Intel Haswell and Broadwell Silicon Variants Detailed
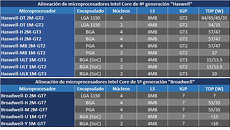
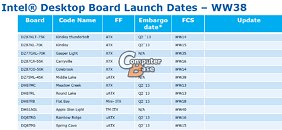
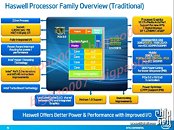
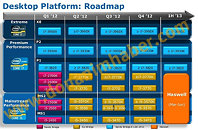
It's no secret that nearly all Intel Core processors are carved out of essentially one or two physical dies, be it the "2M" die that physically features four cores and 8 MB of L3 cache, or the "1M" die, which physically features two cores and 4 MB of L3 cache. The two silicons are further graded for energy-efficiency and performance before being assigned a package most suited to them: desktop LGA, mobile PGA, mobile BGA, and with the introduction of the 4th generation Core "Haswell," SoC (system on chip, a package that's going to be a multi-chip module of the CPU and PCH dies). The SoC package will be designed to conserve PCB real-estate, and will be suited for extremely size-sensitive devices such as Ultrabooks.
The third kind of grading for the two silicons relates to its on-die graphics processor, which makes up over a third of the die area. Depending on the number of programmable shaders and ROPs unlocked, there are two grades: GT2, and GT3, with GT3 being the most powerful. On the desktop front (identified by silicon extension "-DT,") Intel very much will retain dual-core processors, which will make up its Core i3, Pentium, and Celeron processor lines. It will be lead by quad-core parts. All desktop processors feature the GT2 graphics core.
The third kind of grading for the two silicons relates to its on-die graphics processor, which makes up over a third of the die area. Depending on the number of programmable shaders and ROPs unlocked, there are two grades: GT2, and GT3, with GT3 being the most powerful. On the desktop front (identified by silicon extension "-DT,") Intel very much will retain dual-core processors, which will make up its Core i3, Pentium, and Celeron processor lines. It will be lead by quad-core parts. All desktop processors feature the GT2 graphics core.