Intel 10th Generation Comet Lake Desktop Processors and 400-Series Chipsets Announced, Here's what's New
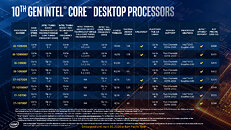
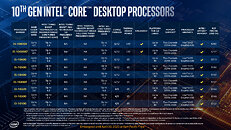
Intel today launched its 10th generation Core desktop processor family and its companion Intel 400-series chipsets. Based on the 14 nm++ silicon fabrication process and built in the new LGA1200 package, the processors are based on the "Comet Lake" microarchitecture. The core design of "Comet Lake" and its IPC are identical to those of "Skylake," however Intel brought significant enhancements to the processor's clock-speed boosting algorithm, increased core- or thread counts across the board, and introduced new features that could interest enthusiasts and overclockers. The uncore component remains largely unchanged from the previous-generation, with support for DDR4 memory and PCI-Express gen 3.0. Use of these processors requires a new socket LGA1200 motherboard, they won't work on older LGA1151 motherboards. You can install any LGA115x-compatible cooler on LGA1200, provided it meets the thermal requirements of the processor you're using.
At the heart of the 10th generation Core processor family is a new 10-core monolithic processor die, which retains the same basic structure as the previous-generation 8-core "Coffee Lake Refresh" die, and 4-core "Skylake." The cores are arranged in two rows, sandwiched by the processor's uncore and iGPU blocks. A ring-bus interconnect binds the various components. The cache hierarchy is unchanged from previous generations as well, with 32 KB each of L1I and L1D caches; 256 KB of dedicated L2 cache per core, and 20 MB of shared L3 cache. The iGPU is the same Gen 9.5 based UHD 630 graphics. As we mentioned earlier, much of Intel's innovation for the 10th generation is with the processor's microcode (boosting algorithms).
At the heart of the 10th generation Core processor family is a new 10-core monolithic processor die, which retains the same basic structure as the previous-generation 8-core "Coffee Lake Refresh" die, and 4-core "Skylake." The cores are arranged in two rows, sandwiched by the processor's uncore and iGPU blocks. A ring-bus interconnect binds the various components. The cache hierarchy is unchanged from previous generations as well, with 32 KB each of L1I and L1D caches; 256 KB of dedicated L2 cache per core, and 20 MB of shared L3 cache. The iGPU is the same Gen 9.5 based UHD 630 graphics. As we mentioned earlier, much of Intel's innovation for the 10th generation is with the processor's microcode (boosting algorithms).