Weebit Nano and DB HiTek Tape-out ReRAM Module in 130nm BCD Process
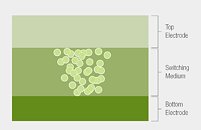
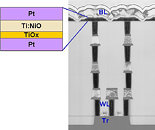
Weebit Nano Limited, a leading developer and licensor of advanced memory technologies for the global semiconductor industry, and tier-1 semiconductor foundry DB HiTek have taped-out (released to manufacturing) a demonstration chip integrating Weebit's embedded Resistive Random-Access Memory (ReRAM or RRAM) module in DB HiTek's 130 nm Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS (BCD) process. The highly integrated demo chips will be used for testing and qualification ahead of customer production, while demonstrating the performance and robustness of Weebit's technology.
This important milestone in the collaboration between Weebit and DB HiTek (previously announced on 19 October 2023) was completed on-schedule as part of the technology transfer process. The companies are working to make Weebit ReRAM available to DB HiTek customers for integration in their systems on chips (SoCs) as embedded non-volatile memory (NVM), and aim to have the technology qualified and ready for production in the second quarter of the 2025 calendar year. Weebit ReRAM is available now to select DB HiTek customers for design prototyping ahead of production.
This important milestone in the collaboration between Weebit and DB HiTek (previously announced on 19 October 2023) was completed on-schedule as part of the technology transfer process. The companies are working to make Weebit ReRAM available to DB HiTek customers for integration in their systems on chips (SoCs) as embedded non-volatile memory (NVM), and aim to have the technology qualified and ready for production in the second quarter of the 2025 calendar year. Weebit ReRAM is available now to select DB HiTek customers for design prototyping ahead of production.