- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,511 (7.49/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
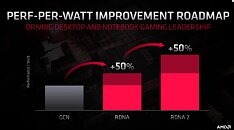
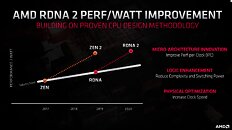
With its 7 nm RDNA architecture that debuted in July 2019, AMD achieved a nearly 50% gain in performance/Watt over the previous "Vega" architecture. At its 2020 Financial Analyst Day event, AMD made a big disclosure: that its upcoming RDNA2 architecture will offer a similar 50% performance/Watt jump over RDNA. The new RDNA2 graphics architecture is expected to leverage 7 nm+ (7 nm EUV), which offers up to 18% transistor-density increase over 7 nm DUV, among other process-level improvements. AMD could tap into this to increase price-performance by serving up more compute units at existing price-points, running at higher clock speeds.
AMD has two key design goals with RDNA2 that helps it close the feature-set gap with NVIDIA: real-time ray-tracing, and variable-rate shading, both of which have been standardized by Microsoft under DirectX 12 DXR and VRS APIs. AMD announced that RDNA2 will feature dedicated ray-tracing hardware on die. On the software side, the hardware will leverage industry-standard DXR 1.1 API. The company is supplying RDNA2 to next-generation game console manufacturers such as Sony and Microsoft, so it's highly likely that AMD's approach to standardized ray-tracing will have more takers than NVIDIA's RTX ecosystem that tops up DXR feature-sets with its own RTX feature-set.


Variable-rate shading is another key feature that has been missing on AMD GPUs. The feature allows a graphics application to apply different rates of shading detail to different areas of the 3D scene being rendered, to conserve system resources. NVIDIA and Intel already implement VRS tier-1 standardized by Microsoft, and NVIDIA "Turing" goes a step further in supporting even VRS tier-2. AMD didn't detail its VRS tier support.
AMD hopes to deploy RDNA2 on everything from desktop discrete client graphics, to professional graphics for creators, to mobile (notebook/tablet) graphics, and lastly cloud graphics (for cloud-based gaming platforms such as Stadia). Its biggest takers, however, will be the next-generation Xbox and PlayStation game consoles, who will also shepherd game developers toward standardized ray-tracing and VRS implementations.
AMD also briefly touched upon the next-generation RDNA3 graphics architecture without revealing any features. All we know about RDNA3 for now, is that it will leverage a process node more advanced than 7 nm (likely 6 nm or 5 nm, AMD won't say); and that it will come out some time between 2021 and 2022. RDNA2 will extensively power AMD client graphics products over the next 5-6 calendar quarters, at least.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
AMD has two key design goals with RDNA2 that helps it close the feature-set gap with NVIDIA: real-time ray-tracing, and variable-rate shading, both of which have been standardized by Microsoft under DirectX 12 DXR and VRS APIs. AMD announced that RDNA2 will feature dedicated ray-tracing hardware on die. On the software side, the hardware will leverage industry-standard DXR 1.1 API. The company is supplying RDNA2 to next-generation game console manufacturers such as Sony and Microsoft, so it's highly likely that AMD's approach to standardized ray-tracing will have more takers than NVIDIA's RTX ecosystem that tops up DXR feature-sets with its own RTX feature-set.




Variable-rate shading is another key feature that has been missing on AMD GPUs. The feature allows a graphics application to apply different rates of shading detail to different areas of the 3D scene being rendered, to conserve system resources. NVIDIA and Intel already implement VRS tier-1 standardized by Microsoft, and NVIDIA "Turing" goes a step further in supporting even VRS tier-2. AMD didn't detail its VRS tier support.
AMD hopes to deploy RDNA2 on everything from desktop discrete client graphics, to professional graphics for creators, to mobile (notebook/tablet) graphics, and lastly cloud graphics (for cloud-based gaming platforms such as Stadia). Its biggest takers, however, will be the next-generation Xbox and PlayStation game consoles, who will also shepherd game developers toward standardized ray-tracing and VRS implementations.
AMD also briefly touched upon the next-generation RDNA3 graphics architecture without revealing any features. All we know about RDNA3 for now, is that it will leverage a process node more advanced than 7 nm (likely 6 nm or 5 nm, AMD won't say); and that it will come out some time between 2021 and 2022. RDNA2 will extensively power AMD client graphics products over the next 5-6 calendar quarters, at least.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site



