- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,537 (7.47/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
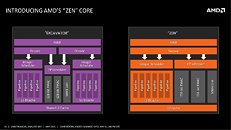
As a quick follow up to our older report on AMD's upcoming "Zen" CPU core micro-architecture being a reversion to the monolithic core design, and a departure from its "Bulldozer" multicore module design which isn't exactly flying off the shelves, a leaked company slide provides us the first glimpse into the core design. Zen looks a lot like "Stars," the core design AMD launched with its Phenom series, except it has a lot more muscle, and one could see significant IPC improvements over the current architecture.
To begin with, Zen features monolithic fetch and decode units. On Bulldozer, two cores inside a module featured dedicated decode and integer units with shared floating-point units. On Zen, there's a monolithic decode unit, and single integer and floating points. The integer unit has 6 pipelines, compared to 4 per core on Bulldozer. The floating point unit has two large 256-bit FMAC (fused-multiply accumulate) units, compared to two 128-bit ones on Bulldozer. The core has a dedicated 512 KB L2 cache. This may be much smaller than the 2 MB per module on Bulldozer, but also indicate that the core is able to push through things fast enough to not need cushioning by a cache (much like Intel's Haswell architecture featuring just 256 KB per core). In a typical multi-core Zen chip, the cores will converge at a large last-level cache, which routes data between them to the processor's uncore, which will feature a DDR4 IMC and a PCI-Express 3.0 root complex.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
To begin with, Zen features monolithic fetch and decode units. On Bulldozer, two cores inside a module featured dedicated decode and integer units with shared floating-point units. On Zen, there's a monolithic decode unit, and single integer and floating points. The integer unit has 6 pipelines, compared to 4 per core on Bulldozer. The floating point unit has two large 256-bit FMAC (fused-multiply accumulate) units, compared to two 128-bit ones on Bulldozer. The core has a dedicated 512 KB L2 cache. This may be much smaller than the 2 MB per module on Bulldozer, but also indicate that the core is able to push through things fast enough to not need cushioning by a cache (much like Intel's Haswell architecture featuring just 256 KB per core). In a typical multi-core Zen chip, the cores will converge at a large last-level cache, which routes data between them to the processor's uncore, which will feature a DDR4 IMC and a PCI-Express 3.0 root complex.

View at TechPowerUp Main Site




 .
.
