- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,427 (7.51/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
SD Association (SDA) today announced the latest evolution of SD Express memory cards doubling microSD Express memory card speed up to 2 GB/s, plus four new SD Express Speed Classes to ensure guaranteed minimum sequential performance levels in the new SD 9.1 specification including support of Multi-stream access and related Power and Thermal Management assuring the guaranteed performance. SD 9.1 helps consumers identify the right card for their device while giving manufacturers new tools to assure minimum level of performance of SD Express memory cards and have means to guide consumers what type of cards will assure specific application operations.
The latest generation of microSD Express uses the PCIe interface delivering a 1,969 megabytes per second (MB/s), nearly 2 gigabytes per second (GB/s) speeds by using the PCIe Gen 4 x1 lane as defined in the latest update to the microSD Addendum version 8 specification. microSD Express was introduced with 985 MB/s speed maximum data transfer rate and the NVMe upper layer protocol in the SD 7.1 specification. The increase in speed gives product designers more storage options and SSD level performance for a variety of size constrained devices requiring easily repairable or upgradeable storage.
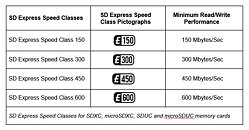
The SD Express Speed Classes are used exclusively on SDXC, SDUC, microSDXC and microSDUC memory cards offering the SD Express bus. Changes in memory technology necessitate the need to define speeds as NAND flash technology continues to evolve. SD Express is the most significant evolution for SD since it was introduced in 2000. It meets new and evolving market needs to support increased performance requirements of controllers, memories, and other application interfaces. SD Express can fully support almost every use case demanding higher speed removable or semi-removable memory cards and is ideal for meeting the growing number of Right to Repair laws.
"By defining minimum assured sequential performance standards for SD Express memory cards, the SDA helps both device manufacturers and consumers ensure the best recording and playback of all types of content," said Hiroyuki Sakamoto, SDA president. "We doubled the speed of microSD Express to 2 GB/s to give product manufacturers more storage options capable of handling the most demanding storage uses making SD Express memory cards a compelling, ecologically sound choice making it easier to repair and upgrade devices."
New Features
In order to optimize the SD Express speed class usage under various power levels and thermal conditions - Leveraging NVMe specifications, SD Express memory card now offer several Power Management settings through Maximum Power (MP) values. The card consumes power up to one of the MP values set by the host device to manage card temperatures. SD Express memory cards use a new Thermal Management feature where the card indicates a group of its specific thermal thresholds. The host device may then set appropriate Thermal Management parameters for the card according to the target class and the selected PCIe bus mode, much like an MP value for power management.
The SD 9.1 specification defines the access rules required to ensure the minimum defined performance of the PCI/NVMe interface in SD Express cards, including multi-stream access of up to eight streams.
The SDA has prepared a whitepaper providing more details about the new features and SD Express Speed Classes defined by SD 9.1.
SD Express
A growing list of devices and memory cards support SD Express. SD Express offers SSD performance levels with transfer speeds up to ~4 GB/sec thanks to the PCI Express (PCIe) and NVMe Express (NVMe) architectures. The first SD Express cards were introduced with SD7.0 specifications for the full-size SD form factor supporting PCIe Gen 3 x1 interface with speeds of 985 MB/s. SD8.0 defines three additional PCIe interfaces - PCIe Gen 4 x1, PCIe G3 x2 and PCIe Gen 4 x2 quadrupling speeds to 4 GB/s. SD7.1 specification added SD Express 985 MB/s to the microSD form factor and the microSD Addendum version 8 specification doubled speeds to 2 GB/s by using PCIe Gen 4 x1. SD Express gigabyte transfer speeds bring new storage opportunities for devices with demanding performance levels capable of moving large amounts of data generated by data-intense wireless or wired communication, super-slow motion video, RAW continuous burst mode and 8K video capture and playback, 360 degree cameras/videos, speed hungry applications running on cards and mobile computing devices, ever evolving gaming systems, multi-channel IoT devices and automotive to name a few.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
The latest generation of microSD Express uses the PCIe interface delivering a 1,969 megabytes per second (MB/s), nearly 2 gigabytes per second (GB/s) speeds by using the PCIe Gen 4 x1 lane as defined in the latest update to the microSD Addendum version 8 specification. microSD Express was introduced with 985 MB/s speed maximum data transfer rate and the NVMe upper layer protocol in the SD 7.1 specification. The increase in speed gives product designers more storage options and SSD level performance for a variety of size constrained devices requiring easily repairable or upgradeable storage.

The SD Express Speed Classes are used exclusively on SDXC, SDUC, microSDXC and microSDUC memory cards offering the SD Express bus. Changes in memory technology necessitate the need to define speeds as NAND flash technology continues to evolve. SD Express is the most significant evolution for SD since it was introduced in 2000. It meets new and evolving market needs to support increased performance requirements of controllers, memories, and other application interfaces. SD Express can fully support almost every use case demanding higher speed removable or semi-removable memory cards and is ideal for meeting the growing number of Right to Repair laws.
"By defining minimum assured sequential performance standards for SD Express memory cards, the SDA helps both device manufacturers and consumers ensure the best recording and playback of all types of content," said Hiroyuki Sakamoto, SDA president. "We doubled the speed of microSD Express to 2 GB/s to give product manufacturers more storage options capable of handling the most demanding storage uses making SD Express memory cards a compelling, ecologically sound choice making it easier to repair and upgrade devices."
New Features
In order to optimize the SD Express speed class usage under various power levels and thermal conditions - Leveraging NVMe specifications, SD Express memory card now offer several Power Management settings through Maximum Power (MP) values. The card consumes power up to one of the MP values set by the host device to manage card temperatures. SD Express memory cards use a new Thermal Management feature where the card indicates a group of its specific thermal thresholds. The host device may then set appropriate Thermal Management parameters for the card according to the target class and the selected PCIe bus mode, much like an MP value for power management.
The SD 9.1 specification defines the access rules required to ensure the minimum defined performance of the PCI/NVMe interface in SD Express cards, including multi-stream access of up to eight streams.
The SDA has prepared a whitepaper providing more details about the new features and SD Express Speed Classes defined by SD 9.1.
SD Express
A growing list of devices and memory cards support SD Express. SD Express offers SSD performance levels with transfer speeds up to ~4 GB/sec thanks to the PCI Express (PCIe) and NVMe Express (NVMe) architectures. The first SD Express cards were introduced with SD7.0 specifications for the full-size SD form factor supporting PCIe Gen 3 x1 interface with speeds of 985 MB/s. SD8.0 defines three additional PCIe interfaces - PCIe Gen 4 x1, PCIe G3 x2 and PCIe Gen 4 x2 quadrupling speeds to 4 GB/s. SD7.1 specification added SD Express 985 MB/s to the microSD form factor and the microSD Addendum version 8 specification doubled speeds to 2 GB/s by using PCIe Gen 4 x1. SD Express gigabyte transfer speeds bring new storage opportunities for devices with demanding performance levels capable of moving large amounts of data generated by data-intense wireless or wired communication, super-slow motion video, RAW continuous burst mode and 8K video capture and playback, 360 degree cameras/videos, speed hungry applications running on cards and mobile computing devices, ever evolving gaming systems, multi-channel IoT devices and automotive to name a few.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site




