- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,452 (7.50/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
Intel's upcoming Xeon "Sapphire Rapids" processor features a memory interface topology that closely resembles that of first-generation AMD EPYC "Rome," thanks to the multi-chip module design of the processor. Back in 2017, Intel's competing "Skylake-SP" Xeon processors were based on monolithic dies. Despite being spread across multiple memory controller tiles, the 6-channel DDR4 memory interface was depicted by Intel as an advantage over EPYC "Rome." AMD's first "Zen" based enterprise processor was a multi-chip module of four 14 nm, 8-core "Zeppelin" dies, each with a 2-channel DDR4 memory interface that added up to the processor's 8-channel I/O. Much like "Sapphire Rapids," a CPU core from any of the four dies had access to memory and I/O controlled by any other die, as the four were networked over the Infinity Fabric interconnect in a configuration that essentially resembled "4P on a stick."
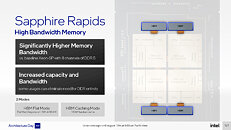
With "Sapphire Rapids," Intel is taking a largely similar approach—it has four compute tiles (dies) instead of a monolithic die, which Intel says helps with scalability in both directions; and each of the four compute tiles has a 2-channel DDR5 or 1024-bit HBM memory interface, which add up to the processor's 8-channel DDR5 total I/O. Intel says that CPU cores from each tile has equal access to memory, last-level cache, and I/O controlled by another die. Inter-tile communication is handled by EMIB physical media (55 micron bump-pitch wiring). UPI 2.0 makes up the inter-socket interconnect. Each of the four compute tiles has 24 UPI 2.0 links that operate at 16 GT/s. Intel didn't detail how memory is presented to the operating system, or the NUMA hierarchy, however much of Intel's engineering effort appears to be focused on making this disjointed memory I/O work as if "Sapphire Rapids" were a monolithic die. The company claims "consistent low-latency, high cross-sectional bandwidth across the SoC."




Another interesting aspect of "Sapphire Rapids" Xeon processors is support for HBM, which could prove a game-changer for the processor in the HPC and high-density compute markets. Specific models of Xeon "Sapphire Rapids" processors could come with on-package HBM. This memory can either be used as a victim-cache for the on-die caches on the compute tiles, vastly improving the memory sub-system; work exclusively as a standalone main memory; or even work as a non-tiered main memory alongside the DDR5 DRAM with flat memory regions. Intel refers to these as software-visible HBM+DDR5, and software-transparent HBM+DDR5 modes.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
With "Sapphire Rapids," Intel is taking a largely similar approach—it has four compute tiles (dies) instead of a monolithic die, which Intel says helps with scalability in both directions; and each of the four compute tiles has a 2-channel DDR5 or 1024-bit HBM memory interface, which add up to the processor's 8-channel DDR5 total I/O. Intel says that CPU cores from each tile has equal access to memory, last-level cache, and I/O controlled by another die. Inter-tile communication is handled by EMIB physical media (55 micron bump-pitch wiring). UPI 2.0 makes up the inter-socket interconnect. Each of the four compute tiles has 24 UPI 2.0 links that operate at 16 GT/s. Intel didn't detail how memory is presented to the operating system, or the NUMA hierarchy, however much of Intel's engineering effort appears to be focused on making this disjointed memory I/O work as if "Sapphire Rapids" were a monolithic die. The company claims "consistent low-latency, high cross-sectional bandwidth across the SoC."




Another interesting aspect of "Sapphire Rapids" Xeon processors is support for HBM, which could prove a game-changer for the processor in the HPC and high-density compute markets. Specific models of Xeon "Sapphire Rapids" processors could come with on-package HBM. This memory can either be used as a victim-cache for the on-die caches on the compute tiles, vastly improving the memory sub-system; work exclusively as a standalone main memory; or even work as a non-tiered main memory alongside the DDR5 DRAM with flat memory regions. Intel refers to these as software-visible HBM+DDR5, and software-transparent HBM+DDR5 modes.

View at TechPowerUp Main Site







