Mar 29th, 2025 21:05 EDT
change timezone
Latest GPU Drivers
New Forum Posts
- Display panel recommendation for low brightness and BFEP (1)
- RX580 BIOS PROBLEM (8)
- i5 14600K or i7 14700K? (8)
- Upgrade from a AMD AM3+ to AM4 or AM5 chipset MB running W10? (51)
- Is the futureproof gaming solution a four drive system? (8)
- RTX 5090 very slow while rendering or video/photo editing. (6)
- GPU Crashing System From Hibernation (8)
- Can you guess Which game it is? (15)
- Dell Workstation Owners Club (3315)
- What are you playing? (23312)
Popular Reviews
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Pulse Review
- ASRock Phantom Gaming B850 Riptide Wi-Fi Review - Amazing Price/Performance
- Samsung 9100 Pro 2 TB Review - The Best Gen 5 SSD
- Assassin's Creed Shadows Performance Benchmark Review - 30 GPUs Compared
- Palit GeForce RTX 5070 GamingPro OC Review
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Nitro+ Review - Beating NVIDIA
- ASRock Radeon RX 9070 XT Taichi OC Review - Excellent Cooling
- Enermax REVOLUTION D.F. 12 850 W Review
- AMD Ryzen 7 9800X3D Review - The Best Gaming Processor
- ASRock Phantom Gaming B860I Lightning Wi-Fi Review
Controversial News Posts
- AMD RDNA 4 and Radeon RX 9070 Series Unveiled: $549 & $599 (260)
- MSI Doesn't Plan Radeon RX 9000 Series GPUs, Skips AMD RDNA 4 Generation Entirely (142)
- Microsoft Introduces Copilot for Gaming (124)
- AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT Reportedly Outperforms RTX 5080 Through Undervolting (119)
- NVIDIA Reportedly Prepares GeForce RTX 5060 and RTX 5060 Ti Unveil Tomorrow (115)
- Over 200,000 Sold Radeon RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT GPUs? AMD Says No Number was Given (100)
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5050, RTX 5060, and RTX 5060 Ti Specifications Leak (96)
- Retailers Anticipate Increased Radeon RX 9070 Series Prices, After Initial Shipments of "MSRP" Models (90)
News Posts matching #Golden Cove
Return to Keyword Browsing
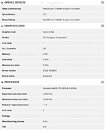
Intel Alder Lake-S Processor with 16c/32t (Hybrid) Spotted on SANDRA Database
Intel's upcoming Core "Alder Lake-S" desktop processor, which is shaping up to be the first Hybrid desktop processor, surfaced on the SiSoft SANDRA benchmark database, as dug up by TUM_APISAK. The chip is reported by SANDRA to be 16-core/32-thread, although this is expected to be a combination of eight "big" high-performance cores, and eight "small" high-efficiency cores, in a multi-core topology similar to Arm big.LITTLE. Other specs read by SANDRA include clock speeds around "1.40 GHz," ten 1.25 MB L2 caches (possibly 8x 1.25 MB for the big "Golden Cove" cores, 2x 1.25 MB for the two groups of small "Gracemont" cores), and 30 MB of L3 cache. The Hybrid processor architecture is expected to introduce several platform-level innovations to the modern desktop, taking advantage of the extremely low power draw of the "Gracemont" cores when the machine isn't grinding serious workloads.

Coreboot Code Hints at Intel "Alder Lake" Core Configurations
Intel's 12th Gen Core EVO "Alder Lake" processors in the LGA1700 package could introduce the company's hybrid core technology to the desktop platform. Coreboot code leaked to the web by Coelacanth's Dream sheds fascinating insights to the way Intel is segmenting these chips. The 10 nm chip will see Intel combine high-performance "Golden Cove" CPU cores with energy-efficient "Gracemont" CPU cores, and up to three tiers of the company's Gen12 Xe integrated graphics. The "Alder Lake" desktop processor has up to eight big cores, up to eight small ones, and up to three tiers of the iGPU (GT0 being disabled iGPU, GT1 being the lower tier, and GT2 being the higher tier).
Segmentation between the various brand extensions appears to be primarily determined by the number of big cores. The topmost SKU has all 8 big and 8 small cores enabled, along with GT1 (lower) tier of the iGPU (possibly to free up power headroom for those many cores). The slightly lower SKU has 8 big cores, 6 small cores, and GT1 graphics. Next up, is 8 big cores, 4 small cores, and GT1 graphics. Then 8+2+GT1, and lastly, 8+0+GT1. The next brand extension is based around 6 big cores, being led by 6+8+GT2, and progressively lower number of small cores and their various iGPU tiers. The lower brand extension is based around 4 big cores with similar segmentation of small cores, and the entry-level parts have 2 big cores, and up to 8 small cores.
Segmentation between the various brand extensions appears to be primarily determined by the number of big cores. The topmost SKU has all 8 big and 8 small cores enabled, along with GT1 (lower) tier of the iGPU (possibly to free up power headroom for those many cores). The slightly lower SKU has 8 big cores, 6 small cores, and GT1 graphics. Next up, is 8 big cores, 4 small cores, and GT1 graphics. Then 8+2+GT1, and lastly, 8+0+GT1. The next brand extension is based around 6 big cores, being led by 6+8+GT2, and progressively lower number of small cores and their various iGPU tiers. The lower brand extension is based around 4 big cores with similar segmentation of small cores, and the entry-level parts have 2 big cores, and up to 8 small cores.

Intel 8-core "Tiger Lake-H" Coming in 2021: Leaked Compal Document
Intel is preparing to launch an 8-core mobile processor based on its 10 nm "Tiger Lake" microarchitecture, according to a corporate memo by leading notebook OEM Compal, which serves major notebook brands such as Acer. The memo was drafted in May, but unearthed by momomo_us. Compal expects Intel to launch the 8-core "Tiger Lake-H" processor in Q1 2021. This is big, as it would be the first large 10 nm client-segment silicon that goes beyond 4 cores. The company's first 10 nm client silicon, "Ice Lake," as well as the "Tiger Lake-U" silicon that's right around the corner, feature up to 4 cores. As an H-segment part, the new 8-core processor could target TDPs in the range of 35-45 W, and notebooks in the "conventional thickness" form-factor, as well as premium gaming notebooks and mobile workstations.
The 8-core "Tiger Lake-H" silicon is the first real sign of Intel's 10 nm yields improving. Up until now, Intel confined 10 nm to the U- and Y-segments (15 W and below), addressing only ultra-portable form-factors. Even here, Intel launched U-segment 14 nm "Comet Lake" parts at competitive prices, to take the market demand off "Ice Lake-U." The H-segment has been exclusively held by "Comet Lake-H." Intel is planning to launch "Ice Lake-SP" Xeon processors later this year, but like all server parts, these are high-margin + low-volume parts. Compal says Intel will refresh the H-segment with a newer 8-core "Comet Lake-H" part in the second half of 2020, possibly to bolster the high-end against the likes of AMD's Ryzen 9 4900H. Later in 2021, Intel is expected to introduce its 10 nm "Alder Lake" processor, including a mobile variant. These processors will feature Hybrid technology, combining "Golden Cove" big CPU cores with "Gracemont" small ones.
The 8-core "Tiger Lake-H" silicon is the first real sign of Intel's 10 nm yields improving. Up until now, Intel confined 10 nm to the U- and Y-segments (15 W and below), addressing only ultra-portable form-factors. Even here, Intel launched U-segment 14 nm "Comet Lake" parts at competitive prices, to take the market demand off "Ice Lake-U." The H-segment has been exclusively held by "Comet Lake-H." Intel is planning to launch "Ice Lake-SP" Xeon processors later this year, but like all server parts, these are high-margin + low-volume parts. Compal says Intel will refresh the H-segment with a newer 8-core "Comet Lake-H" part in the second half of 2020, possibly to bolster the high-end against the likes of AMD's Ryzen 9 4900H. Later in 2021, Intel is expected to introduce its 10 nm "Alder Lake" processor, including a mobile variant. These processors will feature Hybrid technology, combining "Golden Cove" big CPU cores with "Gracemont" small ones.

Intel Ice Lake-SP Processors Get Benchmarked Against AMD EPYC Rome
Intel is preparing to launch its next-generation for server processors and the next in line is the Ice Lake-SP 10 nm CPU. Featuring a Golden Cove CPU and up to 28 cores, the CPU is set to bring big improvements over the past generation of server products called Cascade Lake. Today, thanks to the sharp eye of TUM_APISAK, we have a new benchmark of the Ice Lake-SP platform, which is compared to AMD's EPYC Rome offerings. In the latest GeekBench 4 score, appeared an engineering sample of unknown Ice Lake-SP model with 28 cores, 56 threads, a base frequency of 1.5 GHz, and a boost of 3.19 GHz.
This model was put in a dual-socket configuration that ends up at a total of 56 core and 112 threads, against a single 64 core AMD EPYC 7442 Rome CPU. The dual-socket Intel configuration scored 3424 points in the single-threaded test, where AMD configuration scored notably higher 4398 points. The lower score on Intel's part is possibly due to lower clocks, which should improve in the final product, as this is only an engineering sample. When it comes to the multi-threaded test, Intel configuration scored 38079 points, where the AMD EPYC system did worse and scored 35492 points. The reason for this higher result is unknown, however, it shows that Ice Lake-SP has some potential.
This model was put in a dual-socket configuration that ends up at a total of 56 core and 112 threads, against a single 64 core AMD EPYC 7442 Rome CPU. The dual-socket Intel configuration scored 3424 points in the single-threaded test, where AMD configuration scored notably higher 4398 points. The lower score on Intel's part is possibly due to lower clocks, which should improve in the final product, as this is only an engineering sample. When it comes to the multi-threaded test, Intel configuration scored 38079 points, where the AMD EPYC system did worse and scored 35492 points. The reason for this higher result is unknown, however, it shows that Ice Lake-SP has some potential.

Intel Linux Patch Confirms "Alder Lake" is a Hybrid Core Processor
A Linux kernel patch contributed and signed off by Intel confirms that its upcoming Core "Alder Lake" processor will feature a hybrid core topology, much like Core Hybrid "Lakefield." The patch references "Lakefield" and "Alder Lake" under "Hybrid Core/Atom Processors." The patch possibly gives the Linux kernel awareness of the hybrid core topology, so it can schedule its work between the two types of cores on the silicon accordingly, and avoid rotating between the two core groups. Under the Android project, Linux has been aware of a similar tech from Arm since 2013.
Analogous with Arm big.LITTLE, the Intel Hybrid Core technology involves two kinds of CPU cores on a processor die, the first kind being "high performance," and the second being "low power." On "Lakefield," Intel deployed one "Sunny Cove" high performance core, and four "Tremont" low power cores. The low power cores keep the machine ticking through the vast majority of time when processing workloads requiring the high performance cores aren't present. With "Alder Lake," Intel is expected to scale up this concept, with the silicon rumored to feature eight "Golden Cove" high performance cores, and eight "Gracemont" low power ones. The chip is also expected to feature a Gen12 Xe iGPU.
Analogous with Arm big.LITTLE, the Intel Hybrid Core technology involves two kinds of CPU cores on a processor die, the first kind being "high performance," and the second being "low power." On "Lakefield," Intel deployed one "Sunny Cove" high performance core, and four "Tremont" low power cores. The low power cores keep the machine ticking through the vast majority of time when processing workloads requiring the high performance cores aren't present. With "Alder Lake," Intel is expected to scale up this concept, with the silicon rumored to feature eight "Golden Cove" high performance cores, and eight "Gracemont" low power ones. The chip is also expected to feature a Gen12 Xe iGPU.

Intel "Alder Lake" CPU Core Segmentation Sketched
Intel's 12th Gen Core "Alder Lake-S" desktop processors in the LGA1700 package could see the desktop debut of Intel's Hybrid Technology that it introduced with the mobile segment "Lakefield" processor. Analogous to Arm big.LITTLE, Intel Hybrid Technology is a multi-core processor topology that sees the combination of high-performance CPU cores with smaller high-efficiency cores that keep the PC ticking through the vast majority of the time/tasks when the high-performance cores aren't needed and hence power-gated. The high-performance cores are woken up only as needed. "Lakefield" combines one "Sunny Cove" high-performance core with four "Tremont" low-power cores. "Alder Lake-S" will take this concept further.
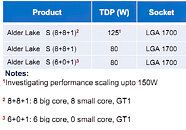
According to Intel slides leaked to the web by HXL (aka @9550pro), the 10 nm-class "Alder Lake-S" silicon will physically feature 8 "Golden Cove" high-performance cores, and 8 "Gracemont" low-power cores, along with a Gen12 iGPU that comes in three tiers - GT0 (iGPU disabled), GT1 (some execution units disabled), and GT2 (all execution units enabled). In its top trim with 125 W TDP, "Alder Lake-S" will be a "16-core" processor with 8 each of "Golden Cove" and "Gracemont" cores enabled. There will be 80 W TDP models with the same 8+8 core configuration, which are probably "locked" parts. Lastly, there the lower wrungs of the product stack will completely lack "small" cores, and be 6+0, with only high-performance cores. A recurring theme with all parts is the GT1 trim of the Gen12 iGPU.
According to Intel slides leaked to the web by HXL (aka @9550pro), the 10 nm-class "Alder Lake-S" silicon will physically feature 8 "Golden Cove" high-performance cores, and 8 "Gracemont" low-power cores, along with a Gen12 iGPU that comes in three tiers - GT0 (iGPU disabled), GT1 (some execution units disabled), and GT2 (all execution units enabled). In its top trim with 125 W TDP, "Alder Lake-S" will be a "16-core" processor with 8 each of "Golden Cove" and "Gracemont" cores enabled. There will be 80 W TDP models with the same 8+8 core configuration, which are probably "locked" parts. Lastly, there the lower wrungs of the product stack will completely lack "small" cores, and be 6+0, with only high-performance cores. A recurring theme with all parts is the GT1 trim of the Gen12 iGPU.

Intel "Alder Lake-S" Confirmed to Introduce LGA1700 Socket, Technical Docs Out for Partners
Intel's Core "Alder Lake-S" desktop processor, which succeeds the 11th generation "Rocket Lake-S," is confirmed to introduce a new CPU socket, LGA1700. This new socket has been churning in the rumor mill since 2019. The LGA1700 socket is Intel's biggest mainstream desktop processor package change since LGA1156, in that the package is now physically larger, and may be cooler-incompatible with LGA115x sockets (Intel H# sockets). The enlargement in package size is seen as an attempt by Intel to give itself real-estate to build future multi-chip modules; while the increased pin-count points to the likelihood of more I/O centralization to the processor package.
The "Alder Lake-S" silicon is rumored to be Intel's first 10 nm-class mainstream desktop processor, combining a hybrid core setup of a number of "Golden Cove" high-performance CPU cores, and a number of "Gracemont" low-power cores. The processor's I/O feature-set is expected to include dual-channel DDR5 memory, PCI-Express gen 4.0, and possibly preparation for gen 5.0 on the motherboard-side. In related news, Intel put out technical documentation for the "Alder Lake-S" microarchitecture and LGA1700 socket. Access however, is restricted to Intel's industrial partners. The company also put out documentation for "Rocket Lake-S."
The "Alder Lake-S" silicon is rumored to be Intel's first 10 nm-class mainstream desktop processor, combining a hybrid core setup of a number of "Golden Cove" high-performance CPU cores, and a number of "Gracemont" low-power cores. The processor's I/O feature-set is expected to include dual-channel DDR5 memory, PCI-Express gen 4.0, and possibly preparation for gen 5.0 on the motherboard-side. In related news, Intel put out technical documentation for the "Alder Lake-S" microarchitecture and LGA1700 socket. Access however, is restricted to Intel's industrial partners. The company also put out documentation for "Rocket Lake-S."

Intel Tiger Lake Processor Spotted with Boost of 5 GHz
Intel is preparing to launch its next-generation Tiger Lake lineup of processors for the middle of 2020. The processors are based on the new "Willow Cove" CPU core, which supposedly brings even more IPC gains compared to previous "Golden Cove" CPU cores found in Ice Lake processors. The Tiger Lake lineup will use Intel's advanced 10 nm+ manufacturing process. This alone should bring some gains in frequency compared to the 10 nm Ice Lake processor generation, which was spotting a maximum of 4.1 GHz boost frequency on 28 W TDP model named Core i7-1068NG7. This processor is labeled as the highest-performing Ice Lake parts available today and the best 10 nm products available so far from Intel.
Thanks to the popular hardware leaker Rogame, we have evidence that the gains from 10 nm+ manufacturing process are real and that Tiger Lake will show us an amazing boost frequency of 5 GHz. In the benchmark, an unknown OEM laptop was spotted running the benchmark with a Tiger Lake CPU. This CPU is a 4 core, 8 threaded model with a base frequency of 2.3 GHz and a surprising boost frequency of 5 GHz. This information should, of course, be taken with a grain of salt until we get more information about the Tiger Lake lineup and their specifications.
Thanks to the popular hardware leaker Rogame, we have evidence that the gains from 10 nm+ manufacturing process are real and that Tiger Lake will show us an amazing boost frequency of 5 GHz. In the benchmark, an unknown OEM laptop was spotted running the benchmark with a Tiger Lake CPU. This CPU is a 4 core, 8 threaded model with a base frequency of 2.3 GHz and a surprising boost frequency of 5 GHz. This information should, of course, be taken with a grain of salt until we get more information about the Tiger Lake lineup and their specifications.

Intel's next LGA1700 Socket to Last Over Two Generations
The upcoming LGA1700 socket by Intel, which makes its debut with 12th generation Core "Alder Lake-S" desktop processors, could be the first in over a decade from the company, to support more than two processor generations. Intel has maintained streak of ensuring that a mainstream desktop CPU socket won't be compatible with more than two generations of Core processors. Controversy brew when the company artificially segmented the LGA1151 socket between the 6th, 7th, and 8th and 9th processor generations, with the latter two requiring a 300-series chipset motherboard and the former two not working on the newer chipset, even though all four generations are pin-compatible, and modders have been able to get the newer chips to work on older 100-series and 200-series motherboards with great success.
According to a NotebookCheck report, Intel is designing the LGA1700 socket to support at least three future generations of Core processors (that's "Alder Lake-S" and two of its successors). This should give the platform a degree of longevity as it introduces several new computing concepts to the client desktop form-factor, such as heterogenous CPU cores. "Alder Lake-S" combines 8 each of low-power "Gracemont" and high performance "Golden Cove" CPU cores in a setup rivaling the Arm big.LITTLE, where light computing workloads and system idling are completely handled by the low-power cores, while the high-performance cores are only woken up from their power-gated slumber as needed, before being put back to sleep when they're not.
According to a NotebookCheck report, Intel is designing the LGA1700 socket to support at least three future generations of Core processors (that's "Alder Lake-S" and two of its successors). This should give the platform a degree of longevity as it introduces several new computing concepts to the client desktop form-factor, such as heterogenous CPU cores. "Alder Lake-S" combines 8 each of low-power "Gracemont" and high performance "Golden Cove" CPU cores in a setup rivaling the Arm big.LITTLE, where light computing workloads and system idling are completely handled by the low-power cores, while the high-performance cores are only woken up from their power-gated slumber as needed, before being put back to sleep when they're not.

Intel's First 7nm Client Microarchitecture is "Meteor Lake"
Intel's first client-segment processor microarchitecture built on its own 7 nm silicon fabrication process will be codenamed "Meteor Lake." The codename began surfacing in driver files and technical documents, one of which was screengrabbed and leaked to the web by Komachi Ensaka. Not much else is known about it, except that it succeeds the 10 nm++ "Alder Lake," an ambitious attempt by Intel to replicate Arm big.LITTLE heterogenous core technology on the x86 architecture, by combining a number of high-power cores with high-efficiency cores on a single piece of silicon. Intel "Lakefield," headed toward mass-production within this year, is the first such heterogenous core.
Older reports throughout 2019-20 speculate "Meteor Lake" (known at the time only by its name), could come out at a time when Intel monetizes its "Golden Cove" high-performance CPU core. It's quite likely that like "Alder Lake," it could be a heterogenous chip targeting several client form-factors, mobile and desktop. The company could leverage its 7 nm process - claimed to rival TSMC 5 nm-class in transistor density - in turning up core-counts over "Alder Lake." We'll learn more about "Meteor Lake" as we crawl toward its 2022 launch window, if it still holds up.
Older reports throughout 2019-20 speculate "Meteor Lake" (known at the time only by its name), could come out at a time when Intel monetizes its "Golden Cove" high-performance CPU core. It's quite likely that like "Alder Lake," it could be a heterogenous chip targeting several client form-factors, mobile and desktop. The company could leverage its 7 nm process - claimed to rival TSMC 5 nm-class in transistor density - in turning up core-counts over "Alder Lake." We'll learn more about "Meteor Lake" as we crawl toward its 2022 launch window, if it still holds up.

Intel 10nm Product Lineup for 2020 Revealed: Alder Lake and Ice Lake Xeons
A leaked Intel internal slide surfaced on Chinese social networks, revealing five new products the company will build on its 10 nm silicon fabrication process. These include the "Alder Lake" heterogenous desktop processor, "Tiger Lake" mobile processor, "Ice Lake" based Xeon Scalable enterprise processors, DG1 discrete GPU, and "Snow Ridge" 5G base-station SoC. Some, if not all of these products, will implement Intel's new 10 nm+ silicon fabrication node that is expected to go live within 2020.
"Alder Lake" is a desktop processor that implements Intel's new heterogenous x86 core design that's making its debut with "Lakefield." The chip features up to 8 larger "Willow Cove" or "Golden Cove" CPU cores, and up to 8 smaller "Tremont" or "Gracemont" cores. This 8-big/8-small combo lets the chip achieve TDP targets around 80 Watts. Next up is "Tiger Lake," Intel's next-generation mobile processor family succeeding "Ice Lake." This microarchitecture implements "Willow Cove" CPU cores in a homogeneous setup, alongside Xe architecture based integrated graphics. "Ice Lake-SP" is Intel's next enterprise architecture that places mature "Sunny Cove" CPU cores in extreme core-count dies. Lastly, there's "Snow Ridge," an SoC purpose built for 5G base-stations. Image quality notwithstanding, these slides don't appear particularly new, and it's likely that COVID-19 has destabilized the roadmap. For instance, "Alder Lake," and "Ice Lake-SP" are expected to be 10 nm++ chips, a node that doesn't go live before 2021.
"Alder Lake" is a desktop processor that implements Intel's new heterogenous x86 core design that's making its debut with "Lakefield." The chip features up to 8 larger "Willow Cove" or "Golden Cove" CPU cores, and up to 8 smaller "Tremont" or "Gracemont" cores. This 8-big/8-small combo lets the chip achieve TDP targets around 80 Watts. Next up is "Tiger Lake," Intel's next-generation mobile processor family succeeding "Ice Lake." This microarchitecture implements "Willow Cove" CPU cores in a homogeneous setup, alongside Xe architecture based integrated graphics. "Ice Lake-SP" is Intel's next enterprise architecture that places mature "Sunny Cove" CPU cores in extreme core-count dies. Lastly, there's "Snow Ridge," an SoC purpose built for 5G base-stations. Image quality notwithstanding, these slides don't appear particularly new, and it's likely that COVID-19 has destabilized the roadmap. For instance, "Alder Lake," and "Ice Lake-SP" are expected to be 10 nm++ chips, a node that doesn't go live before 2021.

Rumor: Intel to Introduce Big.Little Architecture for Desktop With Alder Lake-S, New LGA 1700 Socket
Hold on to your helmets: a wild rumor that Intel may be looking to introduce the same design considerations as they already did with their Lakefield architecture has appeared. According to momomo via Twitter (a user who has already shared many rumors and details in the PC hardware space) as well as some other sources, Intel is looking to bring a Big.Little-like design (which Intel calls Hybrid architecture) to the desktop platform in the form of Alder Lake-S, to be reportedly built on the 10 nm process. While Intel's Lakefield (especially geared for the mobile market) only sported four Atom (Intel's low power) Tremont cores combined with one high-performance Sunny Cove core, Alder Lake-S could sport as many as an 8+8 configuration, with a TDP currently set up to 80 W (and up to 125 W TDP is also set in the revealing slides with a disclosure regarding investigating performance scaling in up to 150 W TDP).
Should this actual Alder Lake-S product materialize in the 10 nm process, this could be a way for Intel to salvage what it can from the 10 nm process for the desktop platform. As we know from multiple reports on the state of Intel's 10 nm, yields and operating frequencies aren't close to what was expected, and Intel's CFO George Davis even said at last week's Morgan Stanley's Analyst Conference that their 10 nm process wouldn't be as profitable as even 22 nm, which does show that Intel is already looking past this process for their 7 nm deployment. A Big.Little design for a desktop architecture does seem like a more plausible design decision for a struggling process than a full 16-core monolithic die such as those Intel currently employs.
Should this actual Alder Lake-S product materialize in the 10 nm process, this could be a way for Intel to salvage what it can from the 10 nm process for the desktop platform. As we know from multiple reports on the state of Intel's 10 nm, yields and operating frequencies aren't close to what was expected, and Intel's CFO George Davis even said at last week's Morgan Stanley's Analyst Conference that their 10 nm process wouldn't be as profitable as even 22 nm, which does show that Intel is already looking past this process for their 7 nm deployment. A Big.Little design for a desktop architecture does seem like a more plausible design decision for a struggling process than a full 16-core monolithic die such as those Intel currently employs.

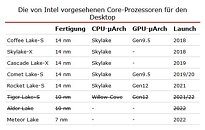
Intel Scraps 10nm for Desktop, Brazen it Out with 14nm Skylake Till 2022?
In a shocking piece of news, Intel has reportedly scrapped plans to launch its 10 nm "Ice Lake" microarchitecture on the client desktop platform. The company will confine its 10 nm microarchitectures, "Ice Lake" and "Tiger Lake" to only the mobile platform, while the desktop platform will see derivatives of "Skylake" hold Intel's fort under the year 2022! Intel gambles that with HyperThreading enabled across the board and increased clock-speeds, it can restore competitiveness with AMD's 7 nm "Zen 2" Ryzen processors with its "Comet Lake" silicon that offers core-counts of up to 10.
"Comet Lake" will be succeeded in 2021 by the 14 nm "Rocket Lake" silicon, which somehow combines a Gen12 iGPU with "Skylake" derived CPU cores, and possibly increased core-counts and clock speeds over "Comet Lake." It's only 2022 that Intel will ship out a truly new microarchitecture on the desktop platform, with "Meteor Lake." This chip will be built on Intel's swanky 7 nm EUV silicon fabrication node, and possibly integrate CPU cores more advanced than even "Willow Cove," possibly "Golden Cove."
"Comet Lake" will be succeeded in 2021 by the 14 nm "Rocket Lake" silicon, which somehow combines a Gen12 iGPU with "Skylake" derived CPU cores, and possibly increased core-counts and clock speeds over "Comet Lake." It's only 2022 that Intel will ship out a truly new microarchitecture on the desktop platform, with "Meteor Lake." This chip will be built on Intel's swanky 7 nm EUV silicon fabrication node, and possibly integrate CPU cores more advanced than even "Willow Cove," possibly "Golden Cove."

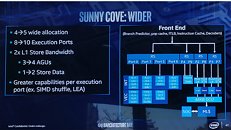
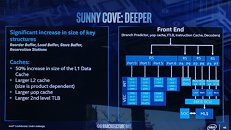
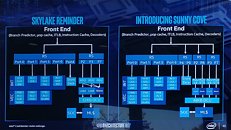
Intel Unveils a Clean-slate CPU Core Architecture Codenamed "Sunny Cove"
Intel today unveiled its first clean-slate CPU core micro-architecture since "Nehalem," codenamed "Sunny Cove." Over the past decade, the 9-odd generations of Core processors were based on incrementally refined descendants of "Nehalem," running all the way down to "Coffee Lake." Intel now wants a clean-slate core design, much like AMD "Zen" is a clean-slate compared to "Stars" or to a large extent even "Bulldozer." This allows Intel to introduce significant gains in IPC (single-thread performance) over the current generation. Intel's IPC growth curve over the past three micro-architectures has remained flat, and only grew single-digit percentages over the generations prior.
It's important to note here, that "Sunny Cove" is the codename for the core design. Intel's earlier codenaming was all-encompassing, covering not just cores, but also uncore, and entire dies. It's up to Intel's future chip-designers to design dies with many of these cores, a future-generation iGPU such as Gen11, and a next-generation uncore that probably integrates PCIe gen 4.0 and DDR5 memory. Intel details "Sunny Cove" as far as mentioning IPC gains, a new ISA (new instruction sets and hardware capabilities, including AVX-512), and improved scalability (ability to increase core-counts without running into latency problems).
It's important to note here, that "Sunny Cove" is the codename for the core design. Intel's earlier codenaming was all-encompassing, covering not just cores, but also uncore, and entire dies. It's up to Intel's future chip-designers to design dies with many of these cores, a future-generation iGPU such as Gen11, and a next-generation uncore that probably integrates PCIe gen 4.0 and DDR5 memory. Intel details "Sunny Cove" as far as mentioning IPC gains, a new ISA (new instruction sets and hardware capabilities, including AVX-512), and improved scalability (ability to increase core-counts without running into latency problems).
Mar 29th, 2025 21:05 EDT
change timezone
Latest GPU Drivers
New Forum Posts
- Display panel recommendation for low brightness and BFEP (1)
- RX580 BIOS PROBLEM (8)
- i5 14600K or i7 14700K? (8)
- Upgrade from a AMD AM3+ to AM4 or AM5 chipset MB running W10? (51)
- Is the futureproof gaming solution a four drive system? (8)
- RTX 5090 very slow while rendering or video/photo editing. (6)
- GPU Crashing System From Hibernation (8)
- Can you guess Which game it is? (15)
- Dell Workstation Owners Club (3315)
- What are you playing? (23312)
Popular Reviews
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Pulse Review
- ASRock Phantom Gaming B850 Riptide Wi-Fi Review - Amazing Price/Performance
- Samsung 9100 Pro 2 TB Review - The Best Gen 5 SSD
- Assassin's Creed Shadows Performance Benchmark Review - 30 GPUs Compared
- Palit GeForce RTX 5070 GamingPro OC Review
- Sapphire Radeon RX 9070 XT Nitro+ Review - Beating NVIDIA
- ASRock Radeon RX 9070 XT Taichi OC Review - Excellent Cooling
- Enermax REVOLUTION D.F. 12 850 W Review
- AMD Ryzen 7 9800X3D Review - The Best Gaming Processor
- ASRock Phantom Gaming B860I Lightning Wi-Fi Review
Controversial News Posts
- AMD RDNA 4 and Radeon RX 9070 Series Unveiled: $549 & $599 (260)
- MSI Doesn't Plan Radeon RX 9000 Series GPUs, Skips AMD RDNA 4 Generation Entirely (142)
- Microsoft Introduces Copilot for Gaming (124)
- AMD Radeon RX 9070 XT Reportedly Outperforms RTX 5080 Through Undervolting (119)
- NVIDIA Reportedly Prepares GeForce RTX 5060 and RTX 5060 Ti Unveil Tomorrow (115)
- Over 200,000 Sold Radeon RX 9070 and RX 9070 XT GPUs? AMD Says No Number was Given (100)
- NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5050, RTX 5060, and RTX 5060 Ti Specifications Leak (96)
- Retailers Anticipate Increased Radeon RX 9070 Series Prices, After Initial Shipments of "MSRP" Models (90)