- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,585 (7.45/day)
- Location
- Dublin, Ireland
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
Possible specifications of the various NVIDIA GeForce "Blackwell" gaming GPUs were leaked to the web by Kopite7kimi, a reliable source with NVIDIA leaks. These are specs of the maxed out silicon, NVIDIA will carve out several GeForce RTX 50-series SKUs based on these chips, which could end up with lower shader counts than those shown here. We've known from older reports that there will be five chips in all, the GB202 being the largest, followed by the GB203, the GB205, the GB206, and the GB207. There is a notable absence of a successor to the AD104, GA104, and TU104, because NVIDIA is trying a slightly different way to approach the performance segment with this generation.
The GB202 is the halo segment chip that will drive the possible RTX 5090 (RTX 4090 successor). This chip is endowed with 192 streaming multiprocessors (SM), or 96 texture processing clusters (TPCs). These 96 TPCs are spread across 12 graphics processing clusters (GPCs), which each have 8 of them. Assuming that "Blackwell" has the same 256 CUDA cores per TPC that the past several generations of NVIDIA gaming GPUs have had, we end up with a total CUDA core count of 24,576. Another interesting aspect about this mega-chip is memory. The GPU implements the next-generation GDDR7 memory, and uses a mammoth 512-bit memory bus. Assuming the 28 Gbps memory speed that was being rumored for NVIDIA's "Blackwell" generation, this chip has 1,792 GB/s of memory bandwidth on tap!
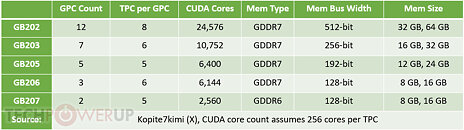
The GB203 is the next chip in the series, and poised to be a successor in name to the current AD103. It generationally reduces the shader counts, counting on the architecture and clock speeds to more than come through for performance; while retaining the 256-bit bus width of the AD103. The net result could be a significantly smaller GPU than the AD103, for better performance. The GB203 is endowed with 10,752 CUDA cores, spread across 84 SM (42 TPCs). The chip has 7 GPCs, each with 6 TPCs. The memory bus, as we mentioned, is 256-bit, and at a memory speed of 28 Gbps, would yield 896 GB/s of bandwidth.
The GB205 will power the lower half of the performance segment in the GeForce "Blackwell" generation. This chip has a rather surprising CUDA core count of just 6,400, spread across 50 SM, which are arranged in 5 GPCs of 5 TPCs, each. The memory bus width is 192-bit. For 28 Gbps, this would result in 672 GB/s of memory bandwidth.
The GB206 drives the mid-range of the series. This chip gets very close to matching the CUDA core count of the GB205, with 6,144 of them. These are spread across 36 SM (18 TPCs). The 18 TPCs span 3 GPCs of 6 TPCs, each. The key differentiator between the GB205 and GB206 is memory bus width, which is narrowed to 128-bit for the GB206. With the same 28 Gbps memory speed being used here, such a chip would end up with 448 GB/s of memory bandwidth.
At the entry level, there is the GB207, a significantly smaller chip with just 2,560 CUDA cores, across 10 SM, spanning two GPCs of 5 TPCs, each. The memory bus width is unchanged at 128-bit, but the memory type used is the older generation GDDR6. Assuming NVIDIA uses 18 Gbps memory speeds, it ends up with 288 GB/s on tap.
NVIDIA is expected to double down on large on-die caches on all its chips, to cushion the memory sub-systems. We expect there to be several other innovations in the areas of ray tracing performance, AI acceleration, and certain other features exclusive to the architecture. The company is expected to debut the series some time in Q4-2024.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source
The GB202 is the halo segment chip that will drive the possible RTX 5090 (RTX 4090 successor). This chip is endowed with 192 streaming multiprocessors (SM), or 96 texture processing clusters (TPCs). These 96 TPCs are spread across 12 graphics processing clusters (GPCs), which each have 8 of them. Assuming that "Blackwell" has the same 256 CUDA cores per TPC that the past several generations of NVIDIA gaming GPUs have had, we end up with a total CUDA core count of 24,576. Another interesting aspect about this mega-chip is memory. The GPU implements the next-generation GDDR7 memory, and uses a mammoth 512-bit memory bus. Assuming the 28 Gbps memory speed that was being rumored for NVIDIA's "Blackwell" generation, this chip has 1,792 GB/s of memory bandwidth on tap!

The GB203 is the next chip in the series, and poised to be a successor in name to the current AD103. It generationally reduces the shader counts, counting on the architecture and clock speeds to more than come through for performance; while retaining the 256-bit bus width of the AD103. The net result could be a significantly smaller GPU than the AD103, for better performance. The GB203 is endowed with 10,752 CUDA cores, spread across 84 SM (42 TPCs). The chip has 7 GPCs, each with 6 TPCs. The memory bus, as we mentioned, is 256-bit, and at a memory speed of 28 Gbps, would yield 896 GB/s of bandwidth.
The GB205 will power the lower half of the performance segment in the GeForce "Blackwell" generation. This chip has a rather surprising CUDA core count of just 6,400, spread across 50 SM, which are arranged in 5 GPCs of 5 TPCs, each. The memory bus width is 192-bit. For 28 Gbps, this would result in 672 GB/s of memory bandwidth.
The GB206 drives the mid-range of the series. This chip gets very close to matching the CUDA core count of the GB205, with 6,144 of them. These are spread across 36 SM (18 TPCs). The 18 TPCs span 3 GPCs of 6 TPCs, each. The key differentiator between the GB205 and GB206 is memory bus width, which is narrowed to 128-bit for the GB206. With the same 28 Gbps memory speed being used here, such a chip would end up with 448 GB/s of memory bandwidth.
At the entry level, there is the GB207, a significantly smaller chip with just 2,560 CUDA cores, across 10 SM, spanning two GPCs of 5 TPCs, each. The memory bus width is unchanged at 128-bit, but the memory type used is the older generation GDDR6. Assuming NVIDIA uses 18 Gbps memory speeds, it ends up with 288 GB/s on tap.
NVIDIA is expected to double down on large on-die caches on all its chips, to cushion the memory sub-systems. We expect there to be several other innovations in the areas of ray tracing performance, AI acceleration, and certain other features exclusive to the architecture. The company is expected to debut the series some time in Q4-2024.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source









 '
'