- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,677 (7.43/day)
- Location
- Dublin, Ireland
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | Gigabyte B550 AORUS Elite V2 |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 16GB DDR4-3200 |
| Video Card(s) | Galax RTX 4070 Ti EX |
| Storage | Samsung 990 1TB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
AMD is developing a new technology that promises to significantly reduce the size on disk of games, as well as reduce the size of game patches and updates. Today's AAA games tend to be over a 100 GB in size, with game updates running into tens of gigabytes, with some of the major updates practically downloading the game all over again. Upcoming games like Call of Duty: Black Ops 6 is reportedly over 300 GB in size, which pushes the game away from those with anything but Internet connections with hundreds of Mbps in speeds. Much of the bulk of the game is made up of visual assets—textures, sprites, and cutscene videos. A modern AAA title could have hundreds of thousands of individual game assets, and sometimes even redundant sets of textures for different image quality settings.
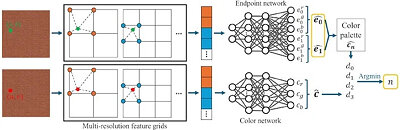
AMD's solution to this problem is the Neural Block Compression technology. The company will get into the nuts and bolts of the tech in its presentation at the 2024 Eurographics Symposium on Rendering (July 3-5), but we have a vague idea of what it could be. Modern games don't drape surfaces of a wireframe with a texture, but also additional layers, such as specular maps, normal maps, roughness maps, etc). AMD's idea is to "flatten" all these layers, including the base texture, into a single asset format, which the game engine could disaggregate into the individual layers using an AI neural network. This is not to be confused with mega-textures—something entirely different, which relies on a single large texture covering all objects in a scene. The idea here is to flatten the various data layers of individual textures and their maps, into a single asset type. In theory, this should yield significant file-size savings, even if it results in some additional compute cost on the client's end.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source
AMD's solution to this problem is the Neural Block Compression technology. The company will get into the nuts and bolts of the tech in its presentation at the 2024 Eurographics Symposium on Rendering (July 3-5), but we have a vague idea of what it could be. Modern games don't drape surfaces of a wireframe with a texture, but also additional layers, such as specular maps, normal maps, roughness maps, etc). AMD's idea is to "flatten" all these layers, including the base texture, into a single asset format, which the game engine could disaggregate into the individual layers using an AI neural network. This is not to be confused with mega-textures—something entirely different, which relies on a single large texture covering all objects in a scene. The idea here is to flatten the various data layers of individual textures and their maps, into a single asset type. In theory, this should yield significant file-size savings, even if it results in some additional compute cost on the client's end.

View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source










