AMD Confirms: Ryzen 9 3950X and Threadripper 3rd Generation Coming in November
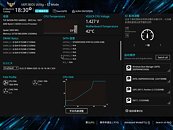
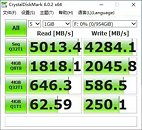
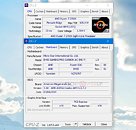
AMD just released an update on their upcoming processor launches this year. First revealed at E3, just a few months ago, the Ryzen 9 3950X is the world's first processor to bring 16-cores and 32-threads to the consumer desktop space. The processor's boost clock is rated at "up to 4.7 GHz", which we might now actually see, thanks to an updated AGESA software that AMD released earlier this month. Base clock for this $749 processor is set at 3.5 GHz, and TDP is 105 W, with 72 MB cache. While AMD said "September" for Ryzen 9 3950X back at E3, it looks like the date got pushed back a little bit, to November, which really makes no difference, in the grand scheme of things.
The second big part of today's announcement is that AMD is indeed working on "Rome"-based third generation Threadripper processors (probably the industry's worst-kept secret), and that these CPUs will also be launching in November, right in time to preempt Intel from having any success with their upcoming Cascade Lake-X processors. Official information on AMD's new HEDT lineup is extremely sparse so far, but if we go by recent leaks, then we should expect new chipsets and up to 32-cores/64-threads.AMD's full statement is quoted below.
The second big part of today's announcement is that AMD is indeed working on "Rome"-based third generation Threadripper processors (probably the industry's worst-kept secret), and that these CPUs will also be launching in November, right in time to preempt Intel from having any success with their upcoming Cascade Lake-X processors. Official information on AMD's new HEDT lineup is extremely sparse so far, but if we go by recent leaks, then we should expect new chipsets and up to 32-cores/64-threads.AMD's full statement is quoted below.