- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,591 (7.45/day)
- Location
- Dublin, Ireland
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | Gigabyte B550 AORUS Elite V2 |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 16GB DDR4-3200 |
| Video Card(s) | Galax RTX 4070 Ti EX |
| Storage | Samsung 990 1TB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
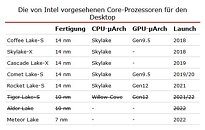
In a shocking piece of news, Intel has reportedly scrapped plans to launch its 10 nm "Ice Lake" microarchitecture on the client desktop platform. The company will confine its 10 nm microarchitectures, "Ice Lake" and "Tiger Lake" to only the mobile platform, while the desktop platform will see derivatives of "Skylake" hold Intel's fort under the year 2022! Intel gambles that with HyperThreading enabled across the board and increased clock-speeds, it can restore competitiveness with AMD's 7 nm "Zen 2" Ryzen processors with its "Comet Lake" silicon that offers core-counts of up to 10.
"Comet Lake" will be succeeded in 2021 by the 14 nm "Rocket Lake" silicon, which somehow combines a Gen12 iGPU with "Skylake" derived CPU cores, and possibly increased core-counts and clock speeds over "Comet Lake." It's only 2022 that Intel will ship out a truly new microarchitecture on the desktop platform, with "Meteor Lake." This chip will be built on Intel's swanky 7 nm EUV silicon fabrication node, and possibly integrate CPU cores more advanced than even "Willow Cove," possibly "Golden Cove."
The HardwareLuxx article making these explosive revelations attributes the sudden change in Intel's plans to the company not being able to scale clock-speeds of "Ice Lake" high enough to establish product leadership. It feels "Skylake," which has IPC parity with "Zen 2," has enough scalability and clock-speed headroom to stay competitive with AMD at high clock-speeds. The company will augment next-generation uncore (revamped memory controllers, support for PCIe gen 4.0, Gen12 iGPU, etc.), with "Skylake" CPU cores, over time. Other areas where Intel could grow its mainstream desktop silicon is cache rebalancing similar to its HEDT chips, and implementing the Mesh Interconnect to maintain low latencies as core-counts enter two-figures.
Interestingly, 10 nm "Ice Lake" remains on Intel's enterprise roadmap, where the company appears more desperate not to cede market-share to AMD, especially as businesses around the world set their 5G plans rolling, springing a cycle of hardware updates in the data-center. 2020 could see the introduction of Xeon Scalable processors based on 10 nm "Ice Lake" microarchitecture with "Sunny Cove" CPU cores. In 2021, the company will introduce the "Sapphire Rapids" Xeon processor with even more cores and larger I/O connectivity, spearheaded with PCI-Express gen 5.0.
Update Oct 15th: Intel has released a statement, denying these claims, read more here.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
"Comet Lake" will be succeeded in 2021 by the 14 nm "Rocket Lake" silicon, which somehow combines a Gen12 iGPU with "Skylake" derived CPU cores, and possibly increased core-counts and clock speeds over "Comet Lake." It's only 2022 that Intel will ship out a truly new microarchitecture on the desktop platform, with "Meteor Lake." This chip will be built on Intel's swanky 7 nm EUV silicon fabrication node, and possibly integrate CPU cores more advanced than even "Willow Cove," possibly "Golden Cove."

The HardwareLuxx article making these explosive revelations attributes the sudden change in Intel's plans to the company not being able to scale clock-speeds of "Ice Lake" high enough to establish product leadership. It feels "Skylake," which has IPC parity with "Zen 2," has enough scalability and clock-speed headroom to stay competitive with AMD at high clock-speeds. The company will augment next-generation uncore (revamped memory controllers, support for PCIe gen 4.0, Gen12 iGPU, etc.), with "Skylake" CPU cores, over time. Other areas where Intel could grow its mainstream desktop silicon is cache rebalancing similar to its HEDT chips, and implementing the Mesh Interconnect to maintain low latencies as core-counts enter two-figures.
Interestingly, 10 nm "Ice Lake" remains on Intel's enterprise roadmap, where the company appears more desperate not to cede market-share to AMD, especially as businesses around the world set their 5G plans rolling, springing a cycle of hardware updates in the data-center. 2020 could see the introduction of Xeon Scalable processors based on 10 nm "Ice Lake" microarchitecture with "Sunny Cove" CPU cores. In 2021, the company will introduce the "Sapphire Rapids" Xeon processor with even more cores and larger I/O connectivity, spearheaded with PCI-Express gen 5.0.
Update Oct 15th: Intel has released a statement, denying these claims, read more here.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site







