Apr 23rd, 2025 18:59 EDT
change timezone
Latest GPU Drivers
New Forum Posts
- RX 9000 series GPU Owners Club (497)
- To distill or not distill what say ye? (67)
- Companies should be called out for this (81)
- What are you playing? (23446)
- 5060 Ti 8GB DOA (255)
- DTS DCH Driver for Realtek HDA [DTS:X APO4 + DTS Interactive] (2151)
- Are the 8 GB cards worth it? (103)
- Just for lolz, Post your 3DMark2001SE Benchmark scores! (95)
- Asus Rx570 o4g cannot losd drivers error code 43 (12)
- EXTREMEHW Invites TECHPOWERUP to our 3RD ANNUAL 96-HOUR FOLDING CHALLENGE April 26th 00:00 UTC (3)
Popular Reviews
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti 8 GB Review - So Many Compromises
- ASRock X870E Taichi Lite Review
- ASUS GeForce RTX 5060 Ti TUF OC 16 GB Review
- Upcoming Hardware Launches 2025 (Updated Apr 2025)
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Pulse Review
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti PCI-Express x8 Scaling
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Nitro+ Review - Beating NVIDIA
- Palit GeForce RTX 5060 Ti Infinity 3 16 GB Review
- AMD Ryzen 7 9800X3D Review - The Best Gaming Processor
- MSI GeForce RTX 5060 Ti Gaming OC 16 GB Review
Controversial News Posts
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti 16 GB SKU Likely Launching at $499, According to Supply Chain Leak (182)
- NVIDIA Sends MSRP Numbers to Partners: GeForce RTX 5060 Ti 8 GB at $379, RTX 5060 Ti 16 GB at $429 (127)
- NVIDIA Launches GeForce RTX 5060 Series, Beginning with RTX 5060 Ti This Week (115)
- Nintendo Confirms That Switch 2 Joy-Cons Will Not Utilize Hall Effect Stick Technology (105)
- Nintendo Switch 2 Launches June 5 at $449.99 with New Hardware and Games (99)
- Sony Increases the PS5 Pricing in EMEA and ANZ by Around 25 Percent (85)
- NVIDIA PhysX and Flow Made Fully Open-Source (77)
- Windows Notepad Gets Microsoft Copilot Integration (75)
News Posts matching #10 nm+
Return to Keyword Browsing
Intel "Tiger Lake" Leverages 10 nm+ SuperFin and SuperMIM Technologies
Intel's upcoming 11th Generation Core "Tiger Lake" processors introduce the company's first major refinement of its 10 nanometer silicon fabrication node, dubbed 10 nm+. The node introduces two key features that work to improve the power characteristics of the silicon, allowing Intel to yield more performance without raising power/thermals over the previous generation. VideoCardz scored a major scoop on 10 nm+, including the introduction of the new SuperFin transistor, and SuperMIM capacitor.
SuperFin is a redesigned FinFET, a nanoscale transistor, which offers increased gate pitch, yielding higher drive current, improved channel mobility, and an improved source/drain, yielding in lower resistance. The other key component of 10 nm+ is SuperMIM, delivering a 5 times increase in metal-insulator-metal capacitance. Intel is yet to put out energy efficiency gain numbers for the process, but promises a "dramatic increase in frequency" over the previous generation, which lines up with leaks of the Core i7-1185G7 shipping with significantly higher clock speeds.
SuperFin is a redesigned FinFET, a nanoscale transistor, which offers increased gate pitch, yielding higher drive current, improved channel mobility, and an improved source/drain, yielding in lower resistance. The other key component of 10 nm+ is SuperMIM, delivering a 5 times increase in metal-insulator-metal capacitance. Intel is yet to put out energy efficiency gain numbers for the process, but promises a "dramatic increase in frequency" over the previous generation, which lines up with leaks of the Core i7-1185G7 shipping with significantly higher clock speeds.

Intel to Clock "Rocket Lake-S" High, Evidence of an ES with 5.00 GHz Boost
Intel's 11th Generation Core "Rocket Lake-S" desktop processors in the LGA1200 package could come with clock speeds that are of the norm these days. Intel appears unwilling to dial down clock speeds in the wake of increased IPC with the new generation "Cypress Cove" CPU cores that drive these processors. Twitter handle "leakbench," which tracks interesting Geekbench results, fished out a database listing for a "Rocket Lake-S" engineering sample with clock speeds of 3.40 GHz base, and 5.00 GHz boost.
The listing has all the telltale signs of "Cypress Cove," such as 48 KB L1D cache, 512 KB per core L2 cache, and 16 MB shared L3 cache for this 8-core/16-thread chip. "Cypress Cove" is rumored to be to be a back-port of Intel's "Willow Cove" CPU core design from its original 10 nm+ node to the 14 nm++. VideoCardz compared this "Rocket Lake-S" ES benchmark result to that of a retail Core i7-10700K, and found its single-threaded performance to be roughly 6.35 percent higher despite a 200 MHz clock-speed deficit, although for some reason, its multi-threaded performance is trailing by over 15 percent.
The listing has all the telltale signs of "Cypress Cove," such as 48 KB L1D cache, 512 KB per core L2 cache, and 16 MB shared L3 cache for this 8-core/16-thread chip. "Cypress Cove" is rumored to be to be a back-port of Intel's "Willow Cove" CPU core design from its original 10 nm+ node to the 14 nm++. VideoCardz compared this "Rocket Lake-S" ES benchmark result to that of a retail Core i7-10700K, and found its single-threaded performance to be roughly 6.35 percent higher despite a 200 MHz clock-speed deficit, although for some reason, its multi-threaded performance is trailing by over 15 percent.

Intel "Willow Cove" Backported to 14nm is "Cypress Cove"?
Intel's 11th generation Core "Rocket Lake-S" desktop processor is fascinating as it introduces Intel's first CPU core IPC uptick in about half a decade. Until now, it was rumored that "Rocket Lake-S" features a back-port of Intel's "Willow Cove" CPU cores to the 14 nm silicon fabrication process. It turns out that Intel doesn't want to call these cores "Willow Cove," which make their debut with the 10 nm+ "Tiger Lake" mobile processors later this Summer. Enter "Cypress Cove." A Moore's Law is Dead video presentation sheds light on this mysterious new codename.
Apparently, "Cypress Cove" is the codename Intel is using to refer to the CPU cores Intel is building with its latest CPU core IP on older 14 nm process. Owing to the process, the IPC of these cores may be different from the "Willow Cove" cores on "Tiger Lake," and to avoid confusion, Intel possibly choosing to give it a different internal codename. In other words, Moore's Law is Dead believes that "Cypress Cove" may not offer the alleged 25% IPC gains over "Skylake" that you could expect instead from "Willow Cove" cores in "Tiger Lake."
Apparently, "Cypress Cove" is the codename Intel is using to refer to the CPU cores Intel is building with its latest CPU core IP on older 14 nm process. Owing to the process, the IPC of these cores may be different from the "Willow Cove" cores on "Tiger Lake," and to avoid confusion, Intel possibly choosing to give it a different internal codename. In other words, Moore's Law is Dead believes that "Cypress Cove" may not offer the alleged 25% IPC gains over "Skylake" that you could expect instead from "Willow Cove" cores in "Tiger Lake."

Possible Intel "Ice Lake-SP" 24-core Xeon Processor Surfaces on Geekbench Database
Intel plans to update its Xeon Scalable server processor family this year with the new "Ice Lake-SP" microarchitecture. Built on the 10 nm+ silicon fabrication process, "Ice Lake-SP" is a high- thru extreme core-count monolithic silicon that features "Sunny Cove" CPU cores that introduce the first real IPC increases over "Skylake." A 24-core/48-thread processor likely based on this silicon surfaced on the Geekbench database, where it posted some impressive numbers given its low clock speeds.
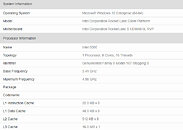
The processor comes with an identification string "GenuineIntel Family 6 Model 106 Stepping 4," with a nominal clock speed of 2.20 GHz, and boost frequency of 2.90 GHz, which points to the possibility of this being an engineering sample. Besides clock speeds and core counts, some basic hardware specs were detected by Geekbench 4. For starters, the processor has an L1D cache size of 48 KB and L1I cache size of 32 KB, which is similar to the client-segment "Ice Lake-U" silicon based Core i7-1065G7, and confirms that this processor uses "Sunny Cove" cores. "Cascade Lake" and "Skylake" cores use 32 KB L1D caches. Also, the dedicated L2 cache per core is 1.25 MB, up from the 1 MB L2 caches on "Cascade Lake." Client-segment "Ice Lake" chips use 512 KB L2 caches. The shared L3 cache is 36 MB (or 1.5 MB slice per core), which loosely aligns with the cache balance of Intel's server and HEDT processors. In this bench run, the processor is backed by 256 GB of memory, of an unknown type or configuration. In the three bench runs, the setup scores roughly 4100 points single-core, and roughly 42000 points multi-core.
The processor comes with an identification string "GenuineIntel Family 6 Model 106 Stepping 4," with a nominal clock speed of 2.20 GHz, and boost frequency of 2.90 GHz, which points to the possibility of this being an engineering sample. Besides clock speeds and core counts, some basic hardware specs were detected by Geekbench 4. For starters, the processor has an L1D cache size of 48 KB and L1I cache size of 32 KB, which is similar to the client-segment "Ice Lake-U" silicon based Core i7-1065G7, and confirms that this processor uses "Sunny Cove" cores. "Cascade Lake" and "Skylake" cores use 32 KB L1D caches. Also, the dedicated L2 cache per core is 1.25 MB, up from the 1 MB L2 caches on "Cascade Lake." Client-segment "Ice Lake" chips use 512 KB L2 caches. The shared L3 cache is 36 MB (or 1.5 MB slice per core), which loosely aligns with the cache balance of Intel's server and HEDT processors. In this bench run, the processor is backed by 256 GB of memory, of an unknown type or configuration. In the three bench runs, the setup scores roughly 4100 points single-core, and roughly 42000 points multi-core.

Intel Reassures Investors of its Server Processor Roadmap: Ice Lake-SP in 2020, Sapphire Rapids in 2021
Intel's Investor Relations head Trey Campbell, in a "fire-side chat" with top investors at the Cowen Virtual Technology Media and Telecom Conference, reaffirmed Intel's commitment to its server processor roadmap. Intel is on course to introducing its 10 nm Xeon "Ice Lake-SP" enterprise processor family by the end of 2020, and "Sapphire Rapids" sometime within 2021.
"Ice Lake-SP" processor will introduce the new "Whitley" platform, with a new 4,189-pin LGA socket, which leverages PCI-Express gen 4.0. While retaining the DDR4 memory standard, the memory interface has been broadened to 8-channel, and reference memory clock speeds are expected to be increased to DDR4-3200. The company's "Sapphire Rapids" processor is expected to shake up the market, as it introduces next-generation I/O, when it launches alongside the "Eagle Stream" platform in 2021. The processor will be built on the refined 10 nm+ silicon fabrication node, feature "Willow Cove" CPU cores, and I/O feature set that sees the introduction of DDR5 memory standard, and PCI-Express gen 5.0.
"Ice Lake-SP" processor will introduce the new "Whitley" platform, with a new 4,189-pin LGA socket, which leverages PCI-Express gen 4.0. While retaining the DDR4 memory standard, the memory interface has been broadened to 8-channel, and reference memory clock speeds are expected to be increased to DDR4-3200. The company's "Sapphire Rapids" processor is expected to shake up the market, as it introduces next-generation I/O, when it launches alongside the "Eagle Stream" platform in 2021. The processor will be built on the refined 10 nm+ silicon fabrication node, feature "Willow Cove" CPU cores, and I/O feature set that sees the introduction of DDR5 memory standard, and PCI-Express gen 5.0.

Intel Tiger Lake Processor Spotted with Boost of 5 GHz
Intel is preparing to launch its next-generation Tiger Lake lineup of processors for the middle of 2020. The processors are based on the new "Willow Cove" CPU core, which supposedly brings even more IPC gains compared to previous "Golden Cove" CPU cores found in Ice Lake processors. The Tiger Lake lineup will use Intel's advanced 10 nm+ manufacturing process. This alone should bring some gains in frequency compared to the 10 nm Ice Lake processor generation, which was spotting a maximum of 4.1 GHz boost frequency on 28 W TDP model named Core i7-1068NG7. This processor is labeled as the highest-performing Ice Lake parts available today and the best 10 nm products available so far from Intel.
Thanks to the popular hardware leaker Rogame, we have evidence that the gains from 10 nm+ manufacturing process are real and that Tiger Lake will show us an amazing boost frequency of 5 GHz. In the benchmark, an unknown OEM laptop was spotted running the benchmark with a Tiger Lake CPU. This CPU is a 4 core, 8 threaded model with a base frequency of 2.3 GHz and a surprising boost frequency of 5 GHz. This information should, of course, be taken with a grain of salt until we get more information about the Tiger Lake lineup and their specifications.
Thanks to the popular hardware leaker Rogame, we have evidence that the gains from 10 nm+ manufacturing process are real and that Tiger Lake will show us an amazing boost frequency of 5 GHz. In the benchmark, an unknown OEM laptop was spotted running the benchmark with a Tiger Lake CPU. This CPU is a 4 core, 8 threaded model with a base frequency of 2.3 GHz and a surprising boost frequency of 5 GHz. This information should, of course, be taken with a grain of salt until we get more information about the Tiger Lake lineup and their specifications.

Intel "Tiger Lake-U" Processor with Relatively High Clock Speed Spotted
An unnamed Intel "Tiger Lake-U" quad-core processor was spotted on Futuremark database by _rogame, featuring 2.80 GHz nominal clock-speeds. Barring the 28 W i7-1068NG7 and i5-1038NG7, which are exclusive for MacBooks and aren't considered U-segment, all current-gen "Ice Lake" client chips have their nominal clock speeds ranging between 1.00 to 1.30 GHz. Given this, 2.80 GHz would qualify as a big jump for a U-segment "Tiger Lake" chip. We know from a separate report that "Tiger Lake" could also offer Turbo Boost frequencies as high as 4.70 GHz for the top Core i7-1185G7 part, a similar jump from the 3.90 GHz max boost of the current-gen i7-1065G7, all while retaining a 15 W nameplate TDP.
The Futuremark database listing only mentions nominal clock of 2.80 GHz, and the CPU core configuration of 4-core/8-thread. The hardcoded CPU name string of this prototype specifies "Tiger Lake U," confirming this is a 15 W part, and not a 28 W part that will be gobbled down by Apple. Intel's newfound clock-speed headroom could be attributed to the company's refined 10 nm+ silicon fabrication node. "Tiger Lake" combines "Willow Cove" CPU cores with an iGPU based on the company's ambitious new Xe graphics architecture, marking its commercial debut. "Tiger Lake" is expected to launch around September-October, 2020.
The Futuremark database listing only mentions nominal clock of 2.80 GHz, and the CPU core configuration of 4-core/8-thread. The hardcoded CPU name string of this prototype specifies "Tiger Lake U," confirming this is a 15 W part, and not a 28 W part that will be gobbled down by Apple. Intel's newfound clock-speed headroom could be attributed to the company's refined 10 nm+ silicon fabrication node. "Tiger Lake" combines "Willow Cove" CPU cores with an iGPU based on the company's ambitious new Xe graphics architecture, marking its commercial debut. "Tiger Lake" is expected to launch around September-October, 2020.

Intel "Tiger Lake" and "Lakefield" to Launch Around September-October, 2020
The 11th generation Intel Core "Tiger Lake" mobile processor and pioneering "Lakefield" heterogenous x86 processor could debut around September or October, 2020, according to a leaked Lenovo internal slide posted by NotebookCheck. It also points to Intel denoting future processors' lithography with Foveros 3D Packaging as simply "3D," and not get into a nanometer number-game with AMD (which is now in 7 nm and on course to 5 nm in 2022). This makes sense as Foveros allows the combination of dies built on different silicon fabrication nodes.
"Tiger Lake" is still denoted as a 10 nm as it's a planar chip. Intel is developing it on a refined 10 nm+ silicon fabrication process, which apparently enables Intel to increase clock speeds without breaking the target power envelope. "Tiger Lake" sees the commercial debut of Intel's ambitious Xe graphics architecture as an iGPU solution. "Lakefield," on the other hand, is a 5-core processor combining four "Tremont" low power x86-64 cores with a "Sunny Cove" high-powered core, in a setup rivaling Arm big.LITTLE, enabling the next generation of mobile computing form-factors, which Intel and its partners are still figuring out under Project Athena.
"Tiger Lake" is still denoted as a 10 nm as it's a planar chip. Intel is developing it on a refined 10 nm+ silicon fabrication process, which apparently enables Intel to increase clock speeds without breaking the target power envelope. "Tiger Lake" sees the commercial debut of Intel's ambitious Xe graphics architecture as an iGPU solution. "Lakefield," on the other hand, is a 5-core processor combining four "Tremont" low power x86-64 cores with a "Sunny Cove" high-powered core, in a setup rivaling Arm big.LITTLE, enabling the next generation of mobile computing form-factors, which Intel and its partners are still figuring out under Project Athena.

Intel Confirms Mid-2020 "Tiger Lake" Launch
Intel earlier today published its Q1 2020 financial results. In its slide deck, the company illustrated many of the facts and numbers detailed in its earnings release, but one item caught our eye: a slide confirms that the company plans to launch its "Tiger Lake" client processor by mid-year (we would place that between June to August, 2020. Intel is quite ambitious about "Tiger Lake," as it forms the microarchitecture behind its most advanced 11th generation Core mobile processors. A slide from a November 2019 investor meet details the key design goals. "Tiger Lake" implements Intel's new "Willow Cove" CPU core design that succeeds "Sunny Cove" cores found inside its "Ice Lake" processors.
"Willow Cove" sees a new cache design, implementation of new transistor optimizations from Intel's 10 nm+ silicon fabrication process, and new security features. Besides "Willow Cove" CPU cores, "Tiger Lake" sees the market debut of the company's ambitious Xe graphics architecture as its iGPU solution. The chip will also support next-generation I/O. Here's hoping Intel is able to step up CPU core-counts with "Tiger Lake." The company was forced to tap into "Comet Lake" for both its 15 W and 45 W markets due to their higher core counts, despite an older CPU core and iGPU architecture than "Ice Lake." In the same slide, Intel mentions that it commenced sampling for "Ice Lake-SP" line of high core-count enterprise processors.
"Willow Cove" sees a new cache design, implementation of new transistor optimizations from Intel's 10 nm+ silicon fabrication process, and new security features. Besides "Willow Cove" CPU cores, "Tiger Lake" sees the market debut of the company's ambitious Xe graphics architecture as its iGPU solution. The chip will also support next-generation I/O. Here's hoping Intel is able to step up CPU core-counts with "Tiger Lake." The company was forced to tap into "Comet Lake" for both its 15 W and 45 W markets due to their higher core counts, despite an older CPU core and iGPU architecture than "Ice Lake." In the same slide, Intel mentions that it commenced sampling for "Ice Lake-SP" line of high core-count enterprise processors.

Intel's Next-Generation Tiger Lake-U Core i7-1165G7 CPU Score Leaks
Intel is preparing to launch its next-generation Tiger Lake-U lineup of CPUs based on the new Willow Cove core that is supposed to bring big IPC gains and plenty of new features. Being a part of the 11th generation of Core CPUs, these processors are expected to arrive sometime in the second half of 2020, built on Intel's 10 nm+ manufacturing process. Thanks to a popular hardware leaker @_rogame, we have found another Tiger Lake-U in the 3D Mark benchmark database. Unlike the last time when we saw Intel's Core i7-1185G7 being run on the 3D Mark tests, we now have test results of its brother - the Core i7-1165G7.
From the 3D Mark report, we can see some details like CPU's base frequency, which is 2.8 GHz in this case. This is just 200 MHz lower compared to the previous Core i7-1185G7 CPU that leaked. The platform used to test the new Core i7-1165G7 CPU was running Windows 10 and had 16 GB of DDR4 SODIMM memory. The new 3D Mark results are already looking promising. From the previous leak of Core i7-1185G7, we saw that Tiger Lake CPU which managed to score 2922 in the CPU test, 1296 in GPU test, and an overall score of 1414. However, this new Core i7-1165G7 CPU is a bit different. In the graphic test, it scores 1150 points, while the CPU test shows an impressive 4750 points. This Core i7-1165G7 result is much higher compared to the more powerful Core i7-1185G7 CPU, which is a bit strange. It could be attributed to a faster memory, but so far we don't know. However, the overall score of the i7-1165G7 is a bit lower compared to i7 1185G7, scoring 1297 points.
From the 3D Mark report, we can see some details like CPU's base frequency, which is 2.8 GHz in this case. This is just 200 MHz lower compared to the previous Core i7-1185G7 CPU that leaked. The platform used to test the new Core i7-1165G7 CPU was running Windows 10 and had 16 GB of DDR4 SODIMM memory. The new 3D Mark results are already looking promising. From the previous leak of Core i7-1185G7, we saw that Tiger Lake CPU which managed to score 2922 in the CPU test, 1296 in GPU test, and an overall score of 1414. However, this new Core i7-1165G7 CPU is a bit different. In the graphic test, it scores 1150 points, while the CPU test shows an impressive 4750 points. This Core i7-1165G7 result is much higher compared to the more powerful Core i7-1185G7 CPU, which is a bit strange. It could be attributed to a faster memory, but so far we don't know. However, the overall score of the i7-1165G7 is a bit lower compared to i7 1185G7, scoring 1297 points.

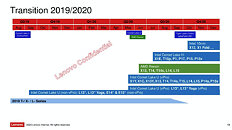
Intel 10nm Product Lineup for 2020 Revealed: Alder Lake and Ice Lake Xeons
A leaked Intel internal slide surfaced on Chinese social networks, revealing five new products the company will build on its 10 nm silicon fabrication process. These include the "Alder Lake" heterogenous desktop processor, "Tiger Lake" mobile processor, "Ice Lake" based Xeon Scalable enterprise processors, DG1 discrete GPU, and "Snow Ridge" 5G base-station SoC. Some, if not all of these products, will implement Intel's new 10 nm+ silicon fabrication node that is expected to go live within 2020.
"Alder Lake" is a desktop processor that implements Intel's new heterogenous x86 core design that's making its debut with "Lakefield." The chip features up to 8 larger "Willow Cove" or "Golden Cove" CPU cores, and up to 8 smaller "Tremont" or "Gracemont" cores. This 8-big/8-small combo lets the chip achieve TDP targets around 80 Watts. Next up is "Tiger Lake," Intel's next-generation mobile processor family succeeding "Ice Lake." This microarchitecture implements "Willow Cove" CPU cores in a homogeneous setup, alongside Xe architecture based integrated graphics. "Ice Lake-SP" is Intel's next enterprise architecture that places mature "Sunny Cove" CPU cores in extreme core-count dies. Lastly, there's "Snow Ridge," an SoC purpose built for 5G base-stations. Image quality notwithstanding, these slides don't appear particularly new, and it's likely that COVID-19 has destabilized the roadmap. For instance, "Alder Lake," and "Ice Lake-SP" are expected to be 10 nm++ chips, a node that doesn't go live before 2021.
"Alder Lake" is a desktop processor that implements Intel's new heterogenous x86 core design that's making its debut with "Lakefield." The chip features up to 8 larger "Willow Cove" or "Golden Cove" CPU cores, and up to 8 smaller "Tremont" or "Gracemont" cores. This 8-big/8-small combo lets the chip achieve TDP targets around 80 Watts. Next up is "Tiger Lake," Intel's next-generation mobile processor family succeeding "Ice Lake." This microarchitecture implements "Willow Cove" CPU cores in a homogeneous setup, alongside Xe architecture based integrated graphics. "Ice Lake-SP" is Intel's next enterprise architecture that places mature "Sunny Cove" CPU cores in extreme core-count dies. Lastly, there's "Snow Ridge," an SoC purpose built for 5G base-stations. Image quality notwithstanding, these slides don't appear particularly new, and it's likely that COVID-19 has destabilized the roadmap. For instance, "Alder Lake," and "Ice Lake-SP" are expected to be 10 nm++ chips, a node that doesn't go live before 2021.

Intel Courts TSMC 6nm and 3nm Nodes for Future Xe GPU Generations
Intel is rumored to be aligning its future-generation Xe GPU development with TSMC's node development cycle, with the company reportedly negotiating with the Taiwanese foundry for 6 nm and 3 nm allocation for its large Xe GPUs. Intel's first Xe discrete GPUs for the market, however, are reportedly built on the company's own 10 nm+ silicon fabrication process.
While Intel's fascination with TSMC 3 nm is understandable, seeking out TSMC's 6 nm node raises eyebrows. Internally referred to as "N6," the 6 nm silicon fabrication node at TSMC is expected to go live either towards the end of 2020 or early 2021, which is when Intel's 10 nm+ node is expected to pick up volume production, beginning with the company's "Tiger Lake" processors. Perhaps a decision has been made internally to ensure that Xe doesn't eat too much into Intel's own foundry capacities meant for processor manufacturing, and to instead outsource Xe manufacturing to third-party foundries like TSMC and Samsung eventually. Way back in April 2019 it was rumored that Intel was evaluating Samsung as a foundry partner for Xe.
While Intel's fascination with TSMC 3 nm is understandable, seeking out TSMC's 6 nm node raises eyebrows. Internally referred to as "N6," the 6 nm silicon fabrication node at TSMC is expected to go live either towards the end of 2020 or early 2021, which is when Intel's 10 nm+ node is expected to pick up volume production, beginning with the company's "Tiger Lake" processors. Perhaps a decision has been made internally to ensure that Xe doesn't eat too much into Intel's own foundry capacities meant for processor manufacturing, and to instead outsource Xe manufacturing to third-party foundries like TSMC and Samsung eventually. Way back in April 2019 it was rumored that Intel was evaluating Samsung as a foundry partner for Xe.

Intel "Panther Canyon" NUC Implements "Tiger Lake" SoC with Xe Graphics
Intel NUC 11 Extreme is the spiritual successor to the "Hades Canyon" and "Skull Canyon" NUC, and implements the company's next-generation 10 nm+ "Tiger Lake" processor. Codenamed "Panther Canyon," the NUC 11 Extreme represents a line of ultra-compact desktops with serious computing power, bringing together the company's highest-performance CPU cores and iGPUs. The "Tiger Lake-U" SoC powering the NUC 11 Extreme will reportedly be configured with a 28-Watt TDP, and will come in Core i3, Core i5, and Core i7 variants.
The "Tiger Lake-U" processor is expected to combine next-generation "Willow Cove" CPU cores with an iGPU based on Intel's new Xe graphics architecture, in what could be the first commercial outing for both. The NUC 11 Extreme "Panther Canyon" will also support up to 64 GB of dual-channel DDR4-3200 memory over SO-DIMMs, an M.2-2280 slot with PCI-Express 4.0 x4 and SATA 6 Gbps wiring, and option for Intel Optane M10 cache memory. On the connectivity front, and Intel AX-201 WLAN card provides 802.11ax Wi-Fi 6, and Bluetooth 5. A 2.5 GbE wired interface will also be available. These will also be among the first NUCs to feature front- and rear-Thunderbolt ports (possibly next-gen 80 Gbps given that the platform implements PCIe gen 4.0). The NUC 11 Extreme "Panther Canyon" is expected to launch some time in the second half of 2020.
The "Tiger Lake-U" processor is expected to combine next-generation "Willow Cove" CPU cores with an iGPU based on Intel's new Xe graphics architecture, in what could be the first commercial outing for both. The NUC 11 Extreme "Panther Canyon" will also support up to 64 GB of dual-channel DDR4-3200 memory over SO-DIMMs, an M.2-2280 slot with PCI-Express 4.0 x4 and SATA 6 Gbps wiring, and option for Intel Optane M10 cache memory. On the connectivity front, and Intel AX-201 WLAN card provides 802.11ax Wi-Fi 6, and Bluetooth 5. A 2.5 GbE wired interface will also be available. These will also be among the first NUCs to feature front- and rear-Thunderbolt ports (possibly next-gen 80 Gbps given that the platform implements PCIe gen 4.0). The NUC 11 Extreme "Panther Canyon" is expected to launch some time in the second half of 2020.

Intel "Rocket Lake" an Adaptation of "Willow Cove" CPU Cores on 14nm?
The "Willow Cove" CPU core design succeeds "Sunny Cove," Intel's first truly new CPU core design in close to 5 years. "Sunny Cove" is implemented in the 10 nm "Ice Lake" microarchitecture, and "Willow Cove" cores are expected to debut with the 10 nm+ "Tiger Lake." It turns out that Intel is working to adapt "Willow Cove" CPU cores onto a 14 nm microarchitecture, and "Rocket Lake" could be it.
Twitter user @chiakokhua, a retired VLSI engineer with high hit-rate on CPU microarchitecture news, made sense of technical documents to point out that "Rocket Lake" is essentially a 14 nm adaptation of "Tiger Lake," but with the iGPU shrunk significantly, to make room for the larger CPU cores. The Gen12 iGPU on "Rocket Lake-S" will feature just 32 execution units (EUs), whilst on "Tiger Lake," it has three times the muscle, with 96 EUs. "Rocket Lake" also replaces "Tiger Lake's" FIVR (fully-integrated voltage regulation) with a conventional SVID VRM architecture.
Twitter user @chiakokhua, a retired VLSI engineer with high hit-rate on CPU microarchitecture news, made sense of technical documents to point out that "Rocket Lake" is essentially a 14 nm adaptation of "Tiger Lake," but with the iGPU shrunk significantly, to make room for the larger CPU cores. The Gen12 iGPU on "Rocket Lake-S" will feature just 32 execution units (EUs), whilst on "Tiger Lake," it has three times the muscle, with 96 EUs. "Rocket Lake" also replaces "Tiger Lake's" FIVR (fully-integrated voltage regulation) with a conventional SVID VRM architecture.

Intel Ice Lake-SP and Cooper Lake-SP Details Leaked
Brainbox, a Korean media outlet, has gathered information on Intel's newest Ice Lake and Cooper Lake server processors from a presentation ASUS held for its server lineup. With Cooper Lake-SP paving the way for the first server CPU model to be released on the new "Whitley" platform, it is supposed to launch in Q2 of 2020. Cooper Lake-SP comes with TDP of 300 W and will be available with configurations of up to 48 cores, but there also should be a 56 core model like the Xeon Platinum 9282, that has a TDP of 400 W. Cooper Lake-SP supports up to 64 PCIe 3.0 lanes, 8 channel memory (16 DIMMs in total) that goes up to 3200 MHz and four Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) links.
Ice Lake-SP, built on the new 10 nm+ manufacturing process, is coming in soon after Cooper Lake-SP release, with a launch window in Q3 of 2020. That is just few months apart from previous CPU launch, so it will be a bit hard to integrate the launches of two rather distinct products. As far as the specifications of Ice Lake-SP goes, it will have up to 38 core for the top end model, within 270 W TDP. It supports 64 PCIe 4.0 lanes with three UPI links. There is also 8 channel memory support, however this time there is an option to use 2nd generation Optane DC Persistent Memory. Both CPU uArches will run on the new LGA 4189 on the P+ socket.
Ice Lake-SP, built on the new 10 nm+ manufacturing process, is coming in soon after Cooper Lake-SP release, with a launch window in Q3 of 2020. That is just few months apart from previous CPU launch, so it will be a bit hard to integrate the launches of two rather distinct products. As far as the specifications of Ice Lake-SP goes, it will have up to 38 core for the top end model, within 270 W TDP. It supports 64 PCIe 4.0 lanes with three UPI links. There is also 8 channel memory support, however this time there is an option to use 2nd generation Optane DC Persistent Memory. Both CPU uArches will run on the new LGA 4189 on the P+ socket.

Intel Clarifies on 10nm Desktop CPUs: Still on the Table, Likely in 2021
Intel in a quick rebuttal to the earlier reports from Monday, clarified that desktop processors based on the 10 nm silicon fabrication node are still on the company's roadmap. "We continue to make great progress on 10 nm, and our current roadmap of 10 nm products includes desktop," the company said in its one-liner. Monday's reports predicted a horror story where Intel would drag its 14 nm "Skylake" derived microarchitecture through to 2022, at which point it would be 7 years old.
The Tom's Hardware report that posts the statement, however, pins 14 nm to still last till 2021, if not the 2022 date predicted in the HardwareLuxx report. Intel will sell "Comet Lake" through 2020, succeeded by "Rocket Lake," which takes up much of 2021. Towards the end of 2021, Intel will release a desktop processor based on its matured 10 nm++ silicon fabrication node, which will lead the company into 2022, when it finally launches 7 nm EUV-based desktop chips.
The Tom's Hardware report that posts the statement, however, pins 14 nm to still last till 2021, if not the 2022 date predicted in the HardwareLuxx report. Intel will sell "Comet Lake" through 2020, succeeded by "Rocket Lake," which takes up much of 2021. Towards the end of 2021, Intel will release a desktop processor based on its matured 10 nm++ silicon fabrication node, which will lead the company into 2022, when it finally launches 7 nm EUV-based desktop chips.

Intel "Tiger Lake" Supports PCIe Gen 4 and Features Xe Graphics, Phantom Canyon NUC Detailed
Intel is working on its next generation gaming-grade NUC, codenamed "Phantom Canyon." When it comes out some time in 2020-21, it will feature Intel's 10 nm+ "Tiger Lake" SoC. Intel detailed this and more in a leaked presentation to industry partners. It describes the launch of of the company's "Ghost Canyon" NUC in Fall 2019 to succeed the current "Hades Canyon" gaming NUC. This box features a Core i9-9980HK processor and discrete graphics options. It will be succeeded in 2020-21 (late 2020 or sometime 2021), by the "Phantom Canyon" NUC that's in development.
The "Phantom Canyon" NUC is powered by a 28 W 10 nm+ "Tiger Lake-U" SoC that features PCI-Express gen 4. The package also implements Intel's "Gen 12" graphics processor that's derived from the Xe architecture it's currently working on, according to Chinese publication PTTWeb. The NUC will also feature discrete graphics options in the price-range of the current GTX 1660 Ti and RTX 2060 ($299 to $349). In related news, we see subtle hints that Intel will give its chipset bus a major update in future generations of its desktop and mobile platforms. Apparently, future platforms could feature DMI spread over 8 lanes as opposed to 4 on current platforms, besides the update to PCIe gen 4. This quadrupling in bandwidth compared to DMI 3.0 (PCIe 3.0 x4) is necessitated by the growth in bandwidth-hungry devices such as NVMe SSDs, external Thunderbolt 3 graphics cards, USB 3.2 flash drives, etc.
The "Phantom Canyon" NUC is powered by a 28 W 10 nm+ "Tiger Lake-U" SoC that features PCI-Express gen 4. The package also implements Intel's "Gen 12" graphics processor that's derived from the Xe architecture it's currently working on, according to Chinese publication PTTWeb. The NUC will also feature discrete graphics options in the price-range of the current GTX 1660 Ti and RTX 2060 ($299 to $349). In related news, we see subtle hints that Intel will give its chipset bus a major update in future generations of its desktop and mobile platforms. Apparently, future platforms could feature DMI spread over 8 lanes as opposed to 4 on current platforms, besides the update to PCIe gen 4. This quadrupling in bandwidth compared to DMI 3.0 (PCIe 3.0 x4) is necessitated by the growth in bandwidth-hungry devices such as NVMe SSDs, external Thunderbolt 3 graphics cards, USB 3.2 flash drives, etc.

Intel "Tiger Lake" Architecture Combines Willow Cove CPU Cores and Xe iGPU
Even as Intel banks on 10 nm "Ice Lake" to pull it out of the 14 nm dark ages, the company is designing a fascinating new monolithic processor SoC die that succeeds it. Codenamed "Tiger Lake," and slated to debut in 2020, this die packs "Willow Cove" CPU cores and an iGPU based on Intel's Xe architecture, not Gen11. "Willow Cove" CPU cores are more advanced than the "Sunny Cove" cores "Ice Lake" packs, featuring a redesigned on-die cache, additional security features, and transistor optimization yielded from the newer 10 nm+ silicon fabrication process.
Intel is already boasting of 1 TFLOP/s compute power of the Gen11 iGPU on "Ice Lake," so it's logical to predict that the Xe based iGPU will be significantly faster. It will also support the latest display standards. The "next-gen I/O" referenced by Intel could be faster NVMe, Thunderbolt, and USB standards that leverage the bandwidth doubling brought about by PCI-Express gen 4.0. Here's the catch: much like "Ice Lake," the new "Tiger Lake" chip will get a mobile debut as Tiger Lake-Y or Tiger Lake-U, and desktop processors could follow later, possibly even 2021, depending on how much pressure it faces from AMD.
Intel is already boasting of 1 TFLOP/s compute power of the Gen11 iGPU on "Ice Lake," so it's logical to predict that the Xe based iGPU will be significantly faster. It will also support the latest display standards. The "next-gen I/O" referenced by Intel could be faster NVMe, Thunderbolt, and USB standards that leverage the bandwidth doubling brought about by PCI-Express gen 4.0. Here's the catch: much like "Ice Lake," the new "Tiger Lake" chip will get a mobile debut as Tiger Lake-Y or Tiger Lake-U, and desktop processors could follow later, possibly even 2021, depending on how much pressure it faces from AMD.
Apr 23rd, 2025 18:59 EDT
change timezone
Latest GPU Drivers
New Forum Posts
- RX 9000 series GPU Owners Club (497)
- To distill or not distill what say ye? (67)
- Companies should be called out for this (81)
- What are you playing? (23446)
- 5060 Ti 8GB DOA (255)
- DTS DCH Driver for Realtek HDA [DTS:X APO4 + DTS Interactive] (2151)
- Are the 8 GB cards worth it? (103)
- Just for lolz, Post your 3DMark2001SE Benchmark scores! (95)
- Asus Rx570 o4g cannot losd drivers error code 43 (12)
- EXTREMEHW Invites TECHPOWERUP to our 3RD ANNUAL 96-HOUR FOLDING CHALLENGE April 26th 00:00 UTC (3)
Popular Reviews
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti 8 GB Review - So Many Compromises
- ASRock X870E Taichi Lite Review
- ASUS GeForce RTX 5060 Ti TUF OC 16 GB Review
- Upcoming Hardware Launches 2025 (Updated Apr 2025)
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Pulse Review
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti PCI-Express x8 Scaling
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Nitro+ Review - Beating NVIDIA
- Palit GeForce RTX 5060 Ti Infinity 3 16 GB Review
- AMD Ryzen 7 9800X3D Review - The Best Gaming Processor
- MSI GeForce RTX 5060 Ti Gaming OC 16 GB Review
Controversial News Posts
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5060 Ti 16 GB SKU Likely Launching at $499, According to Supply Chain Leak (182)
- NVIDIA Sends MSRP Numbers to Partners: GeForce RTX 5060 Ti 8 GB at $379, RTX 5060 Ti 16 GB at $429 (127)
- NVIDIA Launches GeForce RTX 5060 Series, Beginning with RTX 5060 Ti This Week (115)
- Nintendo Confirms That Switch 2 Joy-Cons Will Not Utilize Hall Effect Stick Technology (105)
- Nintendo Switch 2 Launches June 5 at $449.99 with New Hardware and Games (99)
- Sony Increases the PS5 Pricing in EMEA and ANZ by Around 25 Percent (85)
- NVIDIA PhysX and Flow Made Fully Open-Source (77)
- Windows Notepad Gets Microsoft Copilot Integration (75)