- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,343 (7.51/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
AMD released the latest version of the AGESA microcode for Socket AM5 platform. The new version 1.0.0.3 most notably reintroduces a Precision Boost C-state limiter that [accidentally?] got removed with version 1.0.0.2. This limiter prevents the CPU cores from boosting above 5.50 GHz when more than 4 cores are active (i.e. experiencing heavy workload). SkatterBencher demonstrated how this affects performance on Ryzen 7000-series desktop processors.
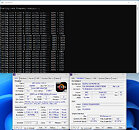
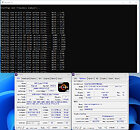
NopBench, a utility developed by ElmorLabs, lets you figure out the maximum boost frequency obtainable as workload scales across available CPU cores (i.e. starting from 1-thread, to n-thread). NopBench invokes the NOP instruction, and measures the number of NOP instructions can be processed per second. To make the NOP throughput comparable among processors of different microarchitectures, an architecture-specific factor is used, which for "Raphael" is 2.5x. By comparing the NOP throughput of a Ryzen 9 7950X processor tested with AGESA 1.0.0.2 to 1.0.0.3 (ASUS ROG Crosshair X670E Extreme BIOS versions 0611 vs. 0705); SkatterBencher was able to confirm that that the boost limiter is back in place, and limits Precision Boost frequency to 5.50 GHz when the NopBench load exceeds 4 cores.

View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source
NopBench, a utility developed by ElmorLabs, lets you figure out the maximum boost frequency obtainable as workload scales across available CPU cores (i.e. starting from 1-thread, to n-thread). NopBench invokes the NOP instruction, and measures the number of NOP instructions can be processed per second. To make the NOP throughput comparable among processors of different microarchitectures, an architecture-specific factor is used, which for "Raphael" is 2.5x. By comparing the NOP throughput of a Ryzen 9 7950X processor tested with AGESA 1.0.0.2 to 1.0.0.3 (ASUS ROG Crosshair X670E Extreme BIOS versions 0611 vs. 0705); SkatterBencher was able to confirm that that the boost limiter is back in place, and limits Precision Boost frequency to 5.50 GHz when the NopBench load exceeds 4 cores.



View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source




