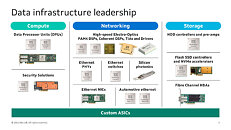
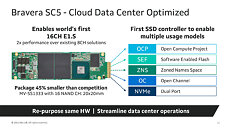
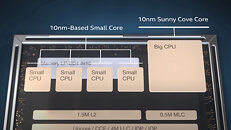
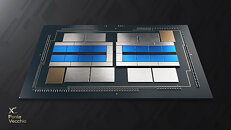
NREL Acquires Next-Generation High Performance Computing System Based on NVIDIA Next-Generation GPU
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has selected Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) to build its third-generation, high performance computing (HPC) system, called Kestrel. Named for a falcon with keen eyesight and intelligence, Kestrel's moniker is apropos for its mission—to rapidly advance the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE's) energy research and development (R&D) efforts to deliver transformative energy solutions to the entire United States.
Installation of the new system will begin in the fall of 2022 in NREL's Energy Systems Integration Facility (ESIF) data center. Kestrel will complement the laboratory's current supercomputer, Eagle, during the transition. When completed—in early 2023—Kestrel will accelerate energy efficiency and renewable energy research at a pace and scale more than five times greater than Eagle, with approximately 44 petaflops of computing power.
Installation of the new system will begin in the fall of 2022 in NREL's Energy Systems Integration Facility (ESIF) data center. Kestrel will complement the laboratory's current supercomputer, Eagle, during the transition. When completed—in early 2023—Kestrel will accelerate energy efficiency and renewable energy research at a pace and scale more than five times greater than Eagle, with approximately 44 petaflops of computing power.