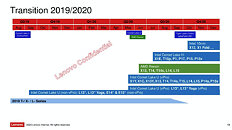
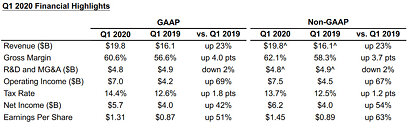
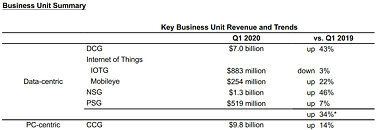
Intel "Tiger Lake" and "Lakefield" to Launch Around September-October, 2020
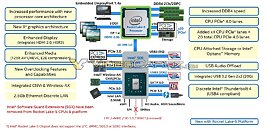
The 11th generation Intel Core "Tiger Lake" mobile processor and pioneering "Lakefield" heterogenous x86 processor could debut around September or October, 2020, according to a leaked Lenovo internal slide posted by NotebookCheck. It also points to Intel denoting future processors' lithography with Foveros 3D Packaging as simply "3D," and not get into a nanometer number-game with AMD (which is now in 7 nm and on course to 5 nm in 2022). This makes sense as Foveros allows the combination of dies built on different silicon fabrication nodes.
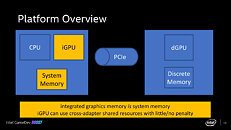
"Tiger Lake" is still denoted as a 10 nm as it's a planar chip. Intel is developing it on a refined 10 nm+ silicon fabrication process, which apparently enables Intel to increase clock speeds without breaking the target power envelope. "Tiger Lake" sees the commercial debut of Intel's ambitious Xe graphics architecture as an iGPU solution. "Lakefield," on the other hand, is a 5-core processor combining four "Tremont" low power x86-64 cores with a "Sunny Cove" high-powered core, in a setup rivaling Arm big.LITTLE, enabling the next generation of mobile computing form-factors, which Intel and its partners are still figuring out under Project Athena.
"Tiger Lake" is still denoted as a 10 nm as it's a planar chip. Intel is developing it on a refined 10 nm+ silicon fabrication process, which apparently enables Intel to increase clock speeds without breaking the target power envelope. "Tiger Lake" sees the commercial debut of Intel's ambitious Xe graphics architecture as an iGPU solution. "Lakefield," on the other hand, is a 5-core processor combining four "Tremont" low power x86-64 cores with a "Sunny Cove" high-powered core, in a setup rivaling Arm big.LITTLE, enabling the next generation of mobile computing form-factors, which Intel and its partners are still figuring out under Project Athena.