Two Unannounced AMD Ryzen Z2 APU Models Leaked, Flagship Could be "AI Z2 Extreme"
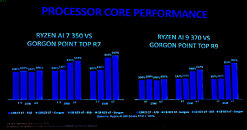
Three months ago, AMD unveiled its Ryzen Z2 APU series at CES 2025—purpose made for deployment in next-gen handheld gaming PCs. The officially announced flagship—Ryzen Z2 Extreme "Strix Point," utilizing Zen 5 and RDNA 3.5 technologies—was previously alluded to by leakers in late 2024; albeit with some curious claims regarding an "odd 3+5 core configuration." Last week, Hoang Anh Phu (@AnhPhuH) presented an alleged expanded lineup of Ryzen Z2 processors—headlined by a mysterious "Ryzen AI Z2 Extreme" SKU.
PC hardware watchdogs believe that this speculative variant will eventually arrive with an enabled XDNA 2 NPU (a first for the series); likely readied to take on Intel's Core Ultra 200V "Lunar Lake" processor family. MSI's Core Ultra 7 258V-powered Claw 8 AI+ and Claw 7 AI+ handhelds launched not too long ago, boasting all sorts of Microsoft Copilot+ capabilities. Mid-way through March, an Xbox executive introduced "Copilot for Gaming." Team Red and manufacturing partners are likely jumping onto this "AI gaming" bandwagon with the aforementioned "AI Ryzen Z2 Extreme" chip, as well as Phu's fanciful "Ryzen Z2 A" model. The latter could be a spin-off of AMD's vanilla Ryzen Z2 "Hawk Point" design, with a "switched on" XDNA NPU.
PC hardware watchdogs believe that this speculative variant will eventually arrive with an enabled XDNA 2 NPU (a first for the series); likely readied to take on Intel's Core Ultra 200V "Lunar Lake" processor family. MSI's Core Ultra 7 258V-powered Claw 8 AI+ and Claw 7 AI+ handhelds launched not too long ago, boasting all sorts of Microsoft Copilot+ capabilities. Mid-way through March, an Xbox executive introduced "Copilot for Gaming." Team Red and manufacturing partners are likely jumping onto this "AI gaming" bandwagon with the aforementioned "AI Ryzen Z2 Extreme" chip, as well as Phu's fanciful "Ryzen Z2 A" model. The latter could be a spin-off of AMD's vanilla Ryzen Z2 "Hawk Point" design, with a "switched on" XDNA NPU.