Atari VCS Console Finally Set To Release in Fall 2020 for $389.99 USD
The Atari VCS was first announced over two years ago in 2018 but has since suffered numerous delays. It looks like there may be light at the end of the tunnel for the Atari VCS 800 with the console now available for pre-order from Atari, GameStop, or Walmart. The console is only available as part of a bundle including the console itself, Wireless Classic Joystick, a Modern Controller, and free copy of Atari Vault of 100 classic arcade and console games. The bundle is priced at 389.99 USD and is expected to ship by the 2020 holiday season.
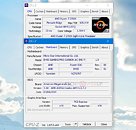
The console features a custom AMD Raven Ridge APU with Vega 3 graphics, paired with 8 GB DDR4 ram, and 32 GB eMMC internal flash storage. The device runs a custom Linux OS but also supports Linux, Windows, Steam OS, or Chrome OS if booting from an external drive. Connectivity consists of 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth 4.0 while I/O includes a single HDMI 2.0 port, gigabit Ethernet port, and quad USB 3.1 connectors. A lower-powered Atari VCS 400 system is also planned with half the ram at 4 GB and is expected to sell for 249.99 USD.
The console features a custom AMD Raven Ridge APU with Vega 3 graphics, paired with 8 GB DDR4 ram, and 32 GB eMMC internal flash storage. The device runs a custom Linux OS but also supports Linux, Windows, Steam OS, or Chrome OS if booting from an external drive. Connectivity consists of 802.11 b/g/n Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth 4.0 while I/O includes a single HDMI 2.0 port, gigabit Ethernet port, and quad USB 3.1 connectors. A lower-powered Atari VCS 400 system is also planned with half the ram at 4 GB and is expected to sell for 249.99 USD.