- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,631 (7.44/day)
- Location
- Dublin, Ireland
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | Gigabyte B550 AORUS Elite V2 |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 16GB DDR4-3200 |
| Video Card(s) | Galax RTX 4070 Ti EX |
| Storage | Samsung 990 1TB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
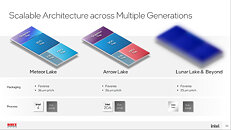
Keeping up with the cadence of two generations of desktop processors per socket, Intel will turn the page of the current LGA1700, with the introduction of the new Socket LGA1851. The processor package will likely have the same dimensions as LGA1700, and the two sockets may share cooler compatibility. The first processor microarchitecture to debut on LGA1851 will be the 14th Gen Core "Meteor Lake-S." These chips will feature a generationally lower CPU core-count compared to "Raptor Lake," but significantly bump the IPC on both the P-cores and E-cores.
"Raptor Lake" is Intel's final monolithic silicon client processor before the company pivots to chiplets built on various foundry nodes, as part of its IDM 2.0 strategy. The client-desktop version of "Meteor Lake," dubbed "Meteor Lake-S," will have a maximum CPU core configuration of 6P+16E (that's 6 performance cores with 16 efficiency cores). The chip has 6 "Redwood Cove" P-cores, and 16 "Crestmont" E-cores. Both of these are expected to receive IPC uplifts, such that the processor will end up faster (and hopefully more efficient) than the top "Raptor Lake-S" part. Particularly, it should be able to overcome the deficit of 2 P-cores.


Intel could find itself with a similar product differentiation problem it faced with the 11th Gen Core "Rocket Lake-S" desktop processors, where the physically low CPU core-count compared to the previous-generation (8-core vs. 10-core for "Comet Lake-S"); meant that both the Core i7-11700K and i9-11900K ended up being 8-core/16-thread processors. Here, we could see 6P+16E being the core-config of nearly all top SKUs, segmented by clock-speeds; while the mid-tier SKUs end up being 6P+8E.
Besides the CPU, "Meteor Lake-S" is expected to debut the new Xe-LPG graphics architecture for the iGPU, which could meet DirectX 12 Ultimate logo requirements. The iGPU on the "Meteor Lake-S" processor is expected to feature 4 Xe Cores, which works out to 64 EUs, and 512 unified shaders. This would still be a significant uplift from the iGPU of "Raptor Lake-S" with 32 EUs.
Intel is expected to restore CPU core-counts back to current levels with the 15th Gen "Arrow Lake-S" (2024-25). These chips are expected to come with core-configurations of up to 8P+16E. While the E-cores are expected to remain the same, the P-cores get a performance uplift, besides the addition of more cores. The "Compute Tile" (the die with the CPU cores) of "Meteor Lake-S" is built on the Intel 4 node (isopower characteristics comparable to TSMC 5 nm); while those of "Arrow Lake-S" will be built on the Intel 20A node (Intel is hyping 20A to be a pathbreaking node competitive with TSMC's sub 2 nm nodes).
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source
"Raptor Lake" is Intel's final monolithic silicon client processor before the company pivots to chiplets built on various foundry nodes, as part of its IDM 2.0 strategy. The client-desktop version of "Meteor Lake," dubbed "Meteor Lake-S," will have a maximum CPU core configuration of 6P+16E (that's 6 performance cores with 16 efficiency cores). The chip has 6 "Redwood Cove" P-cores, and 16 "Crestmont" E-cores. Both of these are expected to receive IPC uplifts, such that the processor will end up faster (and hopefully more efficient) than the top "Raptor Lake-S" part. Particularly, it should be able to overcome the deficit of 2 P-cores.



Intel could find itself with a similar product differentiation problem it faced with the 11th Gen Core "Rocket Lake-S" desktop processors, where the physically low CPU core-count compared to the previous-generation (8-core vs. 10-core for "Comet Lake-S"); meant that both the Core i7-11700K and i9-11900K ended up being 8-core/16-thread processors. Here, we could see 6P+16E being the core-config of nearly all top SKUs, segmented by clock-speeds; while the mid-tier SKUs end up being 6P+8E.
Besides the CPU, "Meteor Lake-S" is expected to debut the new Xe-LPG graphics architecture for the iGPU, which could meet DirectX 12 Ultimate logo requirements. The iGPU on the "Meteor Lake-S" processor is expected to feature 4 Xe Cores, which works out to 64 EUs, and 512 unified shaders. This would still be a significant uplift from the iGPU of "Raptor Lake-S" with 32 EUs.
Intel is expected to restore CPU core-counts back to current levels with the 15th Gen "Arrow Lake-S" (2024-25). These chips are expected to come with core-configurations of up to 8P+16E. While the E-cores are expected to remain the same, the P-cores get a performance uplift, besides the addition of more cores. The "Compute Tile" (the die with the CPU cores) of "Meteor Lake-S" is built on the Intel 4 node (isopower characteristics comparable to TSMC 5 nm); while those of "Arrow Lake-S" will be built on the Intel 20A node (Intel is hyping 20A to be a pathbreaking node competitive with TSMC's sub 2 nm nodes).
View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source




 . It's more a psychological block than anything else
. It's more a psychological block than anything else




