- Joined
- Jan 5, 2006
- Messages
- 18,584 (2.69/day)
| System Name | AlderLake |
|---|---|
| Processor | Intel i7 12700K P-Cores @ 5Ghz |
| Motherboard | Gigabyte Z690 Aorus Master |
| Cooling | Noctua NH-U12A 2 fans + Thermal Grizzly Kryonaut Extreme + 5 case fans |
| Memory | 32GB DDR5 Corsair Dominator Platinum RGB 6000MT/s CL36 |
| Video Card(s) | MSI RTX 2070 Super Gaming X Trio |
| Storage | Samsung 980 Pro 1TB + 970 Evo 500GB + 850 Pro 512GB + 860 Evo 1TB x2 |
| Display(s) | 23.8" Dell S2417DG 165Hz G-Sync 1440p |
| Case | Be quiet! Silent Base 600 - Window |
| Audio Device(s) | Panasonic SA-PMX94 / Realtek onboard + B&O speaker system / Harman Kardon Go + Play / Logitech G533 |
| Power Supply | Seasonic Focus Plus Gold 750W |
| Mouse | Logitech MX Anywhere 2 Laser wireless |
| Keyboard | RAPOO E9270P Black 5GHz wireless |
| Software | Windows 11 |
| Benchmark Scores | Cinebench R23 (Single Core) 1936 @ stock Cinebench R23 (Multi Core) 23006 @ stock |
World's first space HOTEL to begin construction in low Earth orbit in 2025 complete with restaurants, cinemas and rooms for up to 400 guests.
Developed by the Orbital Assembly Corporation (OAC), the Voyager Station could be operational as early as 2027, with the infrastructure built in orbit around the Earth.
The space station will be a large circle and rotate to generate artificial gravity that will be set at a similar level to the gravity found on the surface of the Moon.
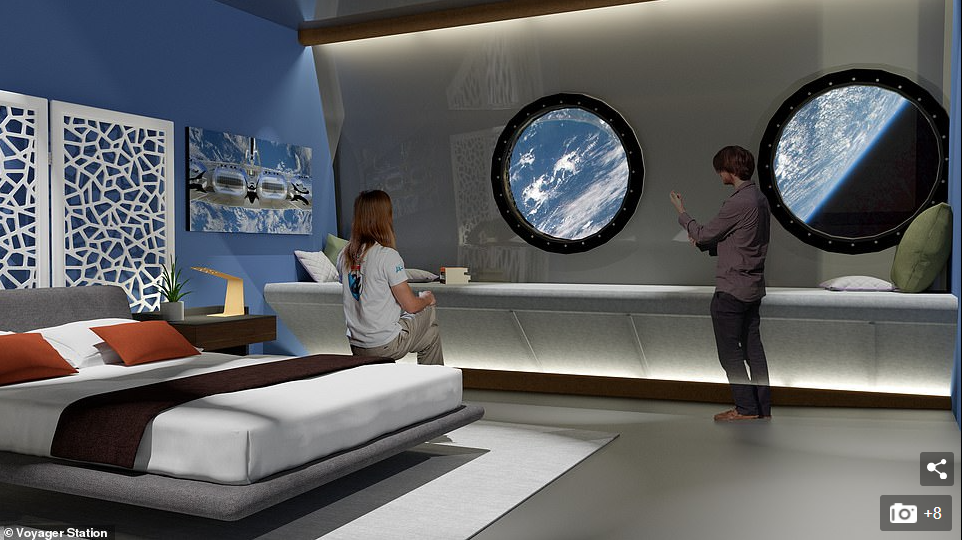
Voyager Station's hotel will include many of the features you might expect from a cruise ship, including themed restaurants, a health spa and a cinema.
It will feature a series of pods attached to the outside of the rotating ring and some of these pods could be sold to the likes of NASA and ESA for space research.
No details of cost to build the space station, or the cost of spending a night in the hotel have been revealed, although OAC say build costs are getting cheaper thanks to reusable launch vehicles like the SpaceX Falcon 9 and the future Starship.
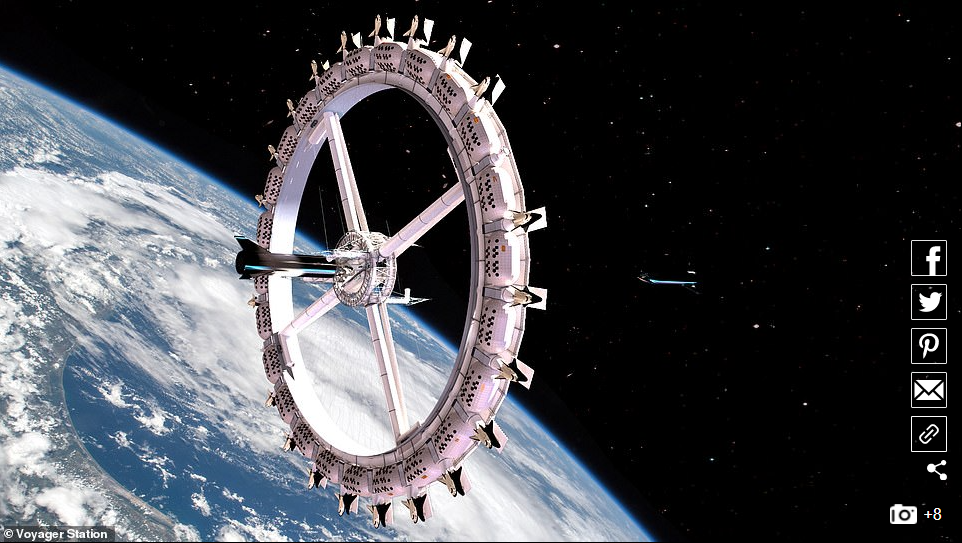
Developed by the Orbital Assembly Corporation (OAC), the Voyager Station could be operational as early as 2027, with the infrastructure built in orbit around the Earth

The space station will be a large circle and rotate to generate artificial gravity that will be set at a similar level to the gravity found on the surface of the Moon

Voyager station's hotel will include many of the features you might expect from a cruise ship, including themed restaurants, a health spa and a cinema
The Voyager Class space station will be made up of a series of rings, with a number of 'modules' attached to the outermost of the rings.
Some of these 24 modules will be run by the Gateway Foundation and will be for things like crew quarters, air, water and power.
They will also include a gym, kitchen, restaurant, bar and other essential facilities for people due to be on the station longer term.
The other modules will be leased or sold to private companies and governments.
For example, people could buy one of the 20x12 metre modules for a private villa or multiple modules to create a hotel with spa, cinema and more.
Government agencies could use the station to house their own science module or as a training centre for astronauts preparing to go to Mars.
The idea of an orbiting space station build around a central, circular wheel goes back to the earliest days of space travel, in an idea by Wernher von Braun.
He was one of the architects of the NASA Apollo programme and in the 1950s proposed a wheel-shaped habitat spinning to create artificial gravity.
The concept for the Voyager station, which is a similar idea but on a much larger scale, first came about in 2012 with the launch of the Gateway Foundation.
OAC, the firm established by the foundation to realise the vision of an orbiting station, was established in 2018 with the goal of it being operational by 2027.
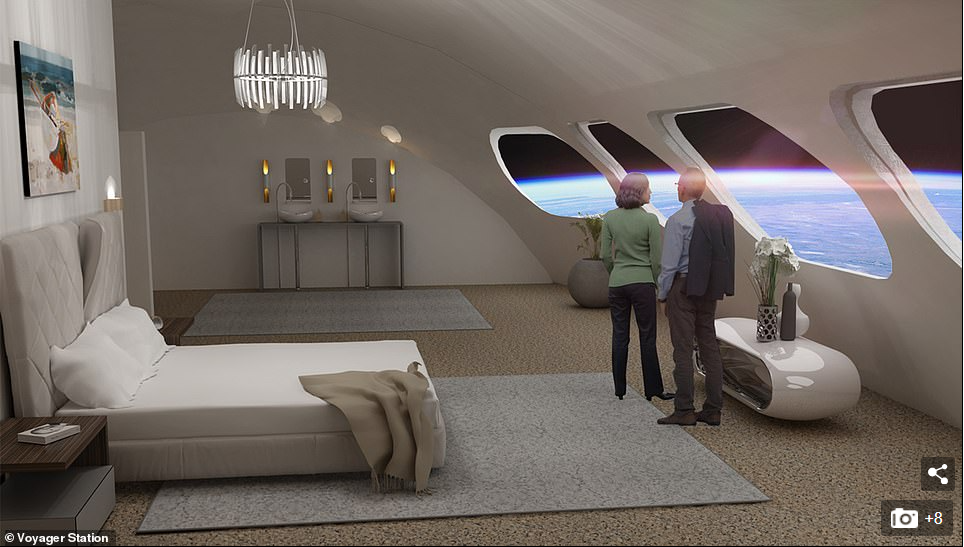

It will feature a series of pods attached to the outside of the rotating ring and some of these pods could be sold to the likes of NASA and ESA for space research
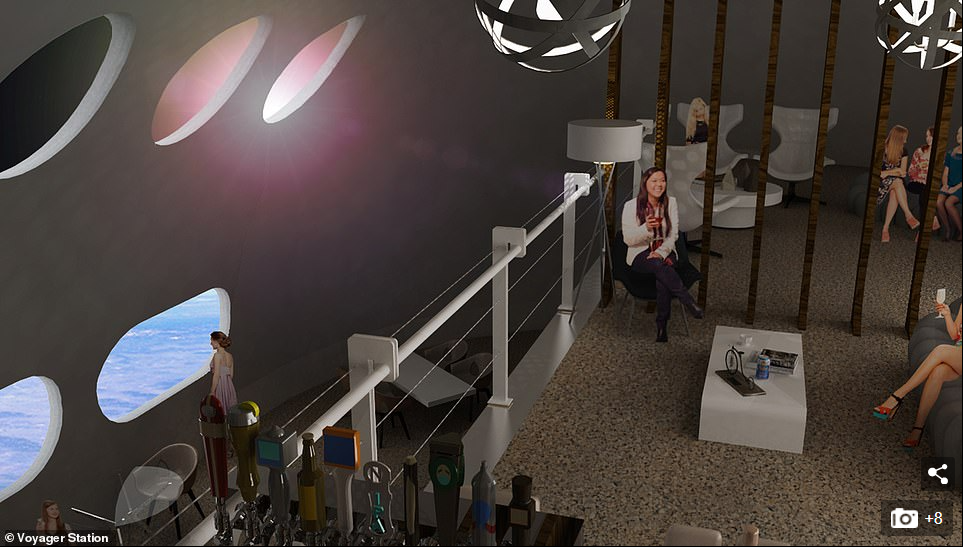

Some of these 24 modules will be run by the Gateway Foundation and will be for things like crew quarters, air, water and power
If fully realised it will be the largest human created object ever put into space.
While the cost of developing and building the space station haven't been revealed, with the launch of the SpaceX Falcon 9 and in future the SpaceX Starship, it has become more viable to put large objects into orbit.
The average cost of launching material to space has been about $8,000 per kg for a long time, but the reusable nature of the Falcon 9 saw this come down to $2,000/kg and SpaceX predicts Starship will bring it to a few hundred dollars.
Starship and other future fully reusable spacecraft will make the station viable as it will allow for regular and rapid connections between Earth and Voyager.
The team include NASA veterans, pilots, engineers and architects, building a system that includes multiple pods for different purposes and a high-speed 'space train'.
Each of these 24 integrated habitation modules will be 20 metres long by 12 metres wide and will carry a different function - from hotel rooms to movie theatres.
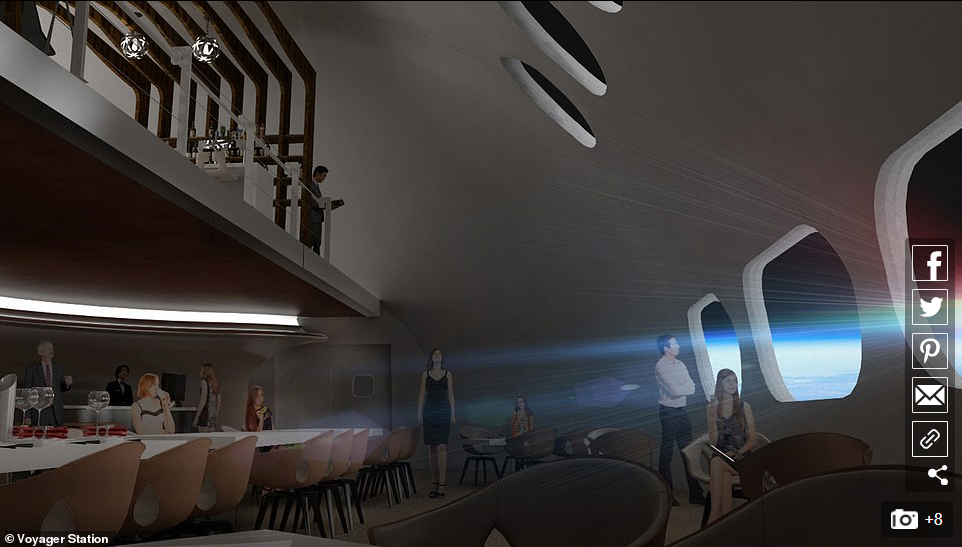
The firm also expects their ring to include viewing lounges, concert venues, bars, libraries, gyms and a spa - all things you'd see on a cruise ship, but this one will cruise around the whole world every 90 minutes.
First the team plan to test the concept with a much smaller scale prototype station and a free-flying microgravity facility similar to the International Space Station.
'This will be the next industrial revolution,' explained John Blincow, founder of the Gateway Foundation, adding it will create a new space industry.
Rotation is 'vital' says Blincow, as it isn't viable to have people on a space station without gravity for long periods of time - and people may want to be in space for months at a time, especially when working in a hotel.
'People need gravity so their bodies won't fall apart,' said Blincow, adding that the station can help understand just how much gravity our bodies need as it will be able to increase or decrease the rate of rotation to have higher or lower gravity.
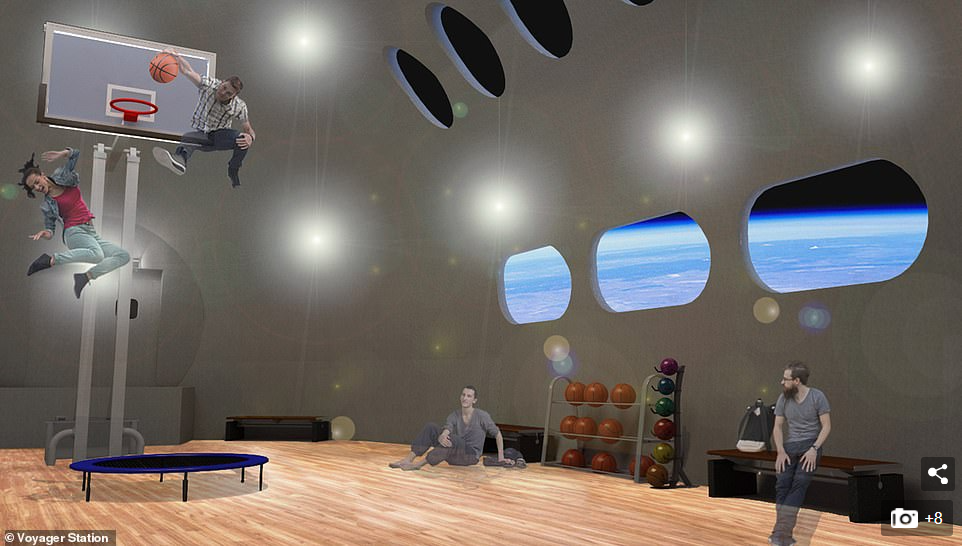

While the cost of developing and building the space station haven't been revealed, with the launch of the SpaceX Falcon 9 and in future the SpaceX Starship, it has become more viable to put large objects into orbit
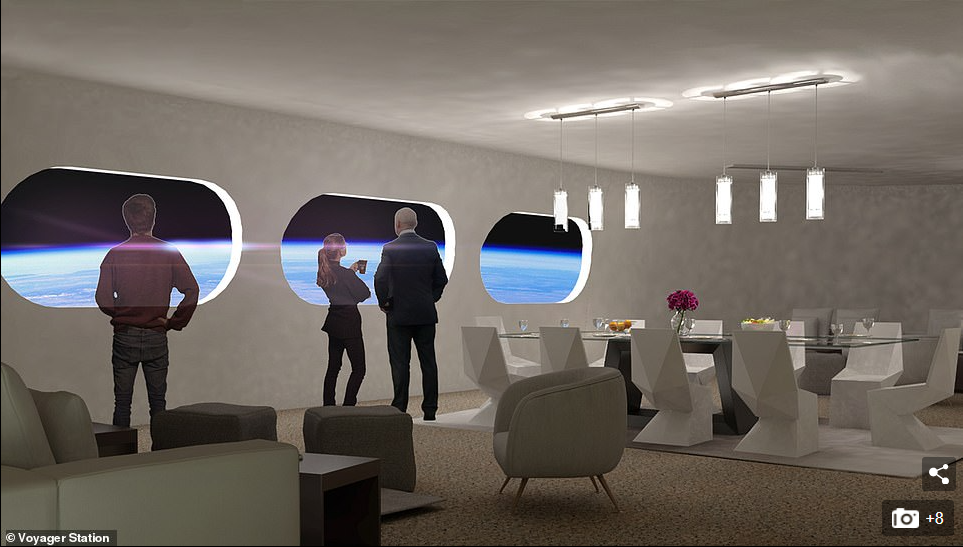

The firm also expects their ring to include viewing lounges, concert venues, bars, libraries, gyms and a spa - all things you'd see on a cruise ship, but this one will cruise around the whole world every 90 minutes
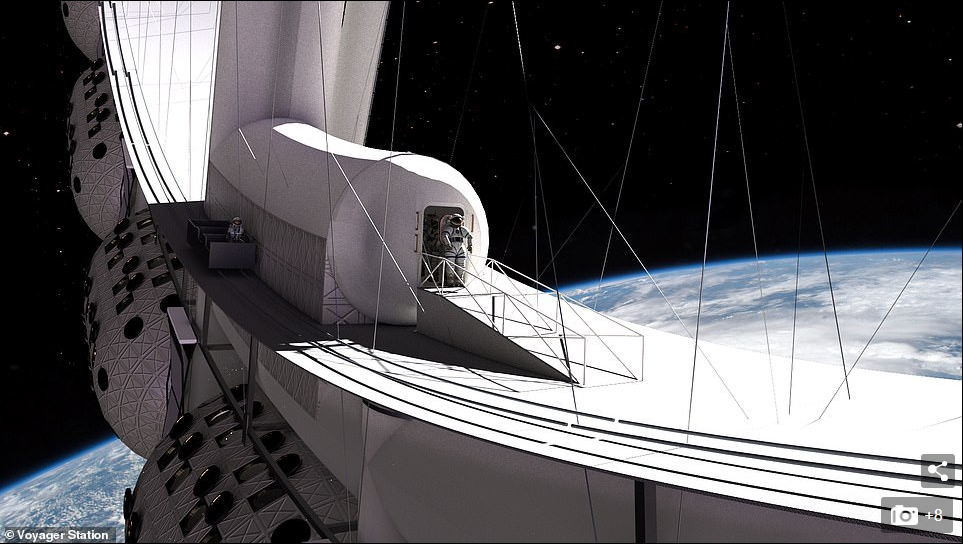

Rotation is 'vital' says Blincow, as it isn't viable to have people on a space station without gravity for long periods of time - and people may want to be in space for months at a time, especially when working in a hotel
When the testing is complete a robot named STAR - Structure Truss Assembly Robot - will build the frame for Voyager in orbi.
The first space construction will be a prototype 61 metre gravity ring in low Earth orbit that can spin up to create gravity at Mars' level - 40% of Earth's gravity.
That will take about two years to construct and has been called a 'near-term demonstrator' - when in space putting it together will take three days.
While the hotel is the initial goal of the artificial gravity space station, the company hope to lease pod space to agencies including NASA and ESA in future.

 www.dailymail.co.uk
www.dailymail.co.uk
- Experts from Orbital Assembly Corporation plan to build the inner spinning wheel using robots in Earth orbit
- Individual pods will then be launched to attach to the outer edges of this spinning wheel
- The pods will include hotel rooms, cinemas, bars, a health spa and restaurants, and could be sold to NASA
- So far there have been no details of what it will cost to build or stay in have been revealed by the firm
Developed by the Orbital Assembly Corporation (OAC), the Voyager Station could be operational as early as 2027, with the infrastructure built in orbit around the Earth.
The space station will be a large circle and rotate to generate artificial gravity that will be set at a similar level to the gravity found on the surface of the Moon.
Voyager Station's hotel will include many of the features you might expect from a cruise ship, including themed restaurants, a health spa and a cinema.
It will feature a series of pods attached to the outside of the rotating ring and some of these pods could be sold to the likes of NASA and ESA for space research.
No details of cost to build the space station, or the cost of spending a night in the hotel have been revealed, although OAC say build costs are getting cheaper thanks to reusable launch vehicles like the SpaceX Falcon 9 and the future Starship.
Developed by the Orbital Assembly Corporation (OAC), the Voyager Station could be operational as early as 2027, with the infrastructure built in orbit around the Earth
The space station will be a large circle and rotate to generate artificial gravity that will be set at a similar level to the gravity found on the surface of the Moon
Voyager station's hotel will include many of the features you might expect from a cruise ship, including themed restaurants, a health spa and a cinema
The Voyager Class space station will be made up of a series of rings, with a number of 'modules' attached to the outermost of the rings.
Some of these 24 modules will be run by the Gateway Foundation and will be for things like crew quarters, air, water and power.
They will also include a gym, kitchen, restaurant, bar and other essential facilities for people due to be on the station longer term.
The other modules will be leased or sold to private companies and governments.
For example, people could buy one of the 20x12 metre modules for a private villa or multiple modules to create a hotel with spa, cinema and more.
Government agencies could use the station to house their own science module or as a training centre for astronauts preparing to go to Mars.
The idea of an orbiting space station build around a central, circular wheel goes back to the earliest days of space travel, in an idea by Wernher von Braun.
He was one of the architects of the NASA Apollo programme and in the 1950s proposed a wheel-shaped habitat spinning to create artificial gravity.
The concept for the Voyager station, which is a similar idea but on a much larger scale, first came about in 2012 with the launch of the Gateway Foundation.
OAC, the firm established by the foundation to realise the vision of an orbiting station, was established in 2018 with the goal of it being operational by 2027.
It will feature a series of pods attached to the outside of the rotating ring and some of these pods could be sold to the likes of NASA and ESA for space research
Some of these 24 modules will be run by the Gateway Foundation and will be for things like crew quarters, air, water and power
If fully realised it will be the largest human created object ever put into space.
While the cost of developing and building the space station haven't been revealed, with the launch of the SpaceX Falcon 9 and in future the SpaceX Starship, it has become more viable to put large objects into orbit.
The average cost of launching material to space has been about $8,000 per kg for a long time, but the reusable nature of the Falcon 9 saw this come down to $2,000/kg and SpaceX predicts Starship will bring it to a few hundred dollars.
Starship and other future fully reusable spacecraft will make the station viable as it will allow for regular and rapid connections between Earth and Voyager.
The team include NASA veterans, pilots, engineers and architects, building a system that includes multiple pods for different purposes and a high-speed 'space train'.
Each of these 24 integrated habitation modules will be 20 metres long by 12 metres wide and will carry a different function - from hotel rooms to movie theatres.
The firm also expects their ring to include viewing lounges, concert venues, bars, libraries, gyms and a spa - all things you'd see on a cruise ship, but this one will cruise around the whole world every 90 minutes.
First the team plan to test the concept with a much smaller scale prototype station and a free-flying microgravity facility similar to the International Space Station.
'This will be the next industrial revolution,' explained John Blincow, founder of the Gateway Foundation, adding it will create a new space industry.
Rotation is 'vital' says Blincow, as it isn't viable to have people on a space station without gravity for long periods of time - and people may want to be in space for months at a time, especially when working in a hotel.
'People need gravity so their bodies won't fall apart,' said Blincow, adding that the station can help understand just how much gravity our bodies need as it will be able to increase or decrease the rate of rotation to have higher or lower gravity.
While the cost of developing and building the space station haven't been revealed, with the launch of the SpaceX Falcon 9 and in future the SpaceX Starship, it has become more viable to put large objects into orbit
The firm also expects their ring to include viewing lounges, concert venues, bars, libraries, gyms and a spa - all things you'd see on a cruise ship, but this one will cruise around the whole world every 90 minutes
Rotation is 'vital' says Blincow, as it isn't viable to have people on a space station without gravity for long periods of time - and people may want to be in space for months at a time, especially when working in a hotel
When the testing is complete a robot named STAR - Structure Truss Assembly Robot - will build the frame for Voyager in orbi.
The first space construction will be a prototype 61 metre gravity ring in low Earth orbit that can spin up to create gravity at Mars' level - 40% of Earth's gravity.
That will take about two years to construct and has been called a 'near-term demonstrator' - when in space putting it together will take three days.
While the hotel is the initial goal of the artificial gravity space station, the company hope to lease pod space to agencies including NASA and ESA in future.

World's first space HOTEL to begin construction in Earth orbit in 2025
Developed by the Orbital Assembly Corporation (OAC), the Voyager Station could be operational as early as 2027, with the infrastructure built in orbit around the Earth.


 theres nothing wrong with dreaming.
theres nothing wrong with dreaming.
 Scalpers in Space.........
Scalpers in Space......... 