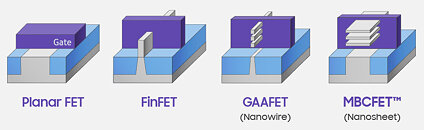
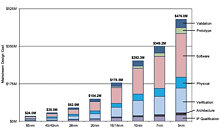
Intel Has Fixed its 7 nm Node, But Outsourcing is Still Going to Happen
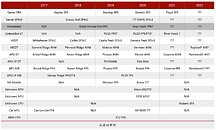
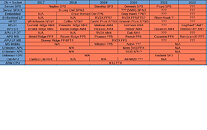
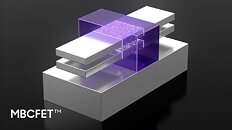
Intel has today reported its Q4 2020 earnings disclosing full-year revenue with the current CEO Bob Swan, upcoming new CEO Pat Gelsinger, and Omar Ishrak, Chairman of Intel's board. During the call, company officials have talked about Intel's earnings and most importantly, addressing the current problems about the company's manufacturing part - semiconductor foundries. Incoming Intel CEO, Pat Gelsinger, has talked about the state of the 7 nm node, giving shareholders reassurance and a will to remain in such a position. He has made an argument that he has personally reviewed the progress of the "health and recovery of the 7 nm program."
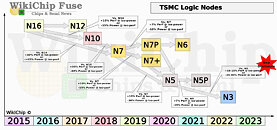
The 7 nm node has been originally delayed by a full year amid the expectations, and as with the 10 nm node, we have believed that it is going to experience similar issues. However, the incoming CEO has reassured everyone that it is very much improving. The new 7 nm node is on track for 2023 delivery, when Intel is expected to compete with the 3 nm node of TSMC. Firstly, Intel will make a debut of the 7 nm node with client processors scheduled for 1H 2023 arrival, with data center models following that. The company leads have confirmed that Intel will stay true to its internal manufacturing, but have stressed that there will still be a need for some outsourcing to happen.
The 7 nm node has been originally delayed by a full year amid the expectations, and as with the 10 nm node, we have believed that it is going to experience similar issues. However, the incoming CEO has reassured everyone that it is very much improving. The new 7 nm node is on track for 2023 delivery, when Intel is expected to compete with the 3 nm node of TSMC. Firstly, Intel will make a debut of the 7 nm node with client processors scheduled for 1H 2023 arrival, with data center models following that. The company leads have confirmed that Intel will stay true to its internal manufacturing, but have stressed that there will still be a need for some outsourcing to happen.