- Joined
- Oct 9, 2007
- Messages
- 47,300 (7.53/day)
- Location
- Hyderabad, India
| System Name | RBMK-1000 |
|---|---|
| Processor | AMD Ryzen 7 5700G |
| Motherboard | ASUS ROG Strix B450-E Gaming |
| Cooling | DeepCool Gammax L240 V2 |
| Memory | 2x 8GB G.Skill Sniper X |
| Video Card(s) | Palit GeForce RTX 2080 SUPER GameRock |
| Storage | Western Digital Black NVMe 512GB |
| Display(s) | BenQ 1440p 60 Hz 27-inch |
| Case | Corsair Carbide 100R |
| Audio Device(s) | ASUS SupremeFX S1220A |
| Power Supply | Cooler Master MWE Gold 650W |
| Mouse | ASUS ROG Strix Impact |
| Keyboard | Gamdias Hermes E2 |
| Software | Windows 11 Pro |
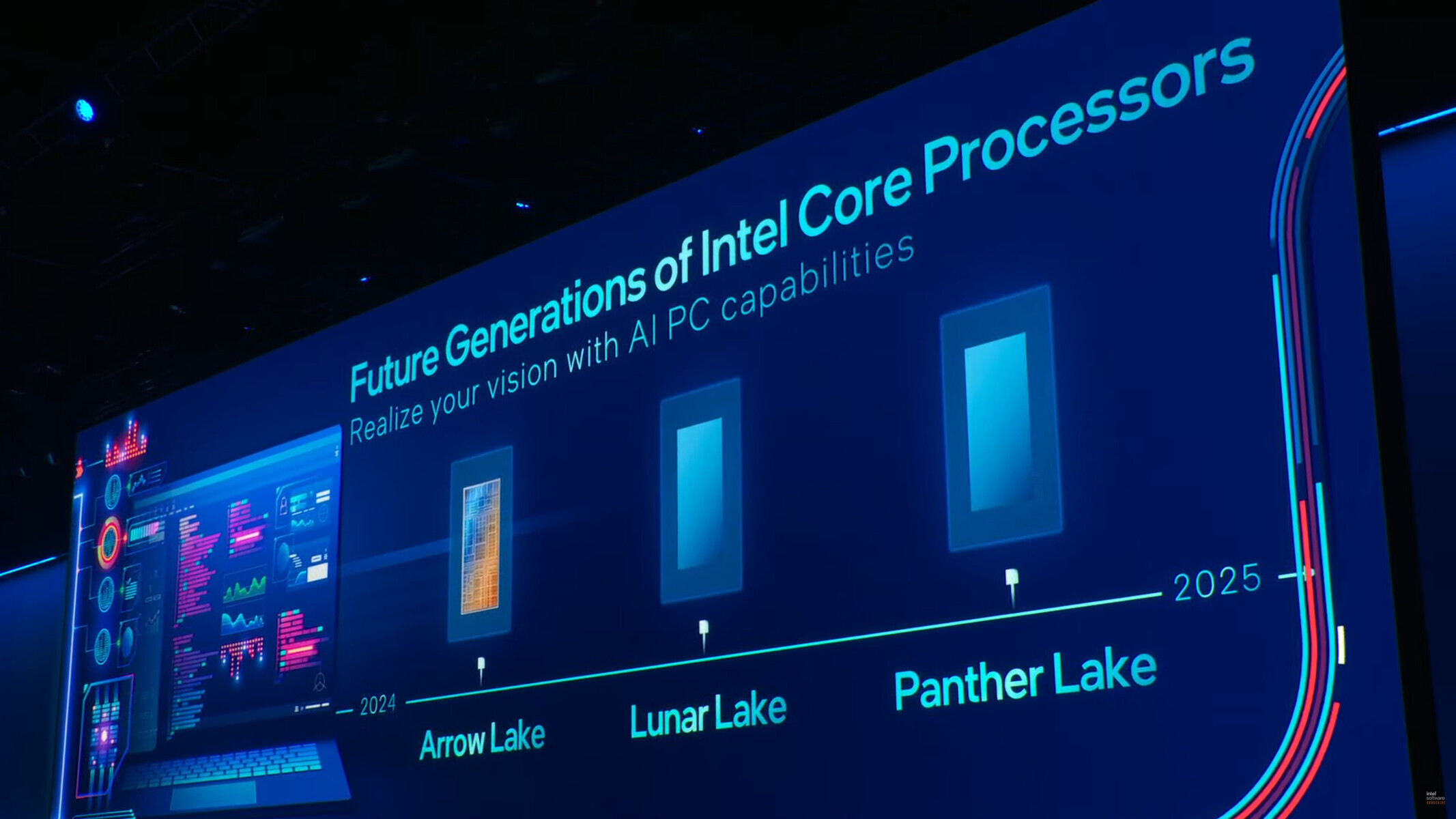
Last week at the Intel Foundry Services Connect event, Intel unveiled its Intel 14A foundry node (1.4 nm-class), to succeed its Intel 18A and Intel 20A nodes, with mass production on this node expected to commence in 2026. It turns out that there is an even more advanced node Intel is working on, which it didn't announce last week, but which was part of an NDA presentation that the company forgot to lift. We're talking about the new Intel 10A node, a 1 nm-class silicon fabrication node that's a generation ahead of Intel 20A. The company says that it expects mass production on the node to begin toward the end of 2027. It is on the backs of these sub-2 nm class nodes, and the impending organizational changes that sees Intel Foundry Services become a more independent commercial entity, that Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger thinks that Intel will become the "TSMC of the West."
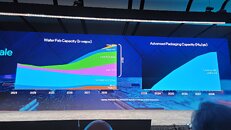
Currently, fabs that utilize EUV (extreme ultraviolet) lithography, namely the Intel 4, Intel 3, and Intel 20A; together make barely 15% of Intel's wafer volumes, with the bulk of the foundry's production focusing on the DUV based Intel 7. EUV-based nodes are expected to linearly grow till 2025, but what's interesting is that Intel doesn't see the kind of multi-year stagnation on Intel 4 and Intel 3 that it's currently experiencing with Intel 7; with wafer volumes of Intel 20A and 18A expected to exceed those of the Intel 4 and Intel 3 within 2025. By 2026, Intel expects that there will be twice as many Intel 20A/18A wafers pushed as Intel 4 and Intel 3. Although they use EUV, Intel 4 and Intel 3 are Intel's final nodes to implement FinFET transistors, as the company transitions to nanosheets with Intel 20A (which are called RibbonFETs in Intel jargon). Intel did not get into the technology behind Intel 10A. The company, along with Samsung and TSMC, demonstrated its stacked CFET transistor in 2023, which will power foundry nodes as nanosheets mature. Intel in its presentation also talked about the next wave of factory automation implemented by IFS, which sees AI-driven "cobots" (collaborative robots) replace humans for more roles in the clean room.


View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source
Currently, fabs that utilize EUV (extreme ultraviolet) lithography, namely the Intel 4, Intel 3, and Intel 20A; together make barely 15% of Intel's wafer volumes, with the bulk of the foundry's production focusing on the DUV based Intel 7. EUV-based nodes are expected to linearly grow till 2025, but what's interesting is that Intel doesn't see the kind of multi-year stagnation on Intel 4 and Intel 3 that it's currently experiencing with Intel 7; with wafer volumes of Intel 20A and 18A expected to exceed those of the Intel 4 and Intel 3 within 2025. By 2026, Intel expects that there will be twice as many Intel 20A/18A wafers pushed as Intel 4 and Intel 3. Although they use EUV, Intel 4 and Intel 3 are Intel's final nodes to implement FinFET transistors, as the company transitions to nanosheets with Intel 20A (which are called RibbonFETs in Intel jargon). Intel did not get into the technology behind Intel 10A. The company, along with Samsung and TSMC, demonstrated its stacked CFET transistor in 2023, which will power foundry nodes as nanosheets mature. Intel in its presentation also talked about the next wave of factory automation implemented by IFS, which sees AI-driven "cobots" (collaborative robots) replace humans for more roles in the clean room.



View at TechPowerUp Main Site | Source