TheLostSwede
News Editor
- Joined
- Nov 11, 2004
- Messages
- 18,348 (2.46/day)
- Location
- Sweden
| System Name | Overlord Mk MLI |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D |
| Motherboard | Gigabyte X670E Aorus Master |
| Cooling | Noctua NH-D15 SE with offsets |
| Memory | 32GB Team T-Create Expert DDR5 6000 MHz @ CL30-34-34-68 |
| Video Card(s) | Gainward GeForce RTX 4080 Phantom GS |
| Storage | 1TB Solidigm P44 Pro, 2 TB Corsair MP600 Pro, 2TB Kingston KC3000 |
| Display(s) | Acer XV272K LVbmiipruzx 4K@160Hz |
| Case | Fractal Design Torrent Compact |
| Audio Device(s) | Corsair Virtuoso SE |
| Power Supply | be quiet! Pure Power 12 M 850 W |
| Mouse | Logitech G502 Lightspeed |
| Keyboard | Corsair K70 Max |
| Software | Windows 10 Pro |
| Benchmark Scores | https://valid.x86.fr/yfsd9w |
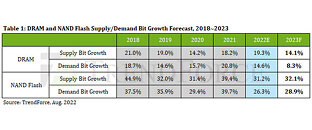
According to TrendForce, DRAM market demand bit growth will only amount to 8.3% in 2023, sub-10% for the first time in history, and far lower than supply-side bit growth of approximately 14.1%. Data indicates the DRAM market to be severely oversupplied at least in 2023 and prices may continue to decline. NAND Flash is still in a state of oversupply and, although prices are expected to fall in the first half of next year, NAND Flash has built-in price elasticity compared to DRAM and average prices are expected to stimulate density growth in the enterprise SSD market after declining for several consecutive quarters. Demand bits are expected to grow by 28.9%, while supply bits will grow by approximately 32.1%.
From the perspective of various applications, rising inflation continues to impact demand in consumer markets, so the primary goal of memory brands has been to prioritize inventory correction. Especially in the past two years, a shortage of upstream components caused by the pandemic led memory brands to overbook purchase orders while sluggish sales on the distribution channel side have resulted in slow depletion of current notebook inventory, resulting in a further weakening of notebook demand in 2023. In terms of PC DRAM, the proportion of DDR4 and LPDDR4X in PC applications will fall further while the penetration rate of LPDDR5 and DDR5 continues to rise. However, the price premium of DDR5 will limit the growth of density in PCs. DRAM density in PCs is estimate to increase by approximately 7% annually in 2023. If manufactures cut DDR5 pricing more aggressively next year, installed capacity may be driven up to 9%, depending on whether DDR5 price concessions can be effectively reconciled with DDR4.
In terms of PC client SSDs, estimated average installed capacity only increased slightly by 11%, the lowest in the past three years. The primary reason is that in the past two years, notebook shipments had spiked due to pandemic demand, simultaneously driving SSD installation rate. Average capacity has readily driven up average capacity growth due to the previous tightening of SSD master IC supply. However, notebook computer whole device costs have maintained an upward trend in the past two years due to the rising price of components, leading to branded PC manufacturers planning relatively conservative SSD capacity demand bits.
Since server shipment forecasts have demonstrated impressive growth in past years, subsequent growth momentum will slow since computational fundamentals are already high. In terms of Server DRAM, due to the advent of fifth generation memory specifications, the new Sapphire Rapids and Genoa platforms have increased the cost of whole devices and average server capacity has begun to encounter restrictions. Instead of the prior practice of merely upgrading the capacity of a single module, demand side considerations will focus more on hardware costs and the practice of ESG strategies. Average capacity increase of server DRAM is forecast to be limited in 2023, with an annual increase of approximately 7%.
In terms of Enterprise SSD, the new Sapphire Rapids and Genoa platforms have begun to upgrade to support the PCIe 5.0 transfer standard in order to meet the needs of HPC and big data computing. The capacity of SSDs must also be upgraded simultaneously to ensure PCIe 5.0 transfer performance. This trend will contribute to the growth of the average capacity of enterprise SSDs next year. In addition, as the overall NAND Flash oversupply continues into 1H23, a reduction in NAND Flash pricing will increase the shipment ratio of products above 4TB and the average annual growth rate of enterprise SSD capacity in 2023 is estimated to be 26%.
As inflation rises, world economies are generally holding a pessimistic view of the consumer market. TrendForce believes, cyclical replacement demand and new demand in emerging regions will lead to a slight increase in smartphone production. In terms of Mobile DRAM, the Android camp currently has sufficient installed capacity to meet the needs of daily systems operation. Therefore, barring impetus provided by innovative applications and considering the cost of whole devices and the low proportion of high-end sales, smartphone brands' willingness to increase installed capacity has fallen accordingly. In terms of the iOS camp, a high degree of operating system optimization reduces demand for mobile DRAM capacity. Mobile DRAM density is estimated to increase by only 5% annually in 2023.
In terms of smartphone NAND Flash, as the penetration rate of 5G smartphones gradually expands and applications require larger installed capacity to meet the needs of high-quality video recording, basic momentum can be seen for increasing NAND Flash density in smartphones. At the same time, the iPhone product portfolio is still moving towards higher capacity across the board and high-end Android models have followed suit with 512 GB as standard, while storage in mid- and low-end models will increase with subsequent upgrades in hardware specifications. Thus, there is still room for growth in overall average capacity. Annual growth of smartphone NAND Flash density is forecast to be maintained at 22.1% in 2023, slightly lower than that in 2022, but still at a high level.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source
From the perspective of various applications, rising inflation continues to impact demand in consumer markets, so the primary goal of memory brands has been to prioritize inventory correction. Especially in the past two years, a shortage of upstream components caused by the pandemic led memory brands to overbook purchase orders while sluggish sales on the distribution channel side have resulted in slow depletion of current notebook inventory, resulting in a further weakening of notebook demand in 2023. In terms of PC DRAM, the proportion of DDR4 and LPDDR4X in PC applications will fall further while the penetration rate of LPDDR5 and DDR5 continues to rise. However, the price premium of DDR5 will limit the growth of density in PCs. DRAM density in PCs is estimate to increase by approximately 7% annually in 2023. If manufactures cut DDR5 pricing more aggressively next year, installed capacity may be driven up to 9%, depending on whether DDR5 price concessions can be effectively reconciled with DDR4.

In terms of PC client SSDs, estimated average installed capacity only increased slightly by 11%, the lowest in the past three years. The primary reason is that in the past two years, notebook shipments had spiked due to pandemic demand, simultaneously driving SSD installation rate. Average capacity has readily driven up average capacity growth due to the previous tightening of SSD master IC supply. However, notebook computer whole device costs have maintained an upward trend in the past two years due to the rising price of components, leading to branded PC manufacturers planning relatively conservative SSD capacity demand bits.
Since server shipment forecasts have demonstrated impressive growth in past years, subsequent growth momentum will slow since computational fundamentals are already high. In terms of Server DRAM, due to the advent of fifth generation memory specifications, the new Sapphire Rapids and Genoa platforms have increased the cost of whole devices and average server capacity has begun to encounter restrictions. Instead of the prior practice of merely upgrading the capacity of a single module, demand side considerations will focus more on hardware costs and the practice of ESG strategies. Average capacity increase of server DRAM is forecast to be limited in 2023, with an annual increase of approximately 7%.
In terms of Enterprise SSD, the new Sapphire Rapids and Genoa platforms have begun to upgrade to support the PCIe 5.0 transfer standard in order to meet the needs of HPC and big data computing. The capacity of SSDs must also be upgraded simultaneously to ensure PCIe 5.0 transfer performance. This trend will contribute to the growth of the average capacity of enterprise SSDs next year. In addition, as the overall NAND Flash oversupply continues into 1H23, a reduction in NAND Flash pricing will increase the shipment ratio of products above 4TB and the average annual growth rate of enterprise SSD capacity in 2023 is estimated to be 26%.
As inflation rises, world economies are generally holding a pessimistic view of the consumer market. TrendForce believes, cyclical replacement demand and new demand in emerging regions will lead to a slight increase in smartphone production. In terms of Mobile DRAM, the Android camp currently has sufficient installed capacity to meet the needs of daily systems operation. Therefore, barring impetus provided by innovative applications and considering the cost of whole devices and the low proportion of high-end sales, smartphone brands' willingness to increase installed capacity has fallen accordingly. In terms of the iOS camp, a high degree of operating system optimization reduces demand for mobile DRAM capacity. Mobile DRAM density is estimated to increase by only 5% annually in 2023.
In terms of smartphone NAND Flash, as the penetration rate of 5G smartphones gradually expands and applications require larger installed capacity to meet the needs of high-quality video recording, basic momentum can be seen for increasing NAND Flash density in smartphones. At the same time, the iPhone product portfolio is still moving towards higher capacity across the board and high-end Android models have followed suit with 512 GB as standard, while storage in mid- and low-end models will increase with subsequent upgrades in hardware specifications. Thus, there is still room for growth in overall average capacity. Annual growth of smartphone NAND Flash density is forecast to be maintained at 22.1% in 2023, slightly lower than that in 2022, but still at a high level.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source


