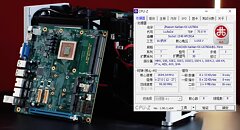
Zhaoxin's KX-7000 8-Core Processor Tested in Detail, Bested by 7 Year Old Core i3
PC Watch recently got hands-on with Shanghai Zhaoxin's latest desktop processor for some in depth testing and published a less than optimistic review comparing it to both the previous generation KX-U6780A and Intel's equally clocked budget quad-core offering from 2017, the 3.6 GHz Core i3-8100. Though Zhaoxin's latest could muscle its way through some multithreaded tests such as Cinebench R23 due to having twice the core count, the single core performance showed to be nearly half that of the i3 in everything from synthetic tests to gaming.
PC Watch tested with the Dragon Quest X Benchmark, a DX9.0c title, to put the spotlight on single core gaming performance even in older games as well as with Final Fantasy XIV running the latest Golden Legacy benchmark released back in April of this year to show off more modern multithreaded gaming. With AMD's RX 6400 handling graphics at 1080p the KX-7000/8 scored around 60% of the i3-8100 in Dragon Quest X, and in Final Fantasy XIV it scored 90% of the i3. The result in Final Fantasy XIV was considered, "somewhat comfortable" for gameplay but still less than optimal. As a comparison point for a modern budget gaming PC option the Ryzen 5 5600G was also included in testing, where in Final Fantasy XIV it was 30% ahead of the KX-7000/8. PC Watch attempted to put the integrated ZX-C1190 to work in games but found that despite supporting modern APIs and features, the performance was no match for the competition.
PC Watch tested with the Dragon Quest X Benchmark, a DX9.0c title, to put the spotlight on single core gaming performance even in older games as well as with Final Fantasy XIV running the latest Golden Legacy benchmark released back in April of this year to show off more modern multithreaded gaming. With AMD's RX 6400 handling graphics at 1080p the KX-7000/8 scored around 60% of the i3-8100 in Dragon Quest X, and in Final Fantasy XIV it scored 90% of the i3. The result in Final Fantasy XIV was considered, "somewhat comfortable" for gameplay but still less than optimal. As a comparison point for a modern budget gaming PC option the Ryzen 5 5600G was also included in testing, where in Final Fantasy XIV it was 30% ahead of the KX-7000/8. PC Watch attempted to put the integrated ZX-C1190 to work in games but found that despite supporting modern APIs and features, the performance was no match for the competition.