Friday, July 11th 2008

Pre-release Tests Conducted on AMD Denreb
Pre-release Tests Conducted on AMD Deneb
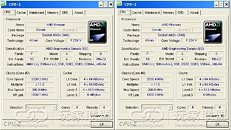
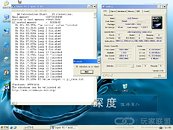
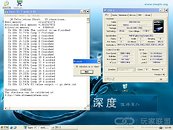
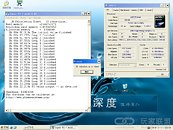
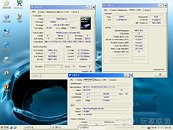
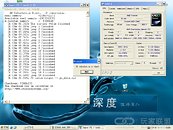
AMD Deneb is the code-name for the 45nm quad-core CPU which AMD plans to release soon. Chinese website ITOCP got their hands on two engineering samples. They used these samples at various clock-speeds set by altering the FSB multiplier and Vcore voltage. These chips were then subjected to rounds of Super Pi 1M benchmark. The results look rather luke-warm compared to what we saw of the Intel Bloomfield chips recently. The Deneb CPUs were supported by an AMD RD790 motherboard and 2 GB of DDR2 800 MHz unganged memory, running at timings of 5-5-5-18. The Phenom X4 Deneb 45nm will feature 6 MB of L3 cache apart from the usual 512 KB L2 caches dedicated to the cores.
Source:
ITOCP
AMD Deneb is the code-name for the 45nm quad-core CPU which AMD plans to release soon. Chinese website ITOCP got their hands on two engineering samples. They used these samples at various clock-speeds set by altering the FSB multiplier and Vcore voltage. These chips were then subjected to rounds of Super Pi 1M benchmark. The results look rather luke-warm compared to what we saw of the Intel Bloomfield chips recently. The Deneb CPUs were supported by an AMD RD790 motherboard and 2 GB of DDR2 800 MHz unganged memory, running at timings of 5-5-5-18. The Phenom X4 Deneb 45nm will feature 6 MB of L3 cache apart from the usual 512 KB L2 caches dedicated to the cores.


164 Comments on Pre-release Tests Conducted on AMD Denreb
In my case I have AGP and Phenom, but Nvidia's Gart driver is compatible with single and dual cores only, when 3 or 4 cores are present, my AGP card turns to PCI mode and I loose half the performance. Don't think it happens on the 865
K
1994 Socket 5 comes out
1995 Socket 7 Replaces Socket 5 Both AMD and Intel Adopt
1997 Slot 1 comes out for Pentium II because of L2 Issues AMD stays Socket7
1998 Socket 370 Arrives for Celeron Later adopted for P3 in 1999 move by intel to cut costs
1999 SlotA arrives for AMD allows L2 Caches on CPU at reasonable cost
2000 Socket A arrives because of advancements to allow onboard L2 Saves Costs
2000 Socket 423 Arrives to support P4 because of new Bus design
2001 Socket 478 arrives becuase of data restrictions on 423
2003 Socket 754 and 940 arrive bring 64bit Support
2003 Socket 775 Arrives brings about high data width and dual cores
2004 Socket 939 Arrives to bring a 128bit mem controller
2006 Socket AM2 Arrives to bring DDR2 support for AM2
Now honestly granted SocketA was in use for a long time, can your SDR KT133 board run an Athlon XP3200? No it can not, you had to upgrade because of chipset limitations, same with K6-2 400 and up, you need a new Super7 board to run them at clock speed force upgrade but for a good reason. Later we get 754 and 940, 940 is for workstations 754 is for Desktops, but no dual channel, so a year later they update it for dual channel and 2 years later update it again for DDR2, which i know we want to bitch but honestly how many issues would there have been if we had gone 939 DDR2 and users bought DDR2 Ram instead of DDR and amd would have gotten alot of flack for it, smart move by them. In 2007 it got an update to AM2+ to better support quads with HT3.0 makes sense to me.
Now to Intel ok. Slot1 was release because at the time onboard L2 was not economical but motherboard L2 @ 66mhz was showing its age this was a move to give us preformace, the move to 370 was because L2 could now go ondie and it saved us money. 423 was so we could have quad pumped bus, and 478 was a fix for a defective design that didnt offer enough pins for the P4's bandwith. 775 was planned again at first to replace 478 and force us, but i belive intel though about it and new they would make a PentiumD.
You do not buy a motherboard in hopes its good next year you buy it to use what you want today. Sockets will always go obsolete as tech advances and even the long standing sockets are not uber as we think look what i said about Socket7 or socket A for that proof
If you're talking about faster speed grades, AMD can't allocate resources to obsolete tech with only one fab running.