Intel Readies 4K-ready NUC NUC5i7RYH Desktop
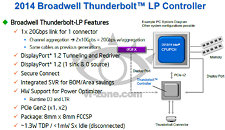
With 4K-ready media center PCs upon us, Intel decided to equip one of its next-gen NUC (next unit of computing) desktops with one of its most powerful integrated graphics solutions, which can either accelerate 4K video, 1080p to 4K upscaling GPU algorithms (think MadVR), or make for a reasonably fast 720p or 900p gaming machine. The NUC5i7RYH from Intel features a Core i5-5557U processor, which integrates Iris 6100 Graphics. Based on the "Broadwell-GT3" silicon, Iris 6100 offers 48 execution units, between 300 and 1100 MHz GPU core frequency, and an L4 eDRAM cache. A passive cooling solution deals with this 28W TDP chip. Other specs include two DDR3-1866 SO-DIMM slots, supporting up to 16 GB of memory, HDMI 1.4a and DisplayPort 1.2 display-outputs, four USB 3.0 ports, including one high-current port.