip-level, there's a large L3 cache, a northbridge that integrates the PCI-Express root complex, and an integrated memory controller. Since the northbridge is completely on the chip, the processor does not need to deal with the rest of the system with a HyperTransport link. It connects to the chipset (which is now relegated to a southbridge, much like Intel's Ibex Peak), using A-Link Express, which like DMI, is essentially a PCI-Express link. It is important to note that all modules and extra-modular components are present on the same piece of silicon die. Because of this design change, Bulldozer processors will come in totally new packages that are not backwards compatible with older AMD sockets such as AM3 or AM2(+).

Expectations
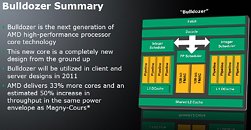
Not surprisingly, AMD isn't talking about Bulldozer as the next big thing since dual-core processors (something it did with Barcelona). AMD currently does have an 8-core and 12-core processors codenamed "Magny-Cours", which are multichip modules of Shanghai (4-core) and Istanbul (6-core) dies. AMD expects an 8-core Bulldozer implementation (built with four modules), to have 50% higher performance-per-watt compared to Magny-Cours.
Market Segments
As mentioned in the graphic before, AMD's modular design allows it to create different products by simply controlling the number of modules on the die (by whichever method). With this, AMD will have processors ready with most PC and server market segments, all the way from desktop PCs, enthusiast-grade PCs, notebooks, to servers. AMD expects to have a full-fledged lineup in 2011. The first Bulldozer CPUs will be sold to the server market.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
AMD is also working on a multi-threading technology of its own to rival Intel's HyperThreading, that exploits Bulldozer's branched integer processing backed by shared floating point design, which AMD believes to be so efficient, that each SMT worker thread can be deemed a core in its own merit, and further be backed by competing threads per "core". AMD is working on another micro-architecture codenamed "Bobcat", which is a downscale implementation of Bulldozer, with which it will take on low-power and high performance per Watt segments that extend from all-in-One PCs all the way down to hand-held devices and 8-inch tablets. We will explore the Bulldozer architecture in some detail.

Bulldozer: The Turbo Diesel Engine
In many respects, the Bulldozer architecture is comparable to a diesel engine. Lower RPM (clock-speeds), high torque (instructions per second). When implemented, Bulldozer-based processors could outperform competing processor architectures at much lower clock speeds, due to one critical area AMD seems to have finally addressed: instructions per clock (IPC), unlike with the 65 nm "Barcelona" or 45 nm "Shanghai" architectures that upped IPC synthetically by using other means (such as backing the cores up with a level-3 cache, upping the uncore/northbridge clock speeds), the 32 nm Bulldozer actually features a broad integer unit with eight integer pipelines split into two portions, each portion having its own scheduler and L1 Data cache.

Parallelism: A Radical Approach?
Back when analysts were pinning high hopes on the Barcelona architecture, their hopes were fueled by early reports suggesting that AMD was using wide 128-bit wide floating point units, leading analysts to believe that AMD may have conquered its biggest nemesis - floating point performance, in turn its pure math crunching abilities. However, that wasn't exactly to be. That's because the processor's overall number crunching abilities were pegged to its floating point performance, ignoring the integer units.

AMD split 8 integers per core into two blocks, each block having four integer pipelines, an integer scheduler for those, and an L1 Data cache. These constitute the lowest level of "dedicated components", dedicated to processor threads. There is a shared floating point unit between the two, with two 128-bit FMACs, arbitrated by a floating point scheduler. The Fetch/Decode, an L2 cache, and the FPU constitute "shared" components.

AMD is implementing a simultaneous multithreading (SMT) technology, it can split each of the "dedicated" components (in this case, the integer unit) to deal with a thread of its own, while sharing certain components with the other integer unit, and effectively make each set of dedicated components a "core" in its own merit of efficiency. This way, the actual core of the Bulldozer die is deemed a "module", a superlative of two cores, and the Bulldozer die (chip) features n-number of modules depending on the model.

So now you have a chip with eight cores with much lower die sizes and transistor counts compared to a hypothetical 32 nm K10 8-core processor. It is unclear whether AMD wants to further push down SMT to the "core" level and run two threads simultaneously over dedicated components, but one thing for sure is that AMD has embraced SMT in some form or another. In all this, the chip-level parallelism is transparent to the operating system, it will only see a fixed number of logical processors, without any special software or driver requirement.
So in one go, AMD shot up its integer performance. Either a thread makes use of one integer unit with its four pipelines, or deals with both the integer units arbitrated by the fetch/decode, and the shared FPU.
Outside the modules
At the chip-level, there's a large L3 cache, a northbridge that integrates the PCI-Express root complex, and an integrated memory controller. Since the northbridge is completely on the chip, the processor does not need to deal with the rest of the system with a HyperTransport link. It connects to the chipset (which is now relegated to a southbridge, much like Intel's Ibex Peak), using A-Link Express, which like DMI, is essentially a PCI-Express link. It is important to note that all modules and extra-modular components are present on the same piece of silicon die. Because of this design change, Bulldozer processors will come in totally new packages that are not backwards compatible with older AMD sockets such as AM3 or AM2(+).

Expectations
Not surprisingly, AMD isn't talking about Bulldozer as the next big thing since dual-core processors (something it did with Barcelona). AMD currently does have an 8-core and 12-core processors codenamed "Magny-Cours", which are multichip modules of Shanghai (4-core) and Istanbul (6-core) dies. AMD expects an 8-core Bulldozer implementation (built with four modules), to have 50% higher performance-per-watt compared to Magny-Cours.

Market Segments
As mentioned in the graphic before, AMD's modular design allows it to create different products by simply controlling the number of modules on the die (by whichever method). With this, AMD will have processors ready with most PC and server market segments, all the way from desktop PCs, enthusiast-grade PCs, notebooks, to servers. AMD expects to have a full-fledged lineup in 2011. The first Bulldozer CPUs will be sold to the server market.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
Last edited:










