- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,572 (7.46/day)
- Location
- Dublin, Ireland
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
Intel today announced the release of its 14th Gen Core HX series "Raptor Lake Refresh" mobile processors. Processor models from this series are supposed to cap off the upper end of Intel's mobile processor portfolio. Although Intel released the Core Ultra "Meteor Lake" mobile processors late last year, those chips cover the U-segment, and H-segment (ultraportable, thin-and-light, and mainstream); with the fastest model being the Core Ultra 165H, which caps out at 6P+8E+2LP. The HX segment, which started out as enthusiast-class, broadened in scope over the years to cover the bulky gaming notebooks and portable workstations. These chips typically have a power rating of 55 W. All chips have maximum turbo power rating of 157 W. Intel is tapping into its "Raptor Lake Refresh" silicon to carve out these processors. This is a monolithic chip built on the Intel 7 process, and its package is a multi-chip module with an on-package PCH.
The lineup begins with the Core i9-14900HX, which maxes out the "Raptor Lake Refresh" silicon, with an 8P+16E core-count, with 2 MB of L2 cache per P-core, 4 MB of L2 cache per E-core cluster, and a shared 36 MB L3 cache. The processor's full I/O is wired out, including support for dual-channel DDR5 (SO-DIMMs only), a PCI-Express 5.0 x16 connection for discrete GPUs, a PCI-Express 4.0 x4 connection for a CPU-attached M.2 NVMe SSD, and DMI 4.0 x8 link between the processor die and the PCH die. This PCH puts out up to 16 PCIe Gen 4 lanes, besides up to 12 Gen 3 lanes, which notebook designers can combine with discrete Thunderbolt 4 controllers, and the likes. You can expect Wi-Fi 7 to be prevalent in this crop of premium gaming notebooks. The i9-14900HX features a P-core maximum boost frequency of 5.80 GHz, and an E-core boost frequency of 4.10 GHz.




The i9-14900HX is the only Core i9 SKU in the series. It is followed by two Core i7 SKUs, namely the Core i7-14700HX and the i7-14650HX. What sets the two apart is the core configuration. While the i7-14700HX gets an 8P+12E configuration, similar to the desktop Core i7-14700K; the i7-14650HX gets an 8P+8E configuration, similar to the desktop i7-13700K. The i7-14700HX has 33 MB of L3 cache, while the i7-14650HX tops out at 30 MB. The i7-14700HX is also given a hefty 5.50 GHz P-core boost, and a 3.90 GHz E-core boost; while the i7-14650HX does 5.20 GHz maximum P-core boost, along with 3.70 GHz E-core boost.
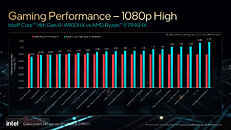
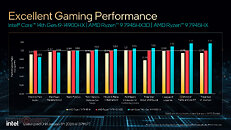


Similar to the Core i7 series, there are two distinct 14th Gen Core i5 HX series SKUs, the i5-14500HX, and the i5-14450HX, differing with core counts and L3 cache size. The i5-14500HX gets a 6P+8E core configuration along with 24 MB of L3 cache; the i5-14450HX has 6P+4E, with 20 MB of L3 cache on tap. The two have maximum P-core boost frequencies of 4.90 GHz and 4.80 GHz, respectively; and E-core boost frequencies of 3.50 GHz.

View at TechPowerUp Main Site
The lineup begins with the Core i9-14900HX, which maxes out the "Raptor Lake Refresh" silicon, with an 8P+16E core-count, with 2 MB of L2 cache per P-core, 4 MB of L2 cache per E-core cluster, and a shared 36 MB L3 cache. The processor's full I/O is wired out, including support for dual-channel DDR5 (SO-DIMMs only), a PCI-Express 5.0 x16 connection for discrete GPUs, a PCI-Express 4.0 x4 connection for a CPU-attached M.2 NVMe SSD, and DMI 4.0 x8 link between the processor die and the PCH die. This PCH puts out up to 16 PCIe Gen 4 lanes, besides up to 12 Gen 3 lanes, which notebook designers can combine with discrete Thunderbolt 4 controllers, and the likes. You can expect Wi-Fi 7 to be prevalent in this crop of premium gaming notebooks. The i9-14900HX features a P-core maximum boost frequency of 5.80 GHz, and an E-core boost frequency of 4.10 GHz.




The i9-14900HX is the only Core i9 SKU in the series. It is followed by two Core i7 SKUs, namely the Core i7-14700HX and the i7-14650HX. What sets the two apart is the core configuration. While the i7-14700HX gets an 8P+12E configuration, similar to the desktop Core i7-14700K; the i7-14650HX gets an 8P+8E configuration, similar to the desktop i7-13700K. The i7-14700HX has 33 MB of L3 cache, while the i7-14650HX tops out at 30 MB. The i7-14700HX is also given a hefty 5.50 GHz P-core boost, and a 3.90 GHz E-core boost; while the i7-14650HX does 5.20 GHz maximum P-core boost, along with 3.70 GHz E-core boost.




Similar to the Core i7 series, there are two distinct 14th Gen Core i5 HX series SKUs, the i5-14500HX, and the i5-14450HX, differing with core counts and L3 cache size. The i5-14500HX gets a 6P+8E core configuration along with 24 MB of L3 cache; the i5-14450HX has 6P+4E, with 20 MB of L3 cache on tap. The two have maximum P-core boost frequencies of 4.90 GHz and 4.80 GHz, respectively; and E-core boost frequencies of 3.50 GHz.

View at TechPowerUp Main Site


