- Joined
- May 14, 2004
- Messages
- 28,475 (3.73/day)
| Processor | Ryzen 7 5700X |
|---|---|
| Memory | 48 GB |
| Video Card(s) | RTX 4080 |
| Storage | 2x HDD RAID 1, 3x M.2 NVMe |
| Display(s) | 30" 2560x1600 + 19" 1280x1024 |
| Software | Windows 10 64-bit |
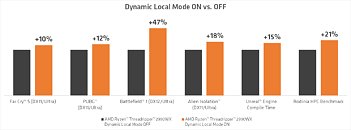
AMD has made a blog post describing an upcoming feature for their Threadripper processors called "Dynamic Local Mode", which should help a lot with gaming performance on AMD's latest flagship CPUs.
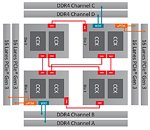
Threadripper uses four dies in a multi-chip package, of which only two have a direct access path to the memory modules. The other two dies have to rely on Infinity Fabric for all their memory accesses, which comes with a significant latency hit. Many compute-heavy applications can run their workloads in the CPU cache, or require only very little memory access; these are not affected. Other applications, especially games, spread their workload over multiple cores, some of which end up with higher memory latency than expected, which results in a suboptimal performance.
The concept of multiple processors having different memory access paths is called NUMA (Non-uniform memory access). While technically it is possible for software to detect the NUMA configuration and attach each thread to the ideal processor core, most applications are not NUMA aware and the adoption rate is very slow, probably due to the low number of systems using such a concept.


In ThreadRipper, using Ryzen Master, users are free to switch between "Local Memory Access" mode or "Distributed Memory Access" mode, with the latter being the default for ThreadRipper, resulting in highest compute application performance. Local Mode on the other hand is better suited to games, but switching between the modes requires a reboot, which is very inconvenient for users.
AMD's new "Dynamic Local Mode" seeks to abolish that requirement by introducing a background process that continually monitors all running applications for their CPU usage and pushes the more busy ones onto the cores that have direct memory access, by adjusting their process affinity mask, which selects which processors the application is allowed to be scheduled on. Applications that require very little CPU are in turn pushed onto the cores with no memory access, because they are not so important for fast execution.
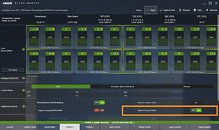
This update will be available starting October 29 in Ryzen Master, and will be automatically enabled unless the user manually chooses to disable it. AMD also plans to open the feature up to even more users by including Dynamic Local Mode as a default package in the AMD Chipset Drivers.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site


Threadripper uses four dies in a multi-chip package, of which only two have a direct access path to the memory modules. The other two dies have to rely on Infinity Fabric for all their memory accesses, which comes with a significant latency hit. Many compute-heavy applications can run their workloads in the CPU cache, or require only very little memory access; these are not affected. Other applications, especially games, spread their workload over multiple cores, some of which end up with higher memory latency than expected, which results in a suboptimal performance.
The concept of multiple processors having different memory access paths is called NUMA (Non-uniform memory access). While technically it is possible for software to detect the NUMA configuration and attach each thread to the ideal processor core, most applications are not NUMA aware and the adoption rate is very slow, probably due to the low number of systems using such a concept.


In ThreadRipper, using Ryzen Master, users are free to switch between "Local Memory Access" mode or "Distributed Memory Access" mode, with the latter being the default for ThreadRipper, resulting in highest compute application performance. Local Mode on the other hand is better suited to games, but switching between the modes requires a reboot, which is very inconvenient for users.
AMD's new "Dynamic Local Mode" seeks to abolish that requirement by introducing a background process that continually monitors all running applications for their CPU usage and pushes the more busy ones onto the cores that have direct memory access, by adjusting their process affinity mask, which selects which processors the application is allowed to be scheduled on. Applications that require very little CPU are in turn pushed onto the cores with no memory access, because they are not so important for fast execution.

This update will be available starting October 29 in Ryzen Master, and will be automatically enabled unless the user manually chooses to disable it. AMD also plans to open the feature up to even more users by including Dynamic Local Mode as a default package in the AMD Chipset Drivers.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site








