- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,314 (7.52/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
NVIDIA today unveiled ChatRTX, the AI assistant that runs locally on your machine, and which is accelerated by your GeForce RTX GPU. NVIDIA had originally launched this as "Chat with RTX" back in February 2024, back then this was regarded more as a public tech demo. We reviewed the application in our feature article. The ChatRTX rebranding is probably aimed at making the name sound more like ChatGPT, which is what the application aims to be—except it runs completely on your machine, and is exhaustively customizable. The most obvious advantage of a locally-run AI assistant is privacy—you are interacting with an assistant that processes your prompt locally, and accelerated by your GPU; the second is that you're not held back by performance bottlenecks by cloud-based assistants.
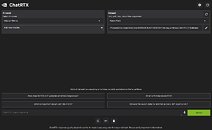
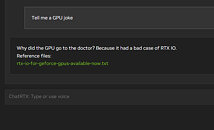
ChatRTX is a major update over the Chat with RTX tech-demo from February. To begin with, the application has several stability refinements from Chat with RTX, which felt a little rough on the edges. NVIDIA has significantly updated the LLMs included with the application, including Mistral 7B INT4, and Llama 2 7B INT4. Support is also added for additional LLMs, including Gemma, a local LLM trained by Google, based on the same technology used to make Google's flagship Gemini model. ChatRTX now also supports ChatGLM3, for both English and Chinese prompts. Perhaps the biggest upgrade ChatRTX is its ability to recognize images on your machine, as it incorporates CLIP (contrastive language-image pre-training) from OpenAI. CLIP is an LLM that recognizes what it's seeing in image collections. Using this feature, you can interact with your image library without the need for metadata. ChatRTX doesn't just take text input—you can speak to it. It now accepts natural voice input, as it integrates the Whisper speech-to-text NLI model.
DOWNLOAD: NVIDIA ChatRTX
As with the original Chat with RTX tech-demo, the new ChatRTX application's biggest feature is its ability to let users switch between AI models, or to let it build and train your own dataset based on text and images on your local machine. You can point it to a folder with documents such as plaintext, Word (doc) and PDFs, as well as images; and it will train itself on answering queries related to the dataset.
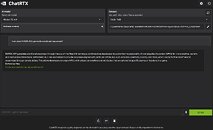
There remain some major limitations with ChatRTX which we had hoped would be fixed since its February release, and that is context—the ability to ask follow-up questions. Apparently, follow-ups are harder to implement than they seem, as the model has to connect the new question to the previous ones and its responses to them. It's also inaccurate in attributing its responses to the right text tiles. The browser-based frontend only supports Chrome and Edge, it's buggy with Firefox.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
ChatRTX is a major update over the Chat with RTX tech-demo from February. To begin with, the application has several stability refinements from Chat with RTX, which felt a little rough on the edges. NVIDIA has significantly updated the LLMs included with the application, including Mistral 7B INT4, and Llama 2 7B INT4. Support is also added for additional LLMs, including Gemma, a local LLM trained by Google, based on the same technology used to make Google's flagship Gemini model. ChatRTX now also supports ChatGLM3, for both English and Chinese prompts. Perhaps the biggest upgrade ChatRTX is its ability to recognize images on your machine, as it incorporates CLIP (contrastive language-image pre-training) from OpenAI. CLIP is an LLM that recognizes what it's seeing in image collections. Using this feature, you can interact with your image library without the need for metadata. ChatRTX doesn't just take text input—you can speak to it. It now accepts natural voice input, as it integrates the Whisper speech-to-text NLI model.



DOWNLOAD: NVIDIA ChatRTX
As with the original Chat with RTX tech-demo, the new ChatRTX application's biggest feature is its ability to let users switch between AI models, or to let it build and train your own dataset based on text and images on your local machine. You can point it to a folder with documents such as plaintext, Word (doc) and PDFs, as well as images; and it will train itself on answering queries related to the dataset.
There remain some major limitations with ChatRTX which we had hoped would be fixed since its February release, and that is context—the ability to ask follow-up questions. Apparently, follow-ups are harder to implement than they seem, as the model has to connect the new question to the previous ones and its responses to them. It's also inaccurate in attributing its responses to the right text tiles. The browser-based frontend only supports Chrome and Edge, it's buggy with Firefox.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site









 It's a good thing I'm more of a "hands on" kind of gal... Go to hell, Skynet Dildo!
It's a good thing I'm more of a "hands on" kind of gal... Go to hell, Skynet Dildo!

