- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,598 (7.45/day)
- Location
- Dublin, Ireland
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | Gigabyte B550 AORUS Elite V2 |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 16GB DDR4-3200 |
| Video Card(s) | Galax RTX 4070 Ti EX |
| Storage | Samsung 990 1TB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
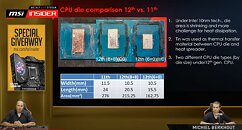
Intel's 12th Gen Core "Alder Lake-S" silicon apparently comes in two variants based on core count. The first one is a larger variant with 8 P cores and 8 E cores, while the second variant is a visibly smaller die with only 6 P cores, no E cores. This was revealed by an MSI Insider video presentation where pictures of LGA1700 packages with the two die types were shown off.
MSI also confirmed die-sizes and dimensions of the two. The larger C0 die measures 10.5 mm x 20.5 mm, working out to 215.25 mm² area. The smaller H0 die measures 10.5 mm x 15.5 mm, and a die area of 162.75 mm². The H0 silicon completely lacks "Gracemont" E-core clusters, and physically features six "Golden Cove" P cores. It's possible that given the 3 MB L3 slice size on the larger C0 silicon, the smaller H0 silicon physically features 18 MB of shared L3 cache.
Apparently the 12th Gen Core i5 series will have two classes of SKUs. One based on the C0 silicon, with 6+4 (P+E) configuration, and the other based on the H0 silicon, with 6+0 core configuration. The already launched Core i5-12600K/KF are 6+4 core, and it's expected that the i5-12600 (non-K) will have the same core-count, too. The lower Core i5 SKUs, such as the i5-12400 and i5-12400F, could be 6+0 core. Intel probably adopted this segmentation within the Core i5 lineup to ensure that the $170-$190 SKUs, such as the i5-12400/F don't cannibalize sales of the i5-12600/K/KF/F. The company had been carrying out similar segmentation within the Core i3 series in the past few generations, where the i3-xx100 and i3-xx300 series SKUs are differentiated with L3 cache sizes.

We recently spotted an i5-12400 engineering sample that confirms this core-configuration. The decision to create a smaller die for desktop could be purely economics-driven. The lower end of the Core i5 series, the Core i3 series, Pentium, and Celeron, sell in high volumes, and it makes sense for Intel to use physically smaller dies to maximize wafer utilization on its latest Intel 7 node (10 nm Enhanced SuperFin). It's also possible that the 12th Gen Core i3 series will be carved out from this silicon, by disabling two of the six P cores.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site
MSI also confirmed die-sizes and dimensions of the two. The larger C0 die measures 10.5 mm x 20.5 mm, working out to 215.25 mm² area. The smaller H0 die measures 10.5 mm x 15.5 mm, and a die area of 162.75 mm². The H0 silicon completely lacks "Gracemont" E-core clusters, and physically features six "Golden Cove" P cores. It's possible that given the 3 MB L3 slice size on the larger C0 silicon, the smaller H0 silicon physically features 18 MB of shared L3 cache.

Apparently the 12th Gen Core i5 series will have two classes of SKUs. One based on the C0 silicon, with 6+4 (P+E) configuration, and the other based on the H0 silicon, with 6+0 core configuration. The already launched Core i5-12600K/KF are 6+4 core, and it's expected that the i5-12600 (non-K) will have the same core-count, too. The lower Core i5 SKUs, such as the i5-12400 and i5-12400F, could be 6+0 core. Intel probably adopted this segmentation within the Core i5 lineup to ensure that the $170-$190 SKUs, such as the i5-12400/F don't cannibalize sales of the i5-12600/K/KF/F. The company had been carrying out similar segmentation within the Core i3 series in the past few generations, where the i3-xx100 and i3-xx300 series SKUs are differentiated with L3 cache sizes.

We recently spotted an i5-12400 engineering sample that confirms this core-configuration. The decision to create a smaller die for desktop could be purely economics-driven. The lower end of the Core i5 series, the Core i3 series, Pentium, and Celeron, sell in high volumes, and it makes sense for Intel to use physically smaller dies to maximize wafer utilization on its latest Intel 7 node (10 nm Enhanced SuperFin). It's also possible that the 12th Gen Core i3 series will be carved out from this silicon, by disabling two of the six P cores.
View at TechPowerUp Main Site









