Windows 11 24H2 Instruction Requirement Affects Older/Incompatible CPUs
Systems running on older hardware could be excluded from upcoming public versions of Windows 11—the recently released preview/insider build (26052) has introduced all sorts of new features including "Sudo for Windows", an improved regedit, and hidden beneath the surface, an AI-flavored Super Resolution settings menu. Early partakers of version 24H2 are running into instruction set-related problems—Windows operating expert, Bob Pony, was one of the unlucky candidates. Microsoft's preview code seems to require a specific instruction set to reach operational status—Pony documented his frustrations on social media: "Using the command line argument "/product server" for setup.exe, BYPASSES the system requirement checks for the Windows 11 24H2 setup program. But unfortunately, after setup completes then reboots into the next stage. It'll be indefinitely stuck on the Windows logo boot screen."
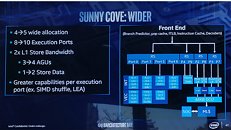
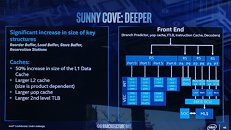
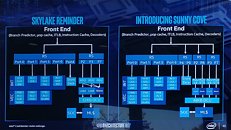
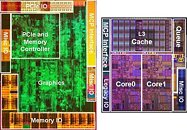
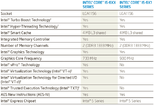
He continued to narrow in on the source of blame: "Windows 11 Version 24H2 Build 26058's setup (if ran in a live Windows Install) now checks for a CPU instruction: PopCnt." The Register provided some history/context on the SSE4 set: "POPCNT/PopCnt counts the number of bits in a machine word that have been set (or different from zero.) You might see it in cryptography and it has been lurking in CPU architectures for years, pre-dating Intel and AMD's implementation by decades." It is believed that Microsoft has deployed PopCnt as part of its push into AI-augmented software features, although a segment of online discussion proposes that an engineer has "accidentally enabled" newer CPU instruction sets. Tom's Hardware marked a line in the sand: "PopCnt has been supported since the Intel Nehalem and AMD Phenom II (microarchitecture) era—14 years ago—so compatibility won't be an issue for any modern systems. The only users that will be affected are enthusiasts running modified versions of Windows 11 on 15+ year-old chips like Core 2 Duos or Athlon 64." Bob Pony's long-serving Core 2 Quad Q9650 processor—a late summer 2008 product—was deemed unworthy by the preview build's setup process.
He continued to narrow in on the source of blame: "Windows 11 Version 24H2 Build 26058's setup (if ran in a live Windows Install) now checks for a CPU instruction: PopCnt." The Register provided some history/context on the SSE4 set: "POPCNT/PopCnt counts the number of bits in a machine word that have been set (or different from zero.) You might see it in cryptography and it has been lurking in CPU architectures for years, pre-dating Intel and AMD's implementation by decades." It is believed that Microsoft has deployed PopCnt as part of its push into AI-augmented software features, although a segment of online discussion proposes that an engineer has "accidentally enabled" newer CPU instruction sets. Tom's Hardware marked a line in the sand: "PopCnt has been supported since the Intel Nehalem and AMD Phenom II (microarchitecture) era—14 years ago—so compatibility won't be an issue for any modern systems. The only users that will be affected are enthusiasts running modified versions of Windows 11 on 15+ year-old chips like Core 2 Duos or Athlon 64." Bob Pony's long-serving Core 2 Quad Q9650 processor—a late summer 2008 product—was deemed unworthy by the preview build's setup process.