Intel's Upcoming Sapphire Rapids Server Processors to Feature up to 56 Cores with HBM Memory
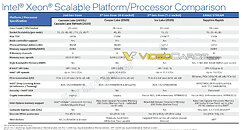
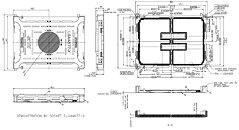
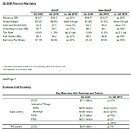
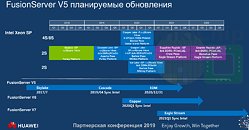
Intel has just launched its Ice Lake-SP lineup of Xeon Scalable processors, featuring the new Sunny Cove CPU core design. Built on the 10 nm node, these processors represent Intel's first 10 nm shipping product designed for enterprise. However, there is another 10 nm product going to be released for enterprise users. Intel is already preparing the Sapphire Rapids generation of Xeon processors and today we get to see more details about it. Thanks to the anonymous tip that VideoCardz received, we have a bit more details like core count, memory configurations, and connectivity options. And Sapphire Rapids is shaping up to be a very competitive platform. Do note that the slide is a bit older, however, it contains useful information.
The lineup will top at 56 cores with 112 threads, where this processor will carry a TDP of 350 Watts, notably higher than its predecessors. Perhaps one of the most interesting notes from the slide is the department of memory. The new platform will make a debut of DDR5 standard and bring higher capacities with higher speeds. Along with the new protocol, the chiplet design of Sapphire Rapids will bring HBM2E memory to CPUs, with up to 64 GBs of it per socket/processor. The PCIe 5.0 standard will also be present with 80 lanes, accompanying four Intel UPI 2.0 links. Intel is also supposed to extend the x86_64 configuration here with AMX/TMUL extensions for better INT8 and BFloat16 processing.
The lineup will top at 56 cores with 112 threads, where this processor will carry a TDP of 350 Watts, notably higher than its predecessors. Perhaps one of the most interesting notes from the slide is the department of memory. The new platform will make a debut of DDR5 standard and bring higher capacities with higher speeds. Along with the new protocol, the chiplet design of Sapphire Rapids will bring HBM2E memory to CPUs, with up to 64 GBs of it per socket/processor. The PCIe 5.0 standard will also be present with 80 lanes, accompanying four Intel UPI 2.0 links. Intel is also supposed to extend the x86_64 configuration here with AMX/TMUL extensions for better INT8 and BFloat16 processing.