AMD Radeon Pro WX 8200 Detailed
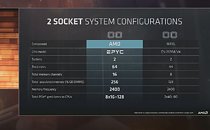
AMD is giving final touches to the new Radeon Pro WX 8200 professional graphics card. Launched over a year following the Radeon Pro WX 9100, the WX 8200 has a leaner feature-set, while continuing to be based on AMD's current IP. The card still uses the 14 nm "Vega 10" MCM, but with a core-config akin to that of the RX Vega 56. You get 56 NGCUs working out to 3,584 stream processors, 224 TMUs, 64 ROPs, and a 4096-bit wide HBM2 memory interface, handling 16 GB of memory on this card. The air-cooled card also has a leaner connectivity load-out, with just four mini-DisplayPort 1.4 connectors (the WX 9100 comes with six). Its 8-pin + 6-pin connectors are positioned at the rear-end to be SSI workstation-friendly. The card surfaced on CompuBench database, in which its performance numbers are only slightly behind those of the WX 9100, but significantly better than the "Polaris 20" based WX 7100. AMD is expected to launch this card at SIGGRAPH 2018.