- Joined
- Aug 19, 2017
- Messages
- 2,905 (1.05/day)
As the global economy enters the post-pandemic era, technologies including 5G, WiFi6/6E, and HPC (high-performance computing) have been advancing rapidly, in turn bringing about a fundamental, structural change in the semiconductor industry as well, according to TrendForce's latest investigations. While the demand for certain devices such as notebook computers and TVs underwent a sharp uptick due to the onset of the stay-at-home economy, this demand will return to pre-pandemic levels once the pandemic has been brought under control as a result of the global vaccination drive. Nevertheless, the worldwide shift to next-gen telecommunication standards has brought about a replacement demand for telecom and networking devices, and this demand will continue to propel the semiconductor industry, resulting in high capacity utilization rates across the major foundries. As certain foundries continue to expand their production capacities this year, TrendForce expects total foundry revenue to reach a historical high of US$94.6 billion this year, an 11% growth YoY.
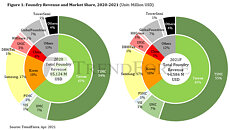
TrendForce's latest analysis also finds that shipments and production volumes of end products will continue to grow in the post-pandemic period. Regarding host computers, the total (or global) shipments of servers and workstations are forecasted to undergo a yearly growth mainly driven by applications that are enabled by 5G and HPC. As for various types of client (or end-user) devices, the annual total production volume of 5G smartphones, in particular, is forecasted to increase by around 113% YoY. The penetration rate of 5G models in the smartphone market is also forecasted to rise to 37% in the same year. Turning to notebook (or laptop) computers, their total shipments in 2021 will register a YoY growth rate of about 15% thanks to the proliferation of the stay-at-home economy. Finally, the governments of many countries introduced consumption subsidies during the pandemic so as to stimulate the domestic economy. Video streaming services have also grown dramatically with respect to content and demand because of the pandemic. As a result, the TV market is seeing a wave of replacement demand as consumers want to purchase the latest models that offer higher resolutions (e.g., 4K and 8K) and network connectivity (i.e., smart TVs). The total shipments of digital TVs in 2021 are forecasted to undergo a YoY growth rate of around 3%.
The high demand for the aforementioned end devices has therefore resulted in a corresponding surging demand for various ICs used in these devices, including CIS, DDI, and PMICs. In addition, the increasing adoption of cloud services, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, has also generated a massive demand for various high-end CPUs and memory products used in the HPC platforms that power said cloud services. On the whole, TrendForce believes that, with demand maintaining a healthy growth momentum for many kinds of end products, semiconductor components that are manufactured with the same foundry nodes will be competing for production capacity. Some categories of ICs will therefore experience a more severe capacity crunch due to the product mix strategies of respective foundries. In the short term, no effective resolution is expected for the undersupply situation in the foundry market.
Certain foundries will continue to expand their production capacities in 2021 as the semiconductor industry undergoes a structural change
With regards to the expansion plans of various foundries this year, tier-one and tier-two foundries will prioritize the development of different process nodes. More specifically, tier-one foundries, including TSMC and Samsung, will focus on the R&D, fab build-out, and capacity expansion for the 5 nm and below nodes in response to the growing chip demand for HPC-related applications. On the other hand, tier-two foundries, including SMIC, UMC, and GlobalFoundries will primarily focus on expanding their production capacities of the 14 nm to 40 nm mature process nodes in order to meet the massive demand for next-gen telecom technologies (such as 5G and WiFi6/6E) and other diverse applications (such as OLED DDI and CIS/ISP). Incidentally, it should be pointed out that SMIC's capacity expansion plans have been constrained after the US Department of Commerce added SMIC to the Entity List, which prohibited the company from procuring US semiconductor equipment. However, SMIC still possesses enough funds for procuring non-US equipment and building new fabs, as the company is not only actively expanding its existing 8-inch and 12-inch wafer capacities, but also proceeding with the construction of its new fab in Beijing.
Apart from the aforementioned companies, other foundries, including PSMC, Tower Semiconductor, Vanguard, and HHGrace, will prioritize the capacity expansion of their 8-inch wafers (which are used for the 55 nm and above nodes) to meet the demand for large-sized DDI, TDDI, and PMICs. These foundries, in contrast with their larger competitors, are primarily focusing on 8-inch capacity expansion due to the relatively high cost of DUV immersion systems used for the 40/45 nm and below processes. For these companies, it is much more economically feasible to instead undertake capacity expansions for the 55/65 nm and above nodes.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site

TrendForce's latest analysis also finds that shipments and production volumes of end products will continue to grow in the post-pandemic period. Regarding host computers, the total (or global) shipments of servers and workstations are forecasted to undergo a yearly growth mainly driven by applications that are enabled by 5G and HPC. As for various types of client (or end-user) devices, the annual total production volume of 5G smartphones, in particular, is forecasted to increase by around 113% YoY. The penetration rate of 5G models in the smartphone market is also forecasted to rise to 37% in the same year. Turning to notebook (or laptop) computers, their total shipments in 2021 will register a YoY growth rate of about 15% thanks to the proliferation of the stay-at-home economy. Finally, the governments of many countries introduced consumption subsidies during the pandemic so as to stimulate the domestic economy. Video streaming services have also grown dramatically with respect to content and demand because of the pandemic. As a result, the TV market is seeing a wave of replacement demand as consumers want to purchase the latest models that offer higher resolutions (e.g., 4K and 8K) and network connectivity (i.e., smart TVs). The total shipments of digital TVs in 2021 are forecasted to undergo a YoY growth rate of around 3%.
The high demand for the aforementioned end devices has therefore resulted in a corresponding surging demand for various ICs used in these devices, including CIS, DDI, and PMICs. In addition, the increasing adoption of cloud services, including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, has also generated a massive demand for various high-end CPUs and memory products used in the HPC platforms that power said cloud services. On the whole, TrendForce believes that, with demand maintaining a healthy growth momentum for many kinds of end products, semiconductor components that are manufactured with the same foundry nodes will be competing for production capacity. Some categories of ICs will therefore experience a more severe capacity crunch due to the product mix strategies of respective foundries. In the short term, no effective resolution is expected for the undersupply situation in the foundry market.
Certain foundries will continue to expand their production capacities in 2021 as the semiconductor industry undergoes a structural change
With regards to the expansion plans of various foundries this year, tier-one and tier-two foundries will prioritize the development of different process nodes. More specifically, tier-one foundries, including TSMC and Samsung, will focus on the R&D, fab build-out, and capacity expansion for the 5 nm and below nodes in response to the growing chip demand for HPC-related applications. On the other hand, tier-two foundries, including SMIC, UMC, and GlobalFoundries will primarily focus on expanding their production capacities of the 14 nm to 40 nm mature process nodes in order to meet the massive demand for next-gen telecom technologies (such as 5G and WiFi6/6E) and other diverse applications (such as OLED DDI and CIS/ISP). Incidentally, it should be pointed out that SMIC's capacity expansion plans have been constrained after the US Department of Commerce added SMIC to the Entity List, which prohibited the company from procuring US semiconductor equipment. However, SMIC still possesses enough funds for procuring non-US equipment and building new fabs, as the company is not only actively expanding its existing 8-inch and 12-inch wafer capacities, but also proceeding with the construction of its new fab in Beijing.
Apart from the aforementioned companies, other foundries, including PSMC, Tower Semiconductor, Vanguard, and HHGrace, will prioritize the capacity expansion of their 8-inch wafers (which are used for the 55 nm and above nodes) to meet the demand for large-sized DDI, TDDI, and PMICs. These foundries, in contrast with their larger competitors, are primarily focusing on 8-inch capacity expansion due to the relatively high cost of DUV immersion systems used for the 40/45 nm and below processes. For these companies, it is much more economically feasible to instead undertake capacity expansions for the 55/65 nm and above nodes.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site

