Intel "Arrow Lake-S" Engineering Sample Posts Over 25% 1T Perf Gain Over i9-13900K, Falls Behind in nT
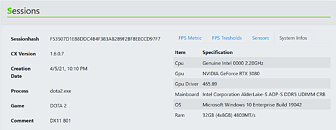
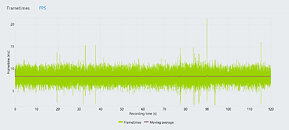
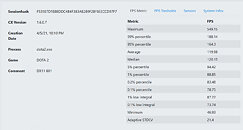
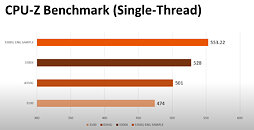
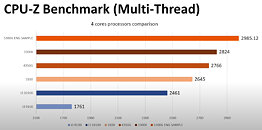
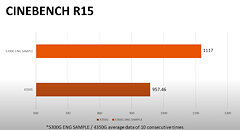
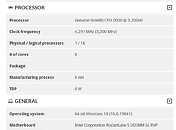
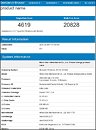
An unnamed Intel Core Ultra "Arrow Lake-S" desktop processor engineering sample (ES) made it to the hands of someone willing to post its CPU-Z Bench screenshot. The processor allegedly scores a whopping 1143.2 points in the CPU-Bench single-thread benchmark; and 12922.4 points in the multithreaded benchmark. When compared with the internal Intel Core i9-13900K reference scores of CPU-Z, the single-thread benchmark score is a staggering 26.71% increase over that of the i9-13900K (902 points); while the multithreaded score is 22% lower.
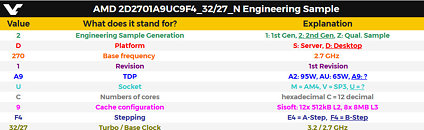
Since we don't know which processor model this "Arrow Lake-S" ES is, we have no way of telling if it is the top SKU with its rumored 8P+16E core configuration, or a mid-tier Core i5 SKU with the expected 6P+8E configuration. The single-threaded test only loads one P-core, and here the IPC of one of the chip's "Lion Cove" P-cores is able to trounce one of the "Raptor Cove" P-cores of the i9-13900K reference score. You also have to understand that the Hyper-Threading plays no role in this thread. Where it could play a role is the multithreaded test. "Lion Cove" lacks HTT support unlike "Raptor Cove," and the i9-13900K is a 24-core/32-thread processor. It's important to note here, that "Arrow Lake" doesn't just have up to 8 "Lion Cove" P-cores, but also up to 16 "Skymont" E-cores that Intel claims to have achieved a massive IPC gain over its predecessor, bringing its IPC in the league of past-generation P-cores such as the "Raptor Cove" or "Golden Cove."
Since we don't know which processor model this "Arrow Lake-S" ES is, we have no way of telling if it is the top SKU with its rumored 8P+16E core configuration, or a mid-tier Core i5 SKU with the expected 6P+8E configuration. The single-threaded test only loads one P-core, and here the IPC of one of the chip's "Lion Cove" P-cores is able to trounce one of the "Raptor Cove" P-cores of the i9-13900K reference score. You also have to understand that the Hyper-Threading plays no role in this thread. Where it could play a role is the multithreaded test. "Lion Cove" lacks HTT support unlike "Raptor Cove," and the i9-13900K is a 24-core/32-thread processor. It's important to note here, that "Arrow Lake" doesn't just have up to 8 "Lion Cove" P-cores, but also up to 16 "Skymont" E-cores that Intel claims to have achieved a massive IPC gain over its predecessor, bringing its IPC in the league of past-generation P-cores such as the "Raptor Cove" or "Golden Cove."