- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,527 (7.48/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
Researchers at the University of California, San Diego, have concluded that solid state drives (SSDs) have a bleak future in the evolution of computing technology. They have discovered that fast flash based storage are facing come pretty glaring technology hurdles during their natural course of evolution, which they don't think it will overcome. To begin with, shrinking (miniaturizing) them, to increase capacity or decrease manufacturing costs, will severely degrade performance beyond a point, 6.5 nm silicon fab process.
The scientists studied 45 different flash chips in various sizes, which showed that scaling of latencies and error-rates are 'tolerable' enough as the technology miniaturizes only till 6.5 nm, or the year 2024, when this fab process will be common, beyond which they question the drives' viability. Beyond this point, the more capacity you squeeze into flash memory chips, the more performance degrade (latency and error-rate scale beyond tolerable scales).
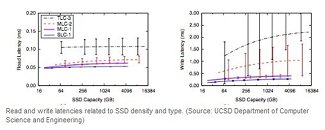
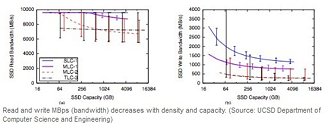
While the density of SSDs grows and the cost per gigabyte shrinks, "everything else about them is poised to get worse," said Laura Grupp, a graduate student at the University of California, San Diego. "This makes the future of SSDs cloudy: While the growing capacity of SSDs and high IOP rates will make them attractive for many applications, the reduction in performance that is necessary to increase capacity while keeping costs in check may make it difficult for SSDs to scale as a viable technology for some applications," the author of the study.
The study, entitled "The Bleak Future of NAND Flash Memory", can be accessed here.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
The scientists studied 45 different flash chips in various sizes, which showed that scaling of latencies and error-rates are 'tolerable' enough as the technology miniaturizes only till 6.5 nm, or the year 2024, when this fab process will be common, beyond which they question the drives' viability. Beyond this point, the more capacity you squeeze into flash memory chips, the more performance degrade (latency and error-rate scale beyond tolerable scales).


While the density of SSDs grows and the cost per gigabyte shrinks, "everything else about them is poised to get worse," said Laura Grupp, a graduate student at the University of California, San Diego. "This makes the future of SSDs cloudy: While the growing capacity of SSDs and high IOP rates will make them attractive for many applications, the reduction in performance that is necessary to increase capacity while keeping costs in check may make it difficult for SSDs to scale as a viable technology for some applications," the author of the study.
The study, entitled "The Bleak Future of NAND Flash Memory", can be accessed here.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site




 (feel like such a woman saying this). I would love to download everything, so I never have to uninstall/install for space, or have shitty transfer speed when the servers are busy (more or less 6 out of 12 months) AND have everything backed up? I'd do the same for movies as well. While streaming is a decent idea, it's just not there yet, and definitely not for games, barely for movies.
(feel like such a woman saying this). I would love to download everything, so I never have to uninstall/install for space, or have shitty transfer speed when the servers are busy (more or less 6 out of 12 months) AND have everything backed up? I'd do the same for movies as well. While streaming is a decent idea, it's just not there yet, and definitely not for games, barely for movies.


