 48
48
ASUS EAH 5830 DirectCU Review
(48 Comments) »Introduction

After a successful launch of the Radeon HD 5000 series DirectX 11 compliant graphics processors, a lineup was created which spans from the very high-end dual-GPU Radeon HD 5970 at its >$500 price point, Radeon HD 5800 series as its performance segment, Radeon HD 5700 as its upper mainstream, HD 5600 as mainstream, and then on the entry-level Radeon HD 5400 and HD 5500 series. There was, however, a scope for expanding the performance segment a little, on both its ends. Until today, the Radeon HD 5850 and Radeon HD 5870 1GB are the only two members of this sub-series, targeting roughly-$300 and roughly-$400 price points, respectively. The next GPU lower down the food chain is the Radeon HD 5770. At its price and offer, it impressed us to the fullest, but there's a void created between this roughly-$160 GPU and the Radeon HD 5850, which is almost twice its price. This is the void that AMD is planning to fill with their latest product release.
Enter the Radeon HD 5830. This GPU is situated in a price-stratum that's between the Radeon HD 5770 and Radeon HD 5850, and, at face value, promises performance and features worth its price, if not more. In this review, we set out to investigate just that: whether AMD managed to fill that void.
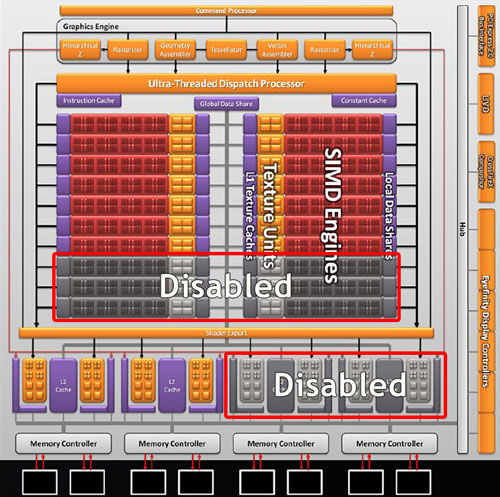
The Radeon HD 5870 is based on AMD's most complex piece of silicon to date. The Cypress GPU, packing well over 2 billion transistors, has all its 1600 stream processors enabled in the Radeon HD 5870, and in the HD 5970. With the Radeon HD 5850, AMD disabled 160 stream processors, lowered clock speeds a little to achieve the ~$300 price-point.
With the new HD 5830, it's going a step further, disabling 480 stream processors leaving still 1120 stream processors. It has also disabled 16 effective raster operation processors (ROPs) leaving 16 left. The memory interface is intact: there's a 256-bit wide memory interface, 1 GB of GDDR5 memory running at 1000 MHz, churning out 128 GB/s of bandwidth - same as that of the HD 5850. The core clock speed is also slightly higher than that of the HD 5850 (800 MHz vs. 725 MHz). In effect, the HD 5830's raster operations capability is about as strong as the Radeon HD 5770, but with a higher shader compute power (with 1120 stream processors), and the memory subsystem of the Radeon HD 5850. An interesting concept.
The grayed-out regions in the diagram above show disabled components. These components are permanently disabled during production of the ASIC and can not be reactivated via software.
Today we have with us the ASUS EAH 5830 DirectCu 1024 MB, a premium non-reference implementation of the Radeon HD 5830. The way its cooler is designed, and going by ASUS' choice of components, the EAH 5830 DirectCu is catered to the value performance enthusiast who can squeeze the last ounce of performance out of it by overclocking.
| Radeon HD 4870 | Radeon HD 5770 | Radeon HD 4890 | GeForce GTX 260 | Radeon HD 5830 | GeForce GTX 275 | Radeon HD 5850 | Radeon HD 5870 | |
| Shader units | 800 | 800 | 800 | 216 | 1120 | 240 | 1440 | 1600 |
| ROPs | 16 | 16 | 16 | 28 | 16 | 28 | 32 | 32 |
| GPU | RV770 | Juniper | RV790 | GT200 | Cypress | GT200 | Cypress | Cypress |
| Transistors | 956M | 1040M | 959M | 1404M | 2154M | 1404M | 2154M | 2154M |
| Memory Size | 512 MB | 1024 MB | 1024 MB | 896 MB | 1024 MB | 896 MB | 1024 MB | 1024 MB |
| Memory Bus Width | 256 bit | 128 bit | 256 bit | 448 bit | 256 bit | 448 bit | 256 bit | 256 bit |
| Core Clock | 750 MHz | 850 MHz | 850 MHz | 620 MHz | 800 MHz | 602 MHz | 725 MHz | 850 MHz |
| Memory Clock | 900 MHz | 1200 MHz | 975 MHz | 1050 MHz | 1000 MHz | 1107 MHz | 1000 MHz | 1200 MHz |
| Price | $155 | $155 | $200 | $200 | $220 | $230 | $300 | $400 |
Packaging & Contents
We received a card without retail packaging or accessories.Products in retail will come with the usual acessories like driver CD, adapters etc.
The Card
ASUS is using a new cooler that is designed to combine low fan noise and cooling performance at an affordable price. You can immediately see the heatpipes coming out of the thermal assembly, conveying a feeling of cooling power.
ASUS has made their card occupy two slots in the system, which is the expected configuration for the HD 5830.
The card has one DVI port, one HDMI port, and one DisplayPort. This is just one of many output configurations that are possible on the new cards, thanks to the overhauled display output logic. Basically the card can drive six TMDS signals that can be combined in any way (a dual-link DVI consumes two TMDS lines). Personally I would have preferred a DVI connector instead of the DP, because more people can potentially use that. ATI also mentioned that AIBs are free to design HD 5830 cards with up to six outputs, but nobody has announced any such products yet.
For HDMI Audio, NVIDIA requires you to feed an external audio source, for example from your motherboard's on-board audio, to the card via SPDIF cable. AMD on the other hand has integrated a sound device inside their GPUs which is the easier solution for most users. Also AMD's integrated sound device has been upgraded to support HDMI 1.3a which includes Dolby TrueHD, DTS-HD, AC-3, DTS and up to 7.1 channel audio with 192 kHz / 24-bit.
CrossFire configurations are supported to improve performance even further.
Here are the front and the back of the card, high-res versions are also available (front, back). If you choose to use these images for voltmods etc, please include a link back to this site or let us post your article.
A Closer Look
ASUS is one of the first companies to adapt the Direct-Touch heatpipe system on a VGA cooler. You can see the two copper heatpipes that sit right above the GPU core. They have been milled flat to make optimum contact with the die.
After removing the main heatsink you are still left with one heatsink sitting on the voltage regulator circuitry.
The VRM heatsink is just a simple metal heatsink - plenty for the cooling requirements of the PWM phases.
ASUS has decided to put one six-pin and one eight-pin connector on their card. In our power testing we saw a maximum power draw of 146W, so this is mostly for show.
The GDDR5 memory chips are made by Samsung, and carry the model number K4G10325FE-HC04. They are specified to run at 2500 MHz (5000 MHz GDDR5 effective).
The GPU voltage is managed by a uP6208 voltage controller, which does support I2C software voltage control with up to ~1.8V. The bundled ASUS SmartDoctor utility supports software voltage control up to 1.35V. Our latest GPU-Z 0.3.9 can also monitor this voltage regulator, but not as detailed as Volterra controllers for example.
This is AMD's Cypress GPU, it comes with a whopping 2154 million transistors and is produced on a 40 nm process at TSMC Taiwan. The Cypress die size is 334 mm². Compared to the GPU on the HD 5850 and HD 5870 this is exactly the same GPU, just with some features disabled.
Our Patreon Silver Supporters can read articles in single-page format.
May 4th, 2024 04:49 EDT
change timezone
Latest GPU Drivers
New Forum Posts
- Unigine Heaven 4.0 Benchmark Scores Part 2 (929)
- What's your latest tech purchase? (20429)
- Alphacool CORE 1 CPU block - bulging with danger of splitting? (78)
- What is your startup time for GIMP? (3)
- Keysfan (12)
- NASA Achieves milestone Solid State Battery (223)
- Change GPU or PSU ? Games look cryspy and sharp with microsuttering (7)
- Outer Worlds getting boring (38)
- Old high quality PSU, or semi-old mid-quality PSU? (60)
- What are the consequences of genetically altering ticks, fleas, and mosquitoes to control their populations? (198)
Popular Reviews
- Finalmouse UltralightX Review
- Meze Audio LIRIC 2nd Generation Closed-Back Headphones Review
- ASRock NUC BOX-155H (Intel Core Ultra 7 155H) Review
- Montech Sky Two GX Review
- Gigabyte GeForce RTX 4070 Ti Super Gaming OC Review
- Upcoming Hardware Launches 2023 (Updated Feb 2024)
- HYTE THICC Q60 240 mm AIO Review
- Alienware Pro Wireless Gaming Keyboard Review
- Ugreen NASync DXP4800 Plus Review
- AMD Ryzen 7 7800X3D Review - The Best Gaming CPU
Controversial News Posts
- Intel Statement on Stability Issues: "Motherboard Makers to Blame" (236)
- Windows 11 Now Officially Adware as Microsoft Embeds Ads in the Start Menu (167)
- AMD to Redesign Ray Tracing Hardware on RDNA 4 (118)
- Sony PlayStation 5 Pro Specifications Confirmed, Console Arrives Before Holidays (117)
- AMD's RDNA 4 GPUs Could Stick with 18 Gbps GDDR6 Memory (114)
- NVIDIA Points Intel Raptor Lake CPU Users to Get Help from Intel Amid System Instability Issues (106)
- AMD "Strix Halo" Zen 5 Mobile Processor Pictured: Chiplet-based, Uses 256-bit LPDDR5X (103)
- AMD Ryzen 9 7900X3D Now at a Mouth-watering $329 (103)
















