TheLostSwede
News Editor
- Joined
- Nov 11, 2004
- Messages
- 18,352 (2.46/day)
- Location
- Sweden
| System Name | Overlord Mk MLI |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D |
| Motherboard | Gigabyte X670E Aorus Master |
| Cooling | Noctua NH-D15 SE with offsets |
| Memory | 32GB Team T-Create Expert DDR5 6000 MHz @ CL30-34-34-68 |
| Video Card(s) | Gainward GeForce RTX 4080 Phantom GS |
| Storage | 1TB Solidigm P44 Pro, 2 TB Corsair MP600 Pro, 2TB Kingston KC3000 |
| Display(s) | Acer XV272K LVbmiipruzx 4K@160Hz |
| Case | Fractal Design Torrent Compact |
| Audio Device(s) | Corsair Virtuoso SE |
| Power Supply | be quiet! Pure Power 12 M 850 W |
| Mouse | Logitech G502 Lightspeed |
| Keyboard | Corsair K70 Max |
| Software | Windows 10 Pro |
| Benchmark Scores | https://valid.x86.fr/yfsd9w |
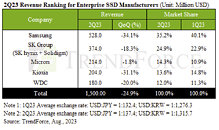
TrendForce research reveals that, due to the impacts of high inflation and economic downturn, CSPs are adopting more conservative strategies when it comes to capital expenditure and consistently reducing their annual server demand forecasts. Currently, CSPs in China have reported a decline in cloud orders compared to last year, leading to a subsequent decrease in annual procurement volumes for enterprise SSDs. In North America, some clients have postponed mass production timelines for new server platforms while ramping up investments in AI servers. These factors have resulted in enterprise SSD orders falling below expectations. Consequently, global enterprise SSD revenue hit an all-time low in the second quarter, totaling just $1,500 million—a QoQ decrease of 24.9%.
Demand for AI servers remains strong in the third quarter, while orders and shipment momentum for general-purpose servers have yet to show signs of recovery. This continues to put pressure on the purchasing volume of enterprise SSDs, and annual bit volume is expected to be lower than last year. Meanwhile, vendors have once again reduced capacity utilization to slow down inventory growth. Server customers still maintain high inventory levels, and their purchasing momentum remains insufficient. This is expected to lead to an approximate 15% QoQ decline in the average price of enterprise SSDs in the third quarter, which may further result in a lackluster revenue performance for the peak season.
However, the sustained surge in demand for AI servers is driving a concurrent rise in the need for Inference Servers to store training model data and results. This has in turn catalyzed the growing adoption rate of high-capacity enterprise SSDs. Specifically, the cost benefits of SK Group's (SK hynix & Solidigm) QLC high-capacity storage are expected to incrementally elevate its market penetration. Additionally, there's growing interest in other technologies like HBM and PCIe 5.0 SSDs. Micron is fast-tracking the development of relevant products, positioning both companies for potential revenue growth in the enterprise SSD market in the near future.
As a leading supplier, Samsung has been acutely affected by this year's downturn in demand for general-purpose servers, which has had a ripple effect on its revenue in the enterprise SSD segment. Starting from the second quarter, there has been a notable shift towards investments in high-end AI computing. This pivot has not only made it challenging to clear existing inventories of general-purpose servers but has also led to a substantial decline in revenue from enterprise SSDs. For the second quarter, the enterprise SSD segment reported revenue of approximately US$528 million, marking a QoQ decrease of 34.1%.
Looking ahead, as enterprises increasingly prioritize AI services with a focus on high-speed computing, DRAM and HBM have emerged as the memory solutions of choice. Given that there's no clear evidence of significant growth in the overall demand for SSDs, Samsung's revenue in the enterprise SSD sector may face additional headwinds.
SK Group has aggressively pursued orders from vendors of general-purpose servers. Despite facing an industry-wide slowdown in production, the company has strategically leveraged its pricing advantage to expand its market share. Further buoyed by a stable flow of orders from North American clients, SK Group's revenue decline was more modest than that of its competitors. For the second quarter, the company's revenue in the enterprise SSD segment stood at approximately US$374 million—a QoQ decrease of 18.3%.
In contrast, Micron has reaped the benefits of consistent SATA SSD orders from general-purpose server vendors, and it has also initiated mass production of 176-layer PCIe SSDs. As a result, the volume of Micron's enterprise SSD shipments saw a marked increase over the first quarter. Among suppliers, Micron recorded the least decline in enterprise SSD sector revenue for the second quarter, registering a mere 1.8% drop QoQ.
In addition to its existing line of SAS products, Kioxia has started mass-supplying PCIe 4.0 SSDs as customer validations were successfully completed. The company's enterprise SSD revenue for the second quarter reached US$204 million—a QoQ decrease of 31.1%. Moving forward, Kioxia aims to elevate its production process to 112 layers and launch PCIe 5.0 products, with an eye on penetrating the AI market.
Western Digital, affected by challenging market conditions and the fact that its next-generation PCIe 4.0 products are yet to reach mass production, posted a second-quarter revenue of merely US$180 million—reflecting a 20% quarter-over-quarter decline. The company has since pivoted its focus to the PCIe sector. Alongside plans to mass-produce PCIe 5.0 interface products by 2024, Western Digital is also gearing up to introduce QLC SSDs. This strategic shift aims to capitalize on the rising adoption of PCIe SSDs in servers, and thereby drive further revenue growth in the enterprise SSD sector.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source
Demand for AI servers remains strong in the third quarter, while orders and shipment momentum for general-purpose servers have yet to show signs of recovery. This continues to put pressure on the purchasing volume of enterprise SSDs, and annual bit volume is expected to be lower than last year. Meanwhile, vendors have once again reduced capacity utilization to slow down inventory growth. Server customers still maintain high inventory levels, and their purchasing momentum remains insufficient. This is expected to lead to an approximate 15% QoQ decline in the average price of enterprise SSDs in the third quarter, which may further result in a lackluster revenue performance for the peak season.

However, the sustained surge in demand for AI servers is driving a concurrent rise in the need for Inference Servers to store training model data and results. This has in turn catalyzed the growing adoption rate of high-capacity enterprise SSDs. Specifically, the cost benefits of SK Group's (SK hynix & Solidigm) QLC high-capacity storage are expected to incrementally elevate its market penetration. Additionally, there's growing interest in other technologies like HBM and PCIe 5.0 SSDs. Micron is fast-tracking the development of relevant products, positioning both companies for potential revenue growth in the enterprise SSD market in the near future.
As a leading supplier, Samsung has been acutely affected by this year's downturn in demand for general-purpose servers, which has had a ripple effect on its revenue in the enterprise SSD segment. Starting from the second quarter, there has been a notable shift towards investments in high-end AI computing. This pivot has not only made it challenging to clear existing inventories of general-purpose servers but has also led to a substantial decline in revenue from enterprise SSDs. For the second quarter, the enterprise SSD segment reported revenue of approximately US$528 million, marking a QoQ decrease of 34.1%.
Looking ahead, as enterprises increasingly prioritize AI services with a focus on high-speed computing, DRAM and HBM have emerged as the memory solutions of choice. Given that there's no clear evidence of significant growth in the overall demand for SSDs, Samsung's revenue in the enterprise SSD sector may face additional headwinds.
SK Group has aggressively pursued orders from vendors of general-purpose servers. Despite facing an industry-wide slowdown in production, the company has strategically leveraged its pricing advantage to expand its market share. Further buoyed by a stable flow of orders from North American clients, SK Group's revenue decline was more modest than that of its competitors. For the second quarter, the company's revenue in the enterprise SSD segment stood at approximately US$374 million—a QoQ decrease of 18.3%.
In contrast, Micron has reaped the benefits of consistent SATA SSD orders from general-purpose server vendors, and it has also initiated mass production of 176-layer PCIe SSDs. As a result, the volume of Micron's enterprise SSD shipments saw a marked increase over the first quarter. Among suppliers, Micron recorded the least decline in enterprise SSD sector revenue for the second quarter, registering a mere 1.8% drop QoQ.
In addition to its existing line of SAS products, Kioxia has started mass-supplying PCIe 4.0 SSDs as customer validations were successfully completed. The company's enterprise SSD revenue for the second quarter reached US$204 million—a QoQ decrease of 31.1%. Moving forward, Kioxia aims to elevate its production process to 112 layers and launch PCIe 5.0 products, with an eye on penetrating the AI market.
Western Digital, affected by challenging market conditions and the fact that its next-generation PCIe 4.0 products are yet to reach mass production, posted a second-quarter revenue of merely US$180 million—reflecting a 20% quarter-over-quarter decline. The company has since pivoted its focus to the PCIe sector. Alongside plans to mass-produce PCIe 5.0 interface products by 2024, Western Digital is also gearing up to introduce QLC SSDs. This strategic shift aims to capitalize on the rising adoption of PCIe SSDs in servers, and thereby drive further revenue growth in the enterprise SSD sector.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source

