Intel 4 Process Node Detailed, Doubling Density with 20% Higher Performance
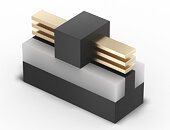
Intel's semiconductors nodes have been quite controversial with the arrival of the 10 nm design. Years in the making, the node got delayed multiple times, and only recently did the general public get the first 10 nm chips. Today, at IEEE's annual VLSI Symposium, we get more details about Intel's upcoming nodes, called Intel 4. Previously referred to as a 7 nm process, Intel 4 is the company's first node to use EUV lithography accompanied by various technologies. The first thing when a new process node is discussed is density. Compared to Intel 7, Intel 4 will double the transistor count for the same area and enable 20% higher performing transistors.
Looking at individual transistor size, the new Intel 4 node represents a very tiny piece of silicon that is even smaller than its predecessor. With a Fin Pitch of 30 nm, Contact Gate Poly Pitch of 50 nm between gates, and Minimum Metal Pitch (M0) of 50 nm, the Intel 4 transistor is significantly smaller compared to the Intel 7 cell, listed in the table below. For scaling, Intel 4 provides double the number of transistors in the same area compared to Intel 7. However, this reasoning is applied only to logic. For SRAM, the new PDK provides 0.77 area reduction, meaning that the same SoC built on Intel 7 will not be half the size of Intel 4, as SRAM plays a significant role in chip design. The Intel 7 HP library can put 80 million transistors on a square millimeter, while Intel 4 HP is capable of 160 million transistors per square millimeter.
Looking at individual transistor size, the new Intel 4 node represents a very tiny piece of silicon that is even smaller than its predecessor. With a Fin Pitch of 30 nm, Contact Gate Poly Pitch of 50 nm between gates, and Minimum Metal Pitch (M0) of 50 nm, the Intel 4 transistor is significantly smaller compared to the Intel 7 cell, listed in the table below. For scaling, Intel 4 provides double the number of transistors in the same area compared to Intel 7. However, this reasoning is applied only to logic. For SRAM, the new PDK provides 0.77 area reduction, meaning that the same SoC built on Intel 7 will not be half the size of Intel 4, as SRAM plays a significant role in chip design. The Intel 7 HP library can put 80 million transistors on a square millimeter, while Intel 4 HP is capable of 160 million transistors per square millimeter.