- Joined
- May 21, 2024
- Messages
- 852 (3.42/day)
Montage Technology today announced that it has successfully sampled its Gen 2 Multiplexed Rank Registering Clock Driver (MRCD) and Multiplexed Rank Data Buffer (MDB) chipset to leading global memory manufacturers. Designed for DDR5 Multiplexed Rank DIMM (MRDIMM), this new chipset supports data rates up to 12800 MT/s, delivering exceptional memory performance for next-generation computing platforms.
The release comes at a crucial time, as AI and big data analytics drive increasing demands for memory bandwidth in data centers. MRDIMM technology has emerged as a key solution to address this challenge, particularly as server processors continue to increase in core count.

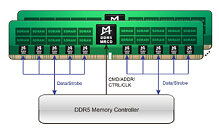
The innovative MRCD and MDB chips are fundamental to MRDIMM operation, featuring a "1+10" buffer architecture where each MRDIMM module incorporates one MRCD with ten MDB chips. In this configuration, the MRCD chip handles buffering and re-driving of address, command, clock, and control signals, while the MDB chips manage data traffic between the memory controller and DRAM chips. This architecture, coupled with double data rate and time-division multiplexing technology, enables simultaneous operation of two memory ranks at standard rates, effectively doubling data throughput.
Montage Technology's Gen 1 MRCD and MDB chipset, supporting speed up to 8800 MT/s, has already secured volume purchases from major memory manufacturers. The new Gen 2 engineering samples push performance boundaries further, achieving 12800 MT/s -- a 45% improvement over the previous generation.

Beyond MRCD and MDB, Montage Technology offers comprehensive memory interface and module support solutions, including RCD, DB, CKD, SPD Hub, PMIC, and TS. Additionally, the company has begun sampling its Gen 5 DDR5 RCD (RCD05) chip in the fourth quarter of 2024, further expanding its industry-leading portfolio. These offerings enable one-stop sourcing for customers while ensuring optimal system integration and performance.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source
The release comes at a crucial time, as AI and big data analytics drive increasing demands for memory bandwidth in data centers. MRDIMM technology has emerged as a key solution to address this challenge, particularly as server processors continue to increase in core count.

The innovative MRCD and MDB chips are fundamental to MRDIMM operation, featuring a "1+10" buffer architecture where each MRDIMM module incorporates one MRCD with ten MDB chips. In this configuration, the MRCD chip handles buffering and re-driving of address, command, clock, and control signals, while the MDB chips manage data traffic between the memory controller and DRAM chips. This architecture, coupled with double data rate and time-division multiplexing technology, enables simultaneous operation of two memory ranks at standard rates, effectively doubling data throughput.
Montage Technology's Gen 1 MRCD and MDB chipset, supporting speed up to 8800 MT/s, has already secured volume purchases from major memory manufacturers. The new Gen 2 engineering samples push performance boundaries further, achieving 12800 MT/s -- a 45% improvement over the previous generation.


"The memory demands of AI and other intensive workloads continue to drive innovation in data center memory architecture," said Stephen Tai, President of Montage Technology. "Our rapid progression from first-generation production to second-generation sampling demonstrates Montage Technology's expertise to DDR5 memory technology. This achievement strengthens our position as a leader in memory interface solutions."
Beyond MRCD and MDB, Montage Technology offers comprehensive memory interface and module support solutions, including RCD, DB, CKD, SPD Hub, PMIC, and TS. Additionally, the company has begun sampling its Gen 5 DDR5 RCD (RCD05) chip in the fourth quarter of 2024, further expanding its industry-leading portfolio. These offerings enable one-stop sourcing for customers while ensuring optimal system integration and performance.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source



