Intel "Ice Lake" IPC Best-Case a Massive 40% Uplift Over "Skylake," 18% on Average
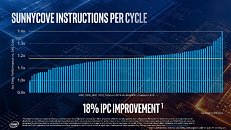
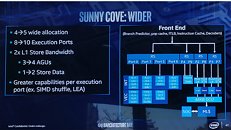
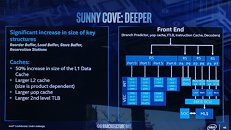
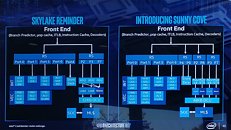
Intel late-May made its first major disclosure of the per-core CPU performance gains achieved with its "Ice Lake" processor that packs "Sunny Cove" CPU cores. Averaged across a spectrum of benchmarks, Intel claims a best-case scenario IPC (instructions per clock) uplift of a massive 40 percent over "Skylake," and a mean uplift of 18 percent. The worst-case scenario sees its performance negligibly below that of "Skylake." Intel's IPC figures are derived entirely across synthetic benchmarks, which include SPEC 2016, SPEC 2017, SYSMark 2014 SE, WebXprt, and CineBench R15. The comparison to "Skylake" is relevant because Intel has been using essentially the same CPU core in the succeeding three generations that include "Kaby Lake" and "Coffee Lake."
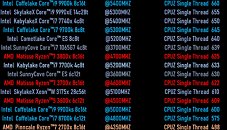
A Chinese tech-forum member with access to an "Ice Lake" 6-core/12-thread sample put the chip through the CPU-Z internal benchmark (test module version 17.01). At a clock-speed of 3.60 GHz, the "Ice Lake" chip allegedly achieved a single-core score of 635 points. To put this number into perspective, a Ryzen 7 3800X "Matisse" supposedly needs to run at 4.70 GHz to match this score, and a Core i7-7700K "Kaby Lake" needs to run at 5.20 GHz. Desktop "Ice Lake" processors are unlikely to launch in 2019. The first "Ice Lake" processors are 4-core/8-thread chips designed for ultraportable notebook platforms, which come out in Q4-2019, and desktop "Ice Lake" parts are expected only in 2020.
A Chinese tech-forum member with access to an "Ice Lake" 6-core/12-thread sample put the chip through the CPU-Z internal benchmark (test module version 17.01). At a clock-speed of 3.60 GHz, the "Ice Lake" chip allegedly achieved a single-core score of 635 points. To put this number into perspective, a Ryzen 7 3800X "Matisse" supposedly needs to run at 4.70 GHz to match this score, and a Core i7-7700K "Kaby Lake" needs to run at 5.20 GHz. Desktop "Ice Lake" processors are unlikely to launch in 2019. The first "Ice Lake" processors are 4-core/8-thread chips designed for ultraportable notebook platforms, which come out in Q4-2019, and desktop "Ice Lake" parts are expected only in 2020.